(USMLE topics) The science behind the GOOD and BAD cholesterol. Cholesterol transport and pathways, drugs used for treatment of atherosclerosis. This video is available for instant download licensing here: https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/hypertensioncholesterol/-/medias/47f9fe8c-8be2-4c09-a87b-a2cddc501d29-cholesterol-metabolism-narrated-animation ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Voice by Vicky Prizmic Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Despite having a BAD reputation as a high-risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, cholesterol is an ESSENTIAL component of all animal cells. It is an INTEGRAL part of the cell membrane, providing membrane FLUIDITY and participating in a number of cellular processes. Cholesterol also serves as a PRECURSOR for production of bile, steroid hormones, and vitamin D. While the body can obtain cholesterol from food, many cells SYNTHESIZE their own ENDOGENOUS cholesterol. Cellular production of cholesterol is under NEGATIVE FEEDBACK control. LOW levels of intracellular cholesterol INDUCE its own production, while HIGH cholesterol levels INHIBIT it. Cholesterol, together with other lipids, is transported in blood plasma within large particles known as LIPOPROTEINS. A lipoprotein is an assembly of lipids and proteins. Lipoproteins are classified based on their DENSITY. Because lipids are LIGHTER than proteins, particles that contain MORE lipids are LARGER in size but have LOWER density. Different types of lipoproteins have different sets of proteins on their surface. These proteins serve as “ADDRESS tags”, determining the DESTINATION, and hence FUNCTION, of each lipoprotein. For example, LOW-density lipoprotein, LDL, carries cholesterol FROM the liver to other tissues, while HIGH-density lipoprotein, HDL, RETURNS excess cholesterol TO the liver. Major events in cholesterol metabolism include: – Dietary cholesterol ABSORBED in the intestine and carried in chylomicron to the liver. – The liver PACKAGES its cholesterol pool – a combination of endogenous and dietary – together with triglycerides, another type of lipid, into particles of VERY-LOW-density lipoprotein, VLDL. – VLDL travels in bloodstream to other organs. During circulation, muscle and adipose tissues EXTRACT triglycerides from VLDL, turning it into LOW-density lipoprotein, LDL. – Peripheral cells TAKE UP LDL by endocytosis, using LDL receptor. Cholesterol is used in cell membrane and other functions. – EXCESS cholesterol is exported from the cells and delivered to HIGH-density lipoprotein, HDL, to be RETURNED to the liver in a process called REVERSE cholesterol transport. – The liver uses cholesterol to produce BILE; bile is secreted to the intestine, where it helps break down fats. Part of this bile is EXCRETED in feces; the rest is RECYCLED back to the liver. LDL has the highest cholesterol content and is the MAJOR carrier of cholesterol in the blood. High levels of LDL in the blood are associated with cholesterol plaque build-up and cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. For this reason, LDL is known as “BAD” cholesterol. On the other hand, HDL is called “GOOD” cholesterol, because it REMOVES EXCESS cholesterol from tissues and bloodstream. Common drugs used to LOWER cholesterol include: INHIBITORS of endogenous cholesterol PRODUCTION; INHIBITORS of intestinal cholesterol ABSORPTION; and INHIBITORS of bile reuptake.
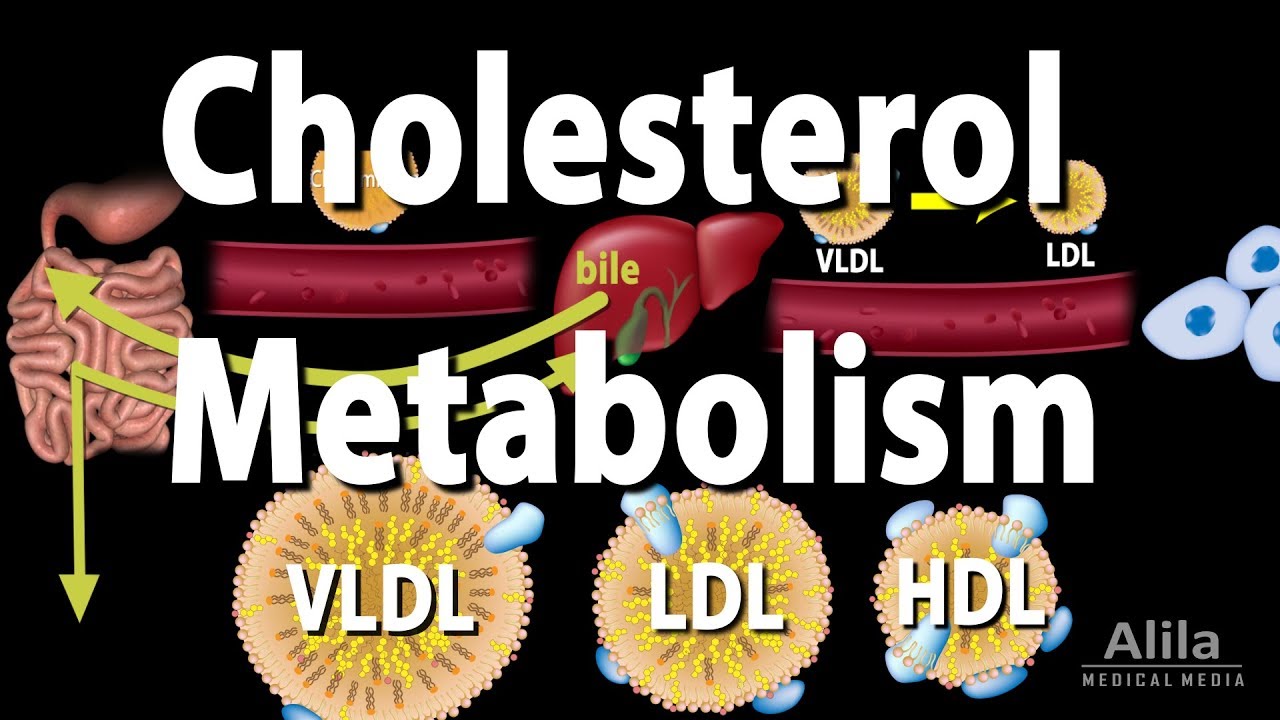
Cholesterol Metabolism, LDL, HDL and other Lipoproteins, Animation
- Post author:admin
- Post published:October 7, 2021
- Post category:Uncategorized
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Are Multivitamins Really Good For You?

Sports Psychiatry Video – 3

Vegetarian sources of Omega 3
5 Things You Didn’t Know About Pee

Sprinter’s Step Up With Bar
BEST Workout & Diet ADVICE for SKINNY GUYS ft. Mike Matthews | How to Build & Gain Muscle FAST

What is Hypertension?

Weight Training Video – 1

CT Coronary Angiogram vs Traditional Angiogram

LOWER ABS UNLEASHED – 3 Exercises! (V-CUT Abs)

ANTIOXIDANTS: THE BASICS | Nutrition 101 Ep. 4

Electrolytes – What Are Electrolytes – Functions Of Electrolytes

How to do a preacher curl for maximum results!!

Final Truth about BCAA + Supplement Giveaway | FitMuscleTV

INTENSE Full Body Workout & Circuit Training – Get in Shape & Improve Overall Fitness
ENT Surgery Video – 4
Diabetes

HGH, Growth Hormones & Plant Hormones Video – 40

finger pulp abscess drainage EXPLOSION of pus – watch to the end for patient POEM

Human Body Video – 4
Telemedicine for Erectile Dysfunction – Tadalafil and Sildenafil

One Hand Triceps Extension-8

Can I Do Keto & Intermittent Fasting If I am a Diabetic on Metformin and Insulin? : Dr.Berg

Pre Surgery Video – 5
Shrugs-1
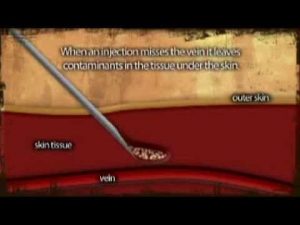
AIVL Vein Care Guide Abscess Formation Animation
Psychiatry & Psychology

Hyperextension With ball-7

Alcohol Video – 2

Table Tennis Video – 4
diazepam farmacologia I

Spa Products Video – 2

The Benefits of a Warm Up and Cool Down

Watch Miguel Angel Jimenez’s Unique Warm-Up Routine | Golf Monthly

Movement Demo – Back Extensions
Velcade Animation with Narration
The Skeletal System- Axial Skeleton

Human growth hormone bodybuilding

Calcium Supplement Video – 2

I’m Having a Vitamin B Complex!! 2 of 2

Kriya Video – 2

