This video and more updated versions of similar videos are available for instant download licensing https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/diabetes ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Diabetes refers to a group of conditions characterized by a high level of blood glucose, commonly referred to as blood sugar. Too much sugar in the blood can cause serious, sometimes life-threatening health problems. There are two types of chronic diabetic conditions: type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Pregnant women may acquire a transient form of the disease called “gestational diabetes” which usually resolves after the birth of baby. Pre-diabetes is when the blood sugar level is at the borderline: higher than normal, but lower than in diabetics. Prediabetes may or may not progress to diabetes. During food digestion, carbohydrates – or carb – break down into glucose which is carried by the bloodstream to various organs of the body. Here, it is either consumed as an energy source – in muscles for example – or is stored for later use in the liver. Insulin is a hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreas and is necessary for glucose intake by target cells. In other words, when insulin is deficient, muscle or liver cells are unable to use or store glucose, and as a result, glucose accumulates in the blood. In healthy people, beta cells of the pancreas produce insulin; insulin binds to its receptor on target cells and induces glucose intake. In type 1 diabetes, beta cells of the pancreas are destroyed by the immune system by mistake. The reason why this happens is unclear, but genetic factors are believed to play a major role. Insulin production is reduced; less insulin binds to its receptor on target cells; less glucose is taken into the cells, more glucose stays in the blood. Type 1 is characterized by early onset, symptoms commonly start suddenly and before the age of 20. Type 1 diabetes is normally managed with insulin injection. Type 1 diabetics are therefore “insulin dependent”. In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas produces enough insulin but something goes wrong either with receptor binding or insulin signaling inside the target cells. The cells are not responsive to insulin and therefore cannot import glucose; glucose stays in the blood. In other words, type 2 diabetics are “insulin resistant”. Here again, genetic factors predispose susceptibility to the disease, but it is believed that lifestyle plays a very important role in type 2. Typically, obesity, inactive lifestyle, and unhealthy diet are associated with higher risk of type 2 diabetes. Type 2 is characterized by adult onset; symptoms usually appear gradually and start after the age of 30. Type 2 diabetes accounts for about 80 to 90% of all diabetics. Management focuses on weight loss and includes a low-carb diet.
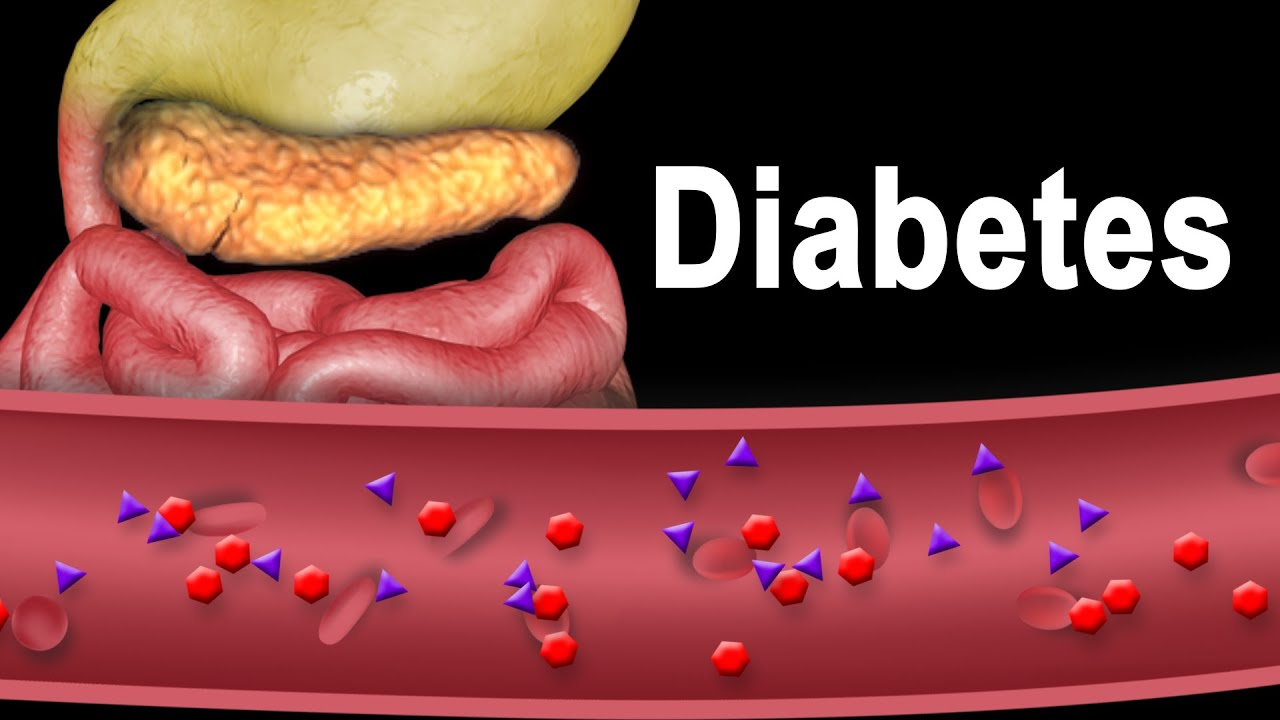
Diabetes Type 1 and Type 2, Animation.
- Post author:
- Post published:June 11, 2021
- Post category:Uncategorized
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

vivoactive 3 – Intro

Diazepam Nursing Considerations, Side Effects, and Mechanism of Action Pharmacology for Nurses

Braucht man BCAA und Kohlenhydrate beim Training?

Minerals – What Are Minerals – What Do Minerals Do – What Are The Essential Minerals

Importance of Antioxidants – Hindi
Understanding Thyroid Function Tests

Triceps Dips-8

What Are The Benefits & Side Effects Of Whey Protein | The scientific Truth | BeerBiceps Gym Tips

Chemicals and your Endocrine System
The difficult journey of the sperm | Signs


Social Psychiatry Video – 2

Risperdal Side Effects

BCAAs Explained in 60 seconds – Should You Supplement With BCAAs?

Is Your Blood TOXIC? Drink this! – Saturday Strategy

Best Fruits You Should Eat While Breastfeeding
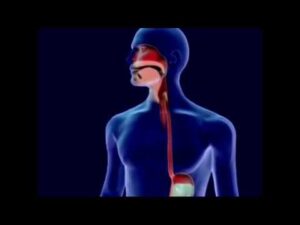
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OF HUMAN/HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PARTS AND FUNCTIONS

Female Body Types And Body Shapes Different Body Types Women Have

Antioxidant Content of 300 Foods

What is Glutamine? | KM Supplement Facts
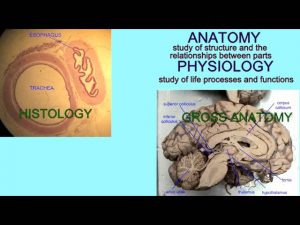
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: DEFINITIONS

Cable V Bar Preacher Curls
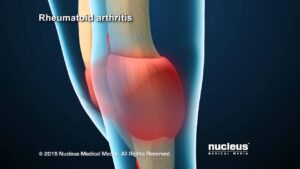
Rheumatology Video – 3

Modified Tricep Dips Demo
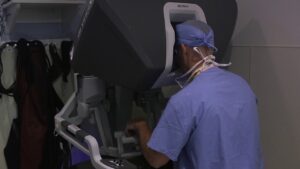
Robotics Surgeries Video – 2

How to Gain Weight Fast | Vegetarian Diet Plan for Weight Gain in Hindi

Anatomy on USMLE — What’s High Yield?

Structure And Growth of Hair

Oblique abs exercises: Side Plank

Which glucose meter is the best on the market?

Best Workout Rep Range (CLASSIC MISTAKE!)

Ripped Upper Body In 20 minutes! FULL WORKOUT | CHEST, BACK, SHOULDERS & ARMS | HOME EDITION

Dumbell front raise for SHOULDERS! (Hindi / Punjabi)

Anabolic Steroids – History, Definition, Use & Abuse Video – 43

Multivitamin supplements and breast cancer

Human Body, Body Building Muscle Building Anatomy Physiology Video – 19

Spa Mineral Video – 4

HGH, Growth Hormones & Plant Hormones Video – 28

Bodybuilding Nutrition, Diet Recipes & Workout – 14

Cardio-Thoracic Physiotherapy Video – 10

Diet vs. Exercise for Weight Loss