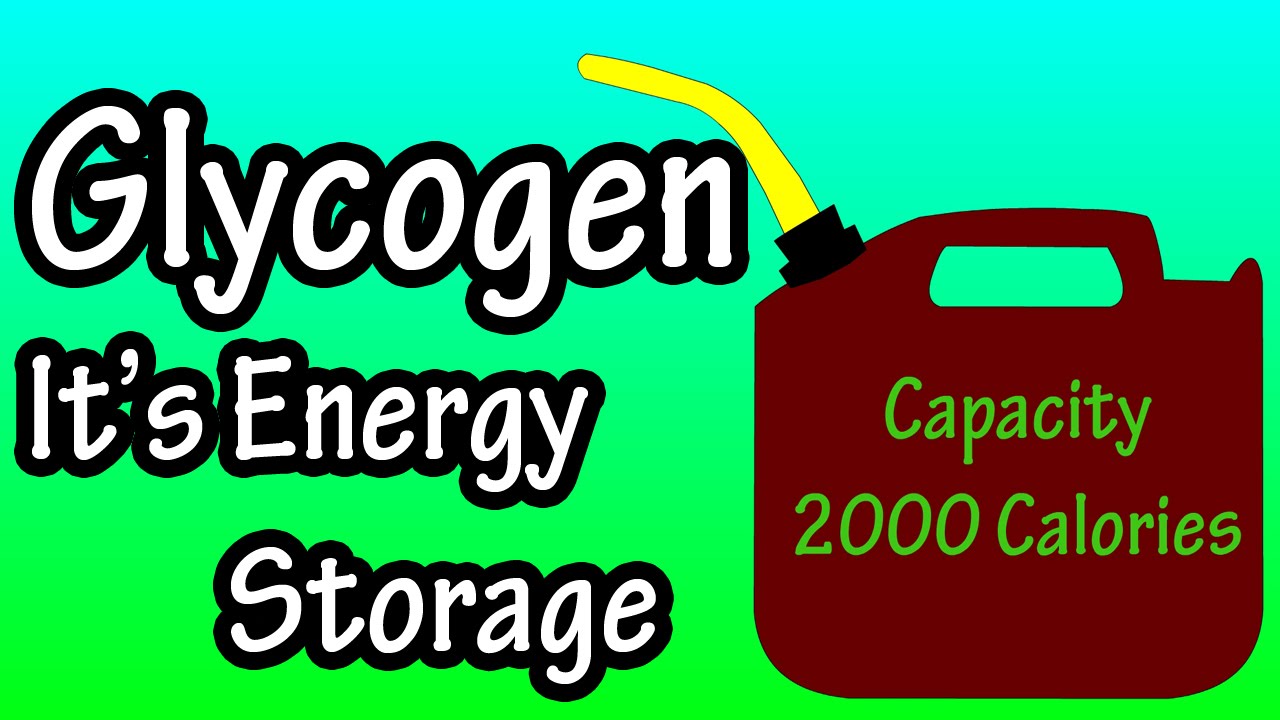
In this video I discuss what is glycogen, some of the functions of glycogen, and how many carbs to fill glycogen stores. I also discuss where glycogen storage takes place and how much glycogen is stored in the body. Transcript What is glycogen? To answer this, we are going to start with carbohydrates. When we eat carbs, our body breaks them down into what is called glucose. Glucose is the main source of energy, or fuel for cells. When the cells are full of fuel, the body takes this extra energy and converts it to glycogen. So, glycogen is a form of energy storage in the body. It is estimated that the body stores about 2000 calories worth of energy as glycogen. It gets stored in mainly 2 places, in muscles, and in the liver. Glycogen that is stored in the liver can be used by other organs and cells in the body. Glycogen that is stored in muscles is not shared, so it is used only by muscle cells. It is estimated that The liver will store about 400 calories of energy, and muscles will store about 1600 calories of energy. Now we are going take a basic look at how this works. Lets say that jack here is about to eat. His liver glycogen tank is ¾ full, and his muscle glycogen tank is 3/4 full. Jack eats his meal, and the carbs are broken down into glucose. Some of this glucose is sent by the liver, into the bloodstream to cells throughout his body. The liver takes the extra glucose and converts it to glycogen and stores it for later use, filling up his liver glycogen tank. In between meals when energy is needed, the liver breaks the glycogen down into glucose and releases it into the bloodstream, as you can see the glycogen tank starts to empty until jack eats again. One note here, fat can also be converted to energy to be used, and I will cover that in another video. The process will be similar in the muscles. Jacks muscle glycogen tank was ¾ full before his meal. After his meal, the tank is full. In between meals, jack is moving around, causing his muscle glycogen tank to become depleted.
Glycogen – What Is Glycogen?
- Post author:
- Post published:May 24, 2021
- Post category:Uncategorized
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Landmine Press for Your Upper Chest (Get Bigger Pecs!)

Seated Bent Over Rear Delt Raise – Shoulder Exercise – Bodybuilding.com

Top 10 Foods to Build Muscle Mass
![Read more about the article BIOTIN for hairloss & other related questions[review] | healthy U](https://videos.drmaheshkumar.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/BIOTIN-for-hairloss-other-related-questionsreview-healthy-U-300x225.jpg)
BIOTIN for hairloss & other related questions[review] | healthy U

Hany Rambod’s 70 Seconds on FST-7 Overhead Tricep Extension (High Pulley)

How to Get Rid of Fever Fast | by Onion | Health Tips

Reishi is anti-androgenic

Calcium Supplement Video – 1

What is DISEASE? What does DISEASE mean? DISEASE meaning, definition, explanation & pronunciation

Archery Video – 4

2D Cartoon Animation Echo

How to make oats IN HINDI with English subtitles

What is motor neurone disease (MND)?

How to get rid of Man Boobs? Workout and Diet Tips.

Incline Dumbbell Bicep Curl Swiss Ball Exercise

Flat Bench Fly-2

What is Diarrhoea? Causes, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment.
Antioxidants in a pinch

nutrition (anemia disease)
Anabolic Steroids – History, Definition, Use & Abuse Video – 19

Preacher Pulley Curl-2
GLUCAGÓN: Secrecion

Results of Incline bench DAILY!
Gynecomastia Patients Talk About Their Surgery Experience

Kidney Function Model

How to Do Back Extensions
how to take ECG

Functions Of Carbohydrates – What Do Carbohydrates Do In The Body – Importance Of Carbohydrates

Instructional Fitness – Seated Leg Press

How To Cool Down After Exercise

Types of Steroids

Top 5 Best Protein Powders Ever
Neurobion fort Tablet of Vitamin B Complex with B12

Couch Tricep Dips
Vitamins and Mineral Sources
How to test for Diabetes Type 2 -a quick urine test for diabetes

Herbs Video – 4
Exercise and Insulin Stimulated Glucose Uptake by Skeletal Muscle

Top 10 Best Vitamin B-Complex Supplements

ESR on Sikshana

Hockey Video – 1