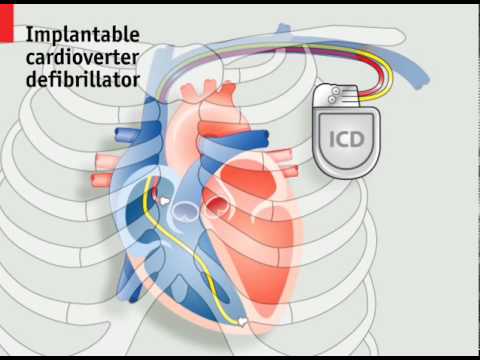
How pacemakers work. Animated explanation of the mechanics of the human heart, and the devices that can assist it Subscribe NOW to The Economist: http://econ.st/1Fsu2Vj Implantable pacemakers and defibrillators are devices that apply electric shocks to maintain the rhythm of the heart and, if necessary, restart it. As the technology improves and the list of treatable conditions grows, the number of devices being implanted is increasing steadily and now exceeds half a million a year. The heart is made up of four chambers; two atria and two ventricles. On each side the atrium is connected to the ventricle by a one-way valve. Blood is pumped as these chambers contract and relax in turn. The beating of a healthy heart is regulated by electrical impulses. The sequence begins as the atria fill with deoxygenated blood from the body on the right and oxygenated blood from the lungs on the left. An electrical signal from the sinoatrial node then causes the atria to contract, forcing blood into the ventricles. The electrical signal is then picked up by the atrioventricular node and directed into the Purkinje fibers in the ventricle walls, causing the ventricles to contract, and the blood is then pumped through the pulmonary valve on the right to the lungs, and the aortic valve on the left to the rest of the body. These valves close and the cycle then restarts. When the sinoatrial node fails to function correctly an artificial pacemaker can be fitted to help regulate the heartbeat with small evenly timed electric shocks. This involves implanting electrodes into one or more of the heart’s chambers, by inserting leads into a vein near the collarbone and implanting a device called the generator just under the skin. For more severe heart conditions an implantable defibrillator or ICD can be used which is also capable of sensing a stopped heart and delivering an electric shock powerful enough to restart it. For some conditions an even more sophisticated device called a CRT ICD can be implanted. This uses a third lead inserted into the left ventricle to resynchronize the ventricles when necessary. However, all these leads can cause problems of their own. Patients with ICDs have a 20% chance of a lead failure within 10 years and replacing leads can require open-heart surgery in about 2% of cases. This has resulted in several efforts to develop new pacemakers that do not depend on leads inside the heart. One design, the subcutaneous ICD, places the lead just outside the heart under the patient’s skin. And wireless designs are now being developed that may eventually do away with the need for leads altogether. Get more The Economist Follow us: https://twitter.com/TheEconomist Like us: https://www.facebook.com/TheEconomist View photos: https://instagram.com/theeconomist/ The Economist videos give authoritative insight and opinion on international news, politics, business, finance, science, technology and the connections between them.
How pacemakers work | The Economist
- Post author:
- Post published:May 24, 2021
- Post category:Uncategorized
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like
Onco Surgery Video – 3
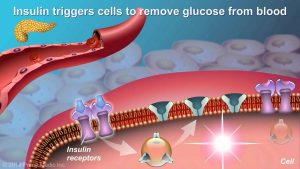
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes

Best Foods for Weight Loss-Healthy Fruits and Vegetables-Top 10 Fruit Benefits

Amino Vital – Plant-Based Amino Acid Nutritional Supplements For Golf

Muscle Building Workout & Squats Video – 24
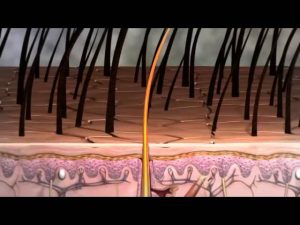
Hair Anatomy

Physiology Of Lactation
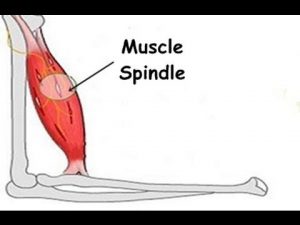
What is the Stretch Reflex or Myotatic Reflex?
![Read more about the article Thyroid Gland and Thyroid Hormones – [T3, T4, Thyroglobulin, Iodide Trapping etc.]](https://videos.drmaheshkumar.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Thyroid-Gland-and-Thyroid-Hormones-T3-T4-Thyroglobulin-Iodide-Trapping-etc-1-300x169.jpg)
Thyroid Gland and Thyroid Hormones – [T3, T4, Thyroglobulin, Iodide Trapping etc.]

Best Time To Take Vitamins and Supplements

Eat These Food Combinations To Lose Belly Fat Natural Way !!!

Shoulder Front Raises With a Rope on Cable for Weight Training : Exercises & Training

Urology Surgery Video – 1
THYROID HORMONES
Sildenafil Citrate

What Type of Protein Is Best For Weight Loss? – Dr.Berg

Propranolol

BEST TIME TO TAKE CREATINE|CREATINE कब लें Pre or Post Workout
Lipids & Fats Video – 2

What is Aerobic Exercise- Cardio and aerobics workouts
Laser Surgeries Video – 5

Thyroid Blood Tests

Keto Diet, Keto Foods, Keto Recipes Video – 30

Canoeing Video – 3
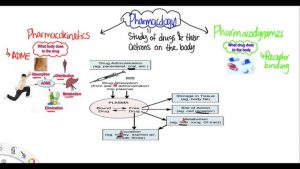
Basics of Pharmacology
Special Population Nutrition
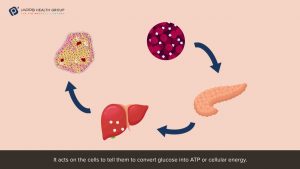
iAPPS Health Group Doctor – Insuline & Glucagon

Oral Skin Nutrition Video – 2

Watch Miguel Angel Jimenez’s Unique Warm-Up Routine | Golf Monthly
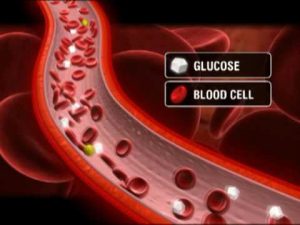
What is Type 1 Diabetes?

New Atkins Diet – Chapter 3: Make your body a fat burning machine

Upright Row-7

HOW TO SUMO DEADLIFT ft. Larry

Definition Fitness

How to Do an Incline Dumbbell Fly | Chest Workout

Priming and firing the Dermojet polymedical
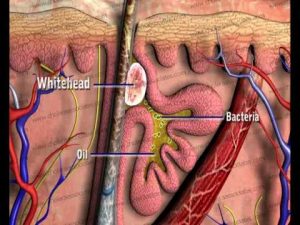
Acne 3D Presentation

Wall Sit-4

What is JAUNDICE? What does JAUNDICE mean? JAUNDICE meaning, definition & explanation

Do multivitamin supplements have side effects? – Revital H Woman(2017)

Lat Pull Down-4