Benzodiazepines are commonly used to treat anxiety disorders and sleep disorders. They are thought to exert their effects in the brain by acting at receptors for the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid, or GABA. In this video, I cover the the mechanism of action for benzodiazepines. TRANSCRIPT: Welcome to 2 minute neuroscience, where I explain neuroscience topics in 2 minutes or less. In this installment I will discuss benzodiazepines. Benzodiazepines are a class of drugs named for their chemical structure that are commonly used to treat anxiety disorders and sleep-related disorders. They include well-known drugs like valium, xanax, and klonopin. There are dozens of drugs in the benzodiazepine class, but the mechanism by which they all exert their effects is thought to be similar. The sedating and anxiety-reducing effects of benzodiazepines are believed to be attributable to the drugs’ actions at receptors for the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyic acid, or GABA. In particular, benzodiazepines act at a subtype of GABA receptors called the GABAa receptor; GABAa receptors that also bind benzodiazepines are sometimes called benzodiazepine receptors. When benzodiazepines bind, or attach, to the GABA receptor, they bind at a location separate from where GABA itself binds, and exert an influence over GABA binding. This type of action is called an allosteric effect, and in the case of benzodiazepines it results in increased action at the GABA receptor. There is not complete consensus on exactly how benzodiazepine binding affects activity at the GABA receptor but there is evidence to suggest that it increases the likelihood that GABA binding will activate the receptor and/or increases the effect that GABA has when it binds to the receptor. That effect is to open an ion channel and allow the passage of negatively charged chloride ions into the neuron. This influx of negatively charged ions pushes the membrane potential further from zero, or hyperpolarizes it, and makes it less likely the neuron will fire an action potential. This type of neural inhibition is the basis for the effects of benzodiazepines, for by inhibiting the activity of neurons that make up networks involved with anxiety and arousal, the drugs are able to produce calming effects. REFERENCES: Gielen MC, Lumb MJ, Smart TG. Benzodiazepines modulate GABAA receptors by regulating the preactivation step after GABA binding. J Neurosci. 2012 Apr 25;32(17):5707-15. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5663-11.2012. Möhler H, Fritschy JM, Rudolph U. A new benzodiazepine pharmacology. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Jan;300(1):2-8.
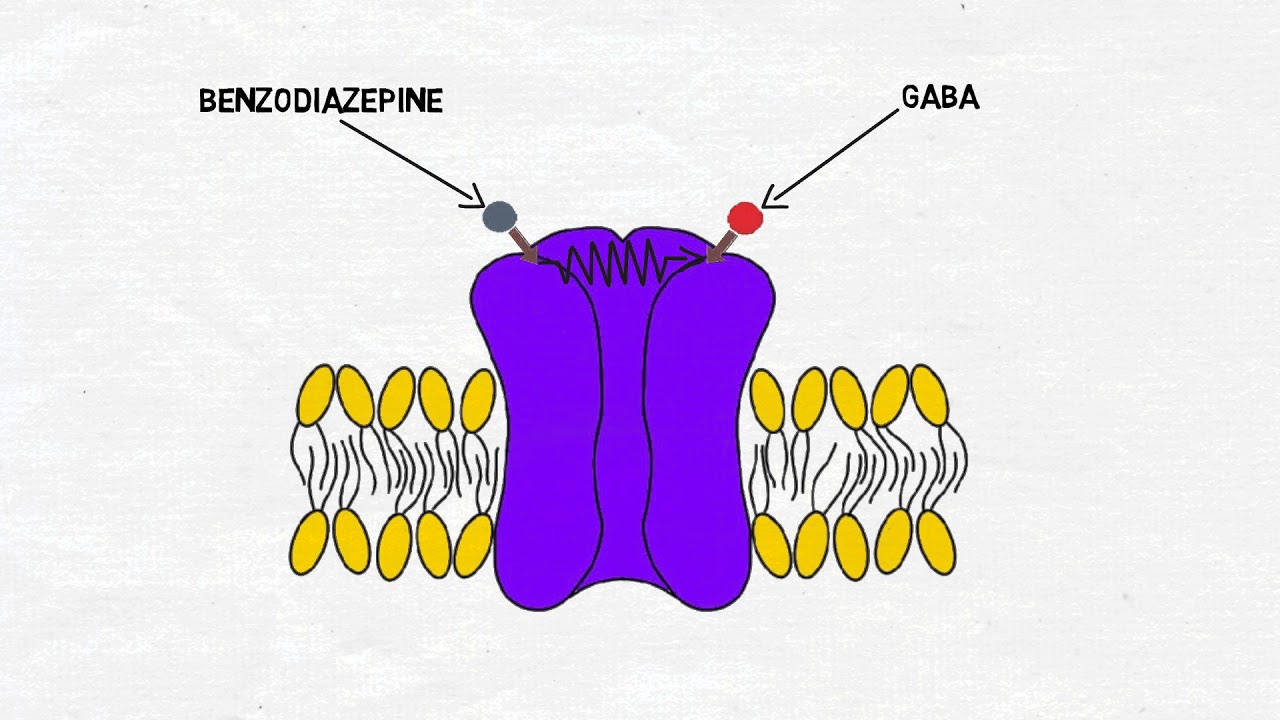
2-Minute Neuroscience: Benzodiazepines
- Post author:
- Post published:May 26, 2021
- Post category:Uncategorized
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Flexibility and Gymnastics Skills. Flexibility Stretches. Professional contortion. yoga flexibility

How to Perform Romanian Deadlift – Hamstring Leg Exercise
severe case of jaundice – v2
Oral And Maxillofacial Surgery Video – 4

Muscle Building Workout & Squats Video – 21

Final Truth about BCAA + Supplement Giveaway | FitMuscleTV
How to give your cat an insulin injection

Swiss Ball Squat With Curl | Legs Biceps Arms Abs Workout
Human Body – Anat & Physio
Liver Protecting Medicine Silymarin

Kidney Ultrasound – What Is It? Does It Hurt?
Orthopedic Surgery Video – 3

Triceps Standing Low Pulley One Arm Triceps Extension
Venous-Insufficiency

Anatomy Terminology – Anatomy Tutorial

World’s Best Fish Oil Capsule | WOW Omega – 3 Fish Oil Capsule Supplement Review in Hindi

Dr Sushmita on Thyroid disorders during pregnancy

Bmi and Bmr in hindi

What Everything In Your Body Is Really Made Of? Genes Explained.

Number One Supplement to Lower Blood Pressure Naturally
Aten 50 Tablet Uses side effects

Which body type do men REALLY like best?

Making A Yoga Routine Video – 3

Is the Traditional BMI Chart Accurate?

What is HEART? HEART meaning & definition – HEART functions – How to pronounce HEART

Xenical

OVERSPEED CABLE SPRINTS – SPEED TRAINING – BUNGEE

Amino Acid Therapy for Mental Health + Addictions

Bowflex® Stretch | Leg Stretches for Flexibility

Barbell Shrugs – Shoulder n Traps – Upper Body Workout Routine

Stability Ball Hyperextension – HASfit Low Back Exercises – Lower Back Exercise

Spa Mineral Video – 1
Thyroid Hormones
DEXA – Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry
What is Cardiovascular Disease? Doctor Akshay Khandelwal Explains
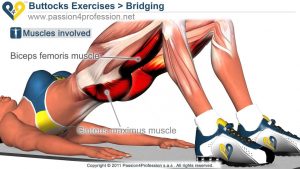
The10 Best Exercises to Lose Weight
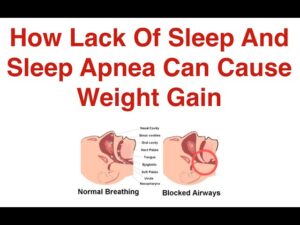
How Lack Of Sleep And Sleep Apnea Can Cause Weight Gain

Military Press – Dumbbells

Alternating hammer curls (standing with dumbbells)
What is Tuberculosis?

How to Do a Preacher Curl | Arm Workout

