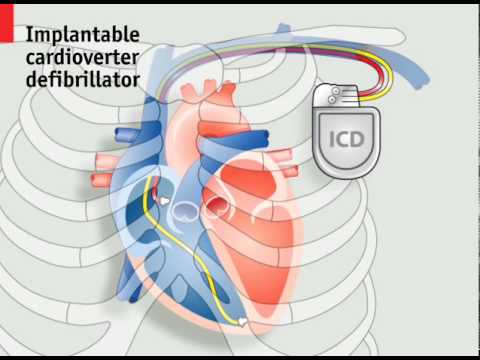
How pacemakers work. Animated explanation of the mechanics of the human heart, and the devices that can assist it Subscribe NOW to The Economist: http://econ.st/1Fsu2Vj Implantable pacemakers and defibrillators are devices that apply electric shocks to maintain the rhythm of the heart and, if necessary, restart it. As the technology improves and the list of treatable conditions grows, the number of devices being implanted is increasing steadily and now exceeds half a million a year. The heart is made up of four chambers; two atria and two ventricles. On each side the atrium is connected to the ventricle by a one-way valve. Blood is pumped as these chambers contract and relax in turn. The beating of a healthy heart is regulated by electrical impulses. The sequence begins as the atria fill with deoxygenated blood from the body on the right and oxygenated blood from the lungs on the left. An electrical signal from the sinoatrial node then causes the atria to contract, forcing blood into the ventricles. The electrical signal is then picked up by the atrioventricular node and directed into the Purkinje fibers in the ventricle walls, causing the ventricles to contract, and the blood is then pumped through the pulmonary valve on the right to the lungs, and the aortic valve on the left to the rest of the body. These valves close and the cycle then restarts. When the sinoatrial node fails to function correctly an artificial pacemaker can be fitted to help regulate the heartbeat with small evenly timed electric shocks. This involves implanting electrodes into one or more of the heart’s chambers, by inserting leads into a vein near the collarbone and implanting a device called the generator just under the skin. For more severe heart conditions an implantable defibrillator or ICD can be used which is also capable of sensing a stopped heart and delivering an electric shock powerful enough to restart it. For some conditions an even more sophisticated device called a CRT ICD can be implanted. This uses a third lead inserted into the left ventricle to resynchronize the ventricles when necessary. However, all these leads can cause problems of their own. Patients with ICDs have a 20% chance of a lead failure within 10 years and replacing leads can require open-heart surgery in about 2% of cases. This has resulted in several efforts to develop new pacemakers that do not depend on leads inside the heart. One design, the subcutaneous ICD, places the lead just outside the heart under the patient’s skin. And wireless designs are now being developed that may eventually do away with the need for leads altogether. Get more The Economist Follow us: https://twitter.com/TheEconomist Like us: https://www.facebook.com/TheEconomist View photos: https://instagram.com/theeconomist/ The Economist videos give authoritative insight and opinion on international news, politics, business, finance, science, technology and the connections between them.
How pacemakers work | The Economist
- Post author:
- Post published:May 24, 2021
- Post category:Uncategorized
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

What is STEROID HORMONE? What does STEROID HORMONE mean? STEROID HORMONE meaning & explanation

Emergency Medicine Video – 2

ideal waist to shoulder ratio – perfect body shape for a man

Bodybuilding Nutrition, Diet Recipes & Workout – 37
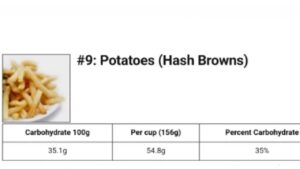
Top 10 Foods Highest In Carbohydrates

Anabolic Steroids – History, Definition, Use & Abuse Video – 45
Why Is Meat a Risk Factor for Diabetes?
Vascular Surgery Video – 1
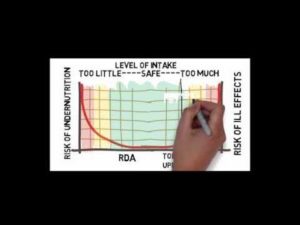
Dietary Reference Intake

SIMPLE LIPIDS NOTE

How To Know If You Have Gynecomastia? – 5 Gynecomastia Symptoms!

No.1 Multivitamins Supplements | at Chemist Shop | 100% Results And 100% Work

Drink One Glass Of Beet Juice Daily And This Will Happen To Your Body

Severe Liver Injury with Orlistat (Xenical, Alli)
Fever, tonsils swelling Homeopathic medicines! R1!! uses and symptoms! Inflammation drops
What is Diabetes

Kidney Problems Due to Preworkout & Creatine Supplements @hodgetwins
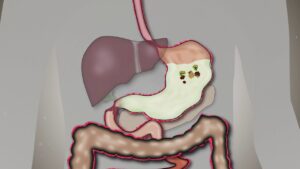
Human Digestive system explained

Fitness Tips : How to Reset Treadmills

Fat Loss, Weight Loss Video – 27

Basic Nutrition Terminology

Health And Fitness Video – 7

Business Spotlight: Back to Basics Nutrition Shop

Functional Training by Suples Training Systems -Circuit Training- Level Suples Fit
Osteoporosis

Testosterone Explained: Everything You Should Know (Made Simple to Understand)

Gynecomastia-Health Tips April 16, 2012

Bent Over Row

7 Pre Workout Meal Options to Lose Fat and Gain Muscle

Pranayama Video – 1
GI Acid Medication *Part 2* (Proton Pump Inhibitor PROTONIX)

Body Mass Index (BMI)

Soccer/ Football Video – 3

What does ornithine mean?

YO Sperm test: They play rugby – but can they swim?
Tenormin (Atenolol)
Orthopedics Video – 4

Respiratory System And Asanas Video – 1
Body Composition
Skeletal System And Asanas Video – 5

Abductor-1

