What is benign prostatic hyperplasia? Benign prostatic hyperplasia––also called BPH––is a condition in men in which the prostate gland is enlarged and not cancerous. Benign prostatic hyperplasia is also called benign prostatic hypertrophy or benign prostatic obstruction. The prostate goes through two main growth periods as a man ages. The first occurs early in puberty, when the prostate doubles in size. The second phase of growth begins around age 25 and continues during most of a man’s life. Benign prostatic hyperplasia often occurs with the second growth phase. As the prostate enlarges, the gland presses against and pinches the urethra. The bladder wall becomes thicker. Eventually, the bladder may weaken and lose the ability to empty completely, leaving some urine in the bladder. The narrowing of the urethra and urinary retention––the inability to empty the bladder completely––cause many of the problems associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia. What causes benign prostatic hyperplasia? The cause of benign prostatic hyperplasia is not well understood; however, it occurs mainly in older men. Benign prostatic hyperplasia does not develop in men whose testicles were removed before puberty. For this reason, some researchers believe factors related to aging and the testicles may cause benign prostatic hyperplasia. Throughout their lives, men produce testosterone, a male hormone, and small amounts of estrogen, a female hormone. As men age, the amount of active testosterone in their blood decreases, which leaves a higher proportion of estrogen. Scientific studies have suggested that benign prostatic hyperplasia may occur because the higher proportion of estrogen within the prostate increases the activity of substances that promote prostate cell growth. Another theory focuses on dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a male hormone that plays a role in prostate development and growth. Some research has indicated that even with a drop in blood testosterone levels, older men continue to produce and accumulate high levels of DHT in the prostate. This accumulation of DHT may encourage prostate cells to continue to grow. Scientists have noted that men who do not produce DHT do not develop benign prostatic hyperplasia. How common is benign prostatic hyperplasia? Benign prostatic hyperplasia is the most common prostate problem for men older than age 50. In 2010, as many as 14 million men in the United States had lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Although benign prostatic hyperplasia rarely causes symptoms before age 40, the occurrence and symptoms increase with age. Benign prostatic hyperplasia affects about 50 percent of men between the ages of 51 and 60 and up to 90 percent of men older than 80. Who is more likely to develop benign prostatic hyperplasia? Men with the following factors are more likely to develop benign prostatic hyperplasia: age 40 years and older family history of benign prostatic hyperplasia medical conditions such as obesity, heart and circulatory disease, and type 2 diabetes lack of physical exercise erectile dysfunction What are the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia? Lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia may include urinary frequency—urination eight or more times a day urinary urgency—the inability to delay urination trouble starting a urine stream a weak or an interrupted urine stream dribbling at the end of urination nocturia—frequent urination during periods of sleep urinary retention urinary incontinence—the accidental loss of urine pain after ejaculation or during urination urine that has an unusual color or smell Symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia most often come from a blocked urethra a bladder that is overworked from trying to pass urine through the blockage How is benign prostatic hyperplasia treated? Treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia may include lifestyle changes medications minimally invasive procedures surgery A health care provider treats benign prostatic hyperplasia based on the severity of symptoms, how much the symptoms affect a man’s daily life, and a man’s preferences. Men may not need treatment for a mildly enlarged prostate unless their symptoms are bothersome and affecting their quality of life. In these cases, instead of treatment, a urologist may recommend regular checkups. If benign prostatic hyperplasia symptoms become bothersome or present a health risk, a urologist most often recommends treatment.
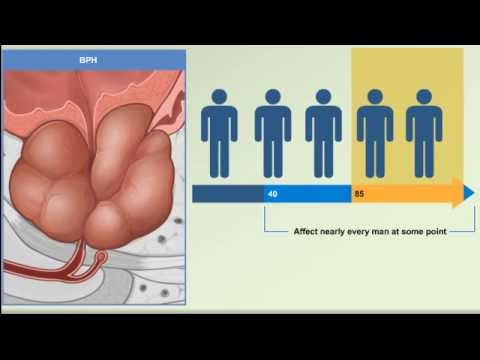
Prostate Enlargement: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia – BPH Causes, Symptoms, Treatment Animation Video
- Post author:
- Post published:May 5, 2021
- Post category:Uncategorized
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Anabolic Androgenic Steroid Misused

Barbell Bench Press-8

Weight Training Video – 5
Muscle Definition – Does Your Training Matter? 8 minute explanation

How To Get V-Shape Back

What is Fish Oil? Omega-3 Benefits & Side Effects Review by Guru Mann

Psychosomatic Medicine Video – 3

Yoga Trainer Personality Video – 6
GLUCAGÓN: Secrecion

Aroma Therapy Video – 2

What To Eat Before A Football Game! FAST & EASY To Prepare!

The Ayurvedic Body Types and Their Characteristics (Vata Pitta Kapha)

Protein Shake on Non Workout Days

Pregnant? Help Protect Your Baby from Whooping Cough
Cardiology Video – 4
Ebola Virus – Mechanism of Action – 3D Medical Animation

Get killer abs with BMR Athlete Bilsen Begovic`
Understanding Cholesterol and its Effects

Keto Diet, Keto Foods, Keto Recipes Video – 5

What is Body Mass Index || What is BMI

Naturade, Weight Gain, Instant Nutrition Drink Mix
SCHILLER electrode placement for resting ECG with standard electrode set

Top 10 Foods That Help Lose Belly Fat – Tips To Burn Belly Fat
SportsTracker: define sport types

7 Foods To Avoid For Liver Health

BCAA Supplements – What Are BCAA’s And How Do They Work? | GuruMann Review

V Push Ups (with clenched fists) – Fitness exercises

Anaerobically Meaning

Forensic Psychiatry Video – 3

10 Bad Habits That Damage Our Brain Or Gets Neurological And Nervous System Diseases & Disorders

Why Do We Get a Fever? | The Dr. Binocs Show | Best Learning Videos For Kids | Peekaboo Kidz

How to do Standing Bicep Cable Curl exactly – Biceps Workout

BICEPS – Narrow Grip Barbell Curl

Nutrition for Muscles building Video – 1

Otorhinolaryngology Video – 4

How To: Overhead Front Raise (With Plate)
Channel Proteins

Muscle Building Workout & Squats Video – 26

Which Spices Fight Inflammation?

FOODS THAT LOWER BLOOD PRESSURE CAN CURE HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE

Sarah Says: What is Liver Function Testing?

