In this video I discuss what is glycogen, some of the functions of glycogen, and how many carbs to fill glycogen stores. I also discuss where glycogen storage takes place and how much glycogen is stored in the body. Transcript What is glycogen? To answer this, we are going to start with carbohydrates. When we eat carbs, our body breaks them down into what is called glucose. Glucose is the main source of energy, or fuel for cells. When the cells are full of fuel, the body takes this extra energy and converts it to glycogen. So, glycogen is a form of energy storage in the body. It is estimated that the body stores about 2000 calories worth of energy as glycogen. It gets stored in mainly 2 places, in muscles, and in the liver. Glycogen that is stored in the liver can be used by other organs and cells in the body. Glycogen that is stored in muscles is not shared, so it is used only by muscle cells. It is estimated that The liver will store about 400 calories of energy, and muscles will store about 1600 calories of energy. Now we are going take a basic look at how this works. Lets say that jack here is about to eat. His liver glycogen tank is ¾ full, and his muscle glycogen tank is 3/4 full. Jack eats his meal, and the carbs are broken down into glucose. Some of this glucose is sent by the liver, into the bloodstream to cells throughout his body. The liver takes the extra glucose and converts it to glycogen and stores it for later use, filling up his liver glycogen tank. In between meals when energy is needed, the liver breaks the glycogen down into glucose and releases it into the bloodstream, as you can see the glycogen tank starts to empty until jack eats again. One note here, fat can also be converted to energy to be used, and I will cover that in another video. The process will be similar in the muscles. Jacks muscle glycogen tank was ¾ full before his meal. After his meal, the tank is full. In between meals, jack is moving around, causing his muscle glycogen tank to become depleted.
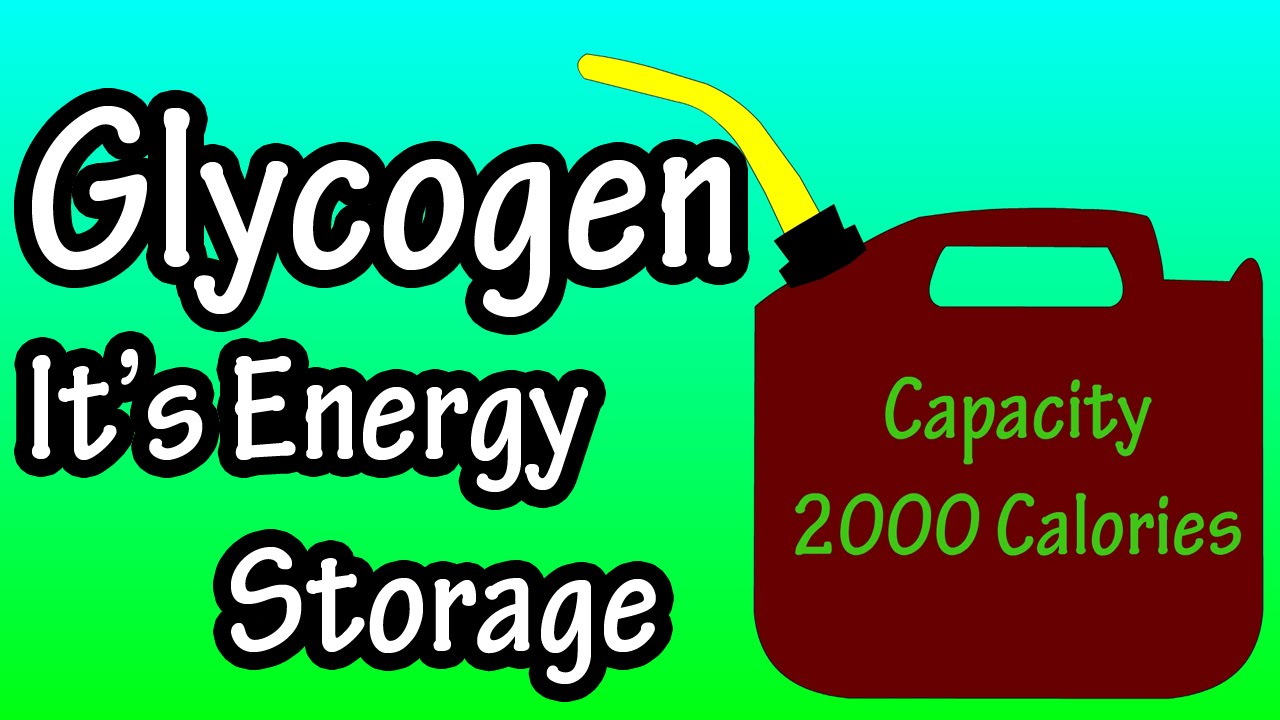
Glycogen – What Is Glycogen?
- Post author:
- Post published:May 27, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

3 Key Muscle-Groups That Make You Look Bigger
Spa Business Video – 2

Barbell Bench Press – HASfit Chest Exercise Demonstration – Flat Bench Presses Form – Pectoral

Can Eating Carbs at Night Make You Gain Weight?

SIMPLE LIPIDS NOTE
Anorectal Surgeries Video – 1
Glucagon and its Functions in HINDI

Thyroid Disease Explained in Telugu | Patient Education I MIC
5 Workouts That Burn belly fat Like Crazy
Thyroid Booster Supplements: 6 Supplements That Boost T3 and T4

Pulley Curl-2

Thyroid hormone and ATP
Steroids BAD! TRT GOOD! The Effects On Your Heart (Latest Studies)

About Lactation Consultant

Anabolic Steroids – History, Definition, Use & Abuse Video – 32

How Testosterone Affects Fat Loss: Real Science of Low-T | Thomas DeLauer

Should You Take BCAAs? (The Truth About BCAA Supplements)

Definition Fitness Strength & Performance Centre

President Trump is taking a prostate drug Propecia often prescribed for hair loss, his physician say

Wexford University Health, Fitness, Nutrition Degrees

Pre/During/Post Workout Drink || SHREDDED NEXT LEVEL by Guru Mann ||

Be Aware: The Risk of Pregnancy While on Isotretinoin

far 212 group 8 : enalapril
Fibroid Treatment Options – Mayo Clinic

What is fat

Reshape Natural Tablets To Lose Weight On ClickOnCare

Male Reproductive System – Hormonal Function and Regulation (sperm synthesis and maturation)
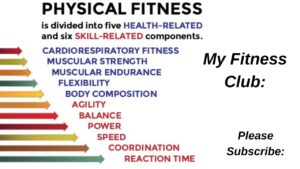
Fitness Definition Components Video – 2

Pediatric Physiotherapy Video – 12

What does ornithine mean?

Joints: Crash Course A&P #20

Muscular Strength Asanas Video – 3

Clinical Psychiatry Video – 3

Insulin Like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) Explained: Everything You Should Know
Contraction

Stop Jogging and Start Sprinting! – How to Sprint and Why it’s Better for Your Health

What Is Vitamin B6? | Vitamins

WHAT TO EAT BEFORE AND AFTER GYM (Best Pre and Post Workout Meals)

What is HORSESHOE KIDNEY? What does HORSESHOE KIDNEY mean? HORSESHOE KIDNEY meaning
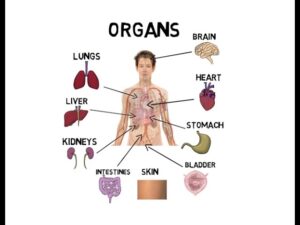
Organs of the body

Wrestling Video – 1

