Diet and nutrition significantly affect sport and exercise performance. The food and fluid which an athlete before, during, and after training and competition affects health and body composition, as well as performance in, and, recovery from, the effects of exercise. An optimum diet can help to maximize athletic performance. Increased participation in physical activity, exercise and sport has the potential to improve the health and well-being of our sedentary population. Increased physical activity can help to reduce obesity, the risk of heart disease, diabetes, some cancers, osteoporosis, and can play a role in promoting positive mental health and psychological wellbeing. Sound knowledge of sport and exercise nutrition can ensure a healthy balance between exercise and diet of individuals and groups of individuals at all levels of fitness. Due consideration must be given to the special nutritional needs imposed by participation in different forms of sport or exercise in combination with the circumstances and characteristics of the individual. Whilst evidence clearly shows that good diet and nutrition are vital for health in all individuals, a growing variety of ‘health’ foods, ergogenic aids, supplements, herbal remedies and functional foods are widely available. These products claim to benefit health and athletic performance but such claims are often unsubstantiated. In addition many nutritional practices in sport (e.g. making weight) are based more on tradition and myth than scientific evidence. There is therefore a growing need for appropriate guidance in relation to sport and exercise nutrition, across a wide-spectrum from amateur to elite professional levels within sports. This programme provides a postgraduate pathway for graduates who wish to pursue a career within the area of sports nutrition.

Sports Nutrition Video – 1
- Post author:admin
- Post published:May 12, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

How To: Dumbbell Shoulder Press
Complete Blood Count with Normal Values

Atenolol (Tenormin) Nursing Pharmacology Considerations
Placements of Chest leads In ECG

Signature Looks For The “Body Types”

Types of Human Body Tissue

Wrestling Video – 2

Complete Tricep Gym Workout Routine! BBRT# 8 (Hindi / Punjabi)

Rens has no emotions after he took Xanax | Drugslab
Intrinsic Clearance – Biliary excretion

Reasons for High Blood Pressure
01 Liver Video
CT Angiography with Dr. Arnder

Calf Stretching & Strengthening Exercise Demonstration

Science of ONION JUICE and natural hair growth

How to Do Back Extensions

How to do Cable Bent Over Triceps Extensions? #91

ReShape Side Effects
3D medical animation – Why people get fat – Warum Menschen Gewicht zunehmen – designidentity
Anaemia

How to Burn Excess Stored Fat Faster

What is BMI & How to calculate it..!!

Diabetes Monitoring – NO MORE PRICKING YOUR FINGERS!

Top 10 High Protein Foods
GE AW CT Perfusion 4D Radiology Imaging Software Video | GE Healthcare

Surface Fitness: Youth Fitness & Performance Training

Orthopedic Surgery Video – 6

Dangers Of Elevated Liver Enzymes

Best Cardio Exercises: High Knees Running In Place

Health Benefits of Barley – Nutritional Information

The Best Protein Powders – Our Favorite Whey Options (NOW!)

How to do Chest Inner Machine Seated Pec Deck Fly correctly? Avoid any injury. #3

The Disturbing Truth about Vitamin Supplements – Sharp Science

Human Body, Body Building Muscle Building Anatomy Physiology Video – 31

Step Up-4

What is the cause of vomiting and diarrhea ? | Good Health for All

Watch Miguel Angel Jimenez’s Unique Warm-Up Routine | Golf Monthly

What are Carbohydrates?

NUTRITION MISTAKES | THE TOP 5

Top Vegan Protein Sources (Plant-Based) | Dr. Berg
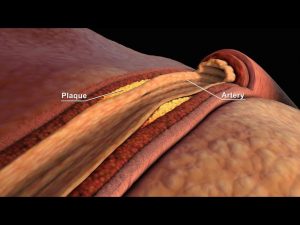
LDL and HDL Cholesterol | Good and Bad Cholesterol | Nucleus Health

