This video is available for instant download licensing here : https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/addiction-science/-/medias/64c6e72c-f3af-4b26-aba2-f4dbfad29cca-mechanism-of-drug-addiction-in-the-brain-narrated-animation ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Addiction is a neurological disorder that affects the reward system in the brain. In a healthy person, the reward system reinforces important behaviors that are essential for survival such as eating, drinking, sex, and social interaction. For example, the reward system ensures that you reach for food when you are hungry, because you know that after eating you will feel good. In other words, it makes the activity of eating pleasurable and memorable, so you would want to do it again and again whenever you feel hungry. Drugs of abuse hijack this system, turning the person’s natural needs into drug needs. The brain consists of billions of neurons, or nerve cells, which communicate via chemical messages, or neurotransmitters. When a neuron is sufficiently stimulated, an electrical impulse called an action potential is generated and travels down the axon to the nerve terminal. Here, it triggers the release of a neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft – a space between neurons. The neurotransmitter then binds to a receptor on a neighboring neuron, generating a signal in it, thereby transmitting the information to that neuron. The major reward pathways involve transmission of the neurotransmitter dopamine from the ventral tegmental area – the VTA – of the midbrain to the limbic system and the frontal cortex. Engaging in enjoyable activities generates action potentials in dopamine-producing neurons of the VTA. This causes dopamine release from the neurons into the synaptic space. Dopamine then binds to and stimulates dopamine-receptor on the receiving neuron. This stimulation by dopamine is believed to produce the pleasurable feelings or rewarding effect. Dopamine molecules are then removed from the synaptic space and transported back in to the transmitting neuron by a special protein called dopamine-transporter. Most drugs of abuse increase the level of dopamine in the reward pathway. Some drugs such as alcohol, heroin, and nicotine indirectly excite the dopamine-producing neurons in the VTA so that they generate more action potentials. Cocaine acts at the nerve terminal. It binds to dopamine-transporter and blocks the re-uptake of dopamine. Methamphetamine – a psychostimulant – acts similarly to cocaine in blocking dopamine removal. In addition, it can enter the neuron, into the dopamine-containing vesicles where it triggers dopamine release even in the absence of action potentials. Different drugs act different way but the common outcome is that dopamine builds-up in the synapse to a much greater amount than normal. This causes a continuous stimulation, maybe over-stimulation of receiving neurons and is responsible for prolonged and intense euphoria experienced by drug users. Repeated exposure to dopamine surges caused by drugs eventually de-sensitizes the reward system. The system is no longer responsive to everyday stimuli; the only thing that is rewarding is the drug. That is how drugs change the person’s life priority. After some time, even the drug loses its ability to reward and higher doses are required to achieve the rewarding effect. This ultimately leads to drug overdose.
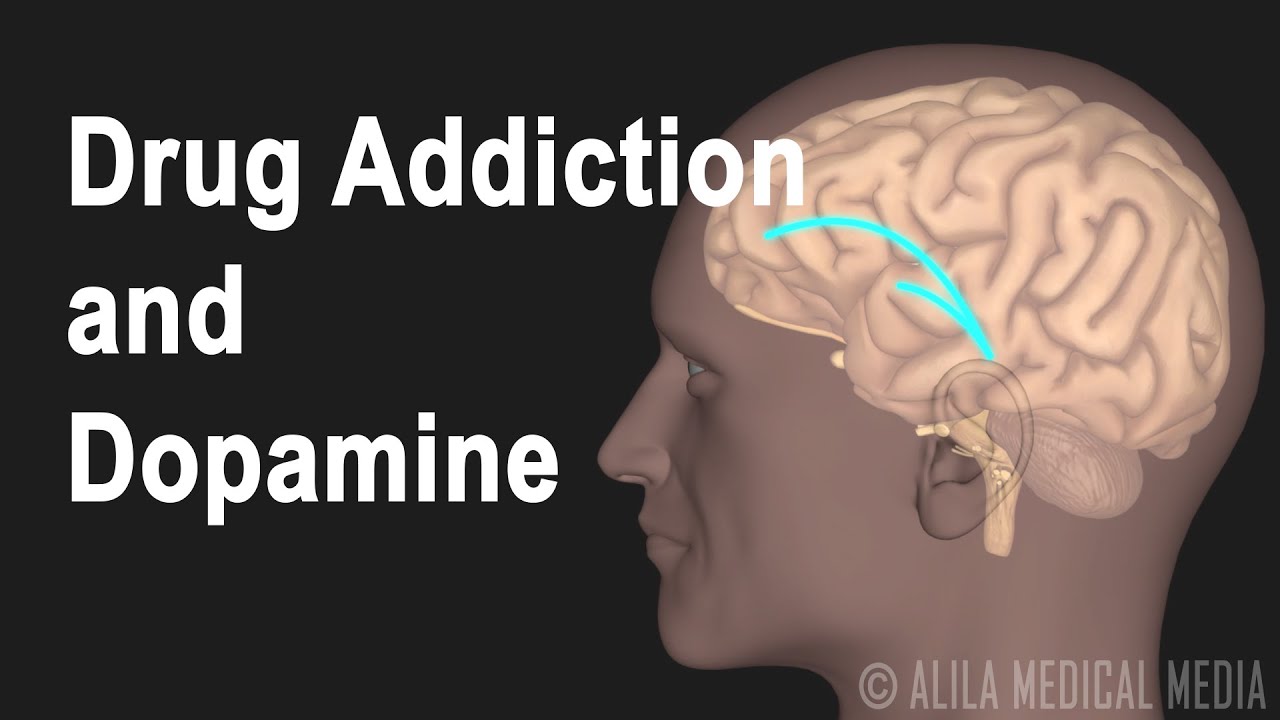
Mechanism of Drug Addiction in the Brain, Animation.
- Post author:
- Post published:May 25, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Early Signs of Osteoporosis

Fitness Model Nutrition Plan (EXACTLY WHAT SHE EATS!!)

Changes in Lipid Profile after Bariatric Surgery

Erector Spinae Back Extension-6

Nutrition 101: Macronutrient Set Up Guide (5 Minutes or Less)

Elbow Plank to Side Plank Lift Exercise

Social Psychiatry Video – 2

atlas in motion – INSULIN (ft. adri)

How much sperm count is needed for IUI or IVF?-Dr. Kasi Sellappan

Testosterone & Androgenic Effects Video – 14
Oral Route of Administration

Exercise Videos- Dumbbell Row on Ball

Foods Nutrition Video – 1

When You Burn Fat, Where Does it Go?

Zumba Cooldown / Stretch – Let me Love you (Remix)

FIVE FOODS FOR HAIR LOSS – DIET FOR HEALTHY HAIR

Decline Bench Press-2
What Are Antioxidants? (Mental Health Guru)
How To: Skull Crushers

Why You Need Vitamin B Complex

Anabolism and Catabolism

Spa Types Video – 4

6 Pack Diet Plan Disaster (CALORIE CUTTING!)

7 Most Useful Antioxidants for Skin
Onco Surgery Video – 3

6 Tips To Naturally Increase Your HGH (Human Growth Hormone)

Stability Ball Back Extension

Glutamine and L-Glutamine Explained!…Plus, Why You Should Be Taking It

Dexa Scan Explanation

Best Cardio To Drop Your Body Fat Percentage (SIMPLE TRICK)

High Pulley Overhead Triceps Extension – Step by Step Tutorial

3 GREAT Static Dumbbell Exercises | Doing Something New

Yoga Guide Video – 2

Why Can the Same Drug Treat Heart Attacks and Anxiety?
Latissimus Dorsi Bent Over Row-6
Kidney disease types and causes – Health Sutra
Anatomy & Physiology Online – Cardiac conduction system and its relationship with ECG

Step Up-4

Clinical Supplementation Video – 3

are you ready for alli? – find out at myalli.com

Grow Taller Exercises Top 8 Best Stretching Exercises to Increase Height- grow taller

