Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Cerebral Strokes, for Patient Education. This video is available for instant download licensing here : https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/strokes/-/medias/af9a4579-4ac2-4b5d-908a-f3d71834eaf2-brain-stroke-narrated-animation ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Voice by: Sue Stern. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. A stroke occurs when the blood supply to a certain part of the brain is reduced or interrupted. Without oxygen and nutrients from the blood, brain cells cannot function properly and eventually die. There are 2 major types of strokes: ISCHEMIC stroke caused by a BLOCKED artery, and HEMORRHAGIC stroke caused by a RUPTURED artery. Ischemic stroke happens when a blood clot OBSTRUCTS an artery. In some patients, the clot forms locally, inside the blood vessels that supply the brain. This occurs when fatty deposits in an artery, or cholesterol plaques, rupture and trigger blood clotting. In other cases, a clot may travel to the brain from elsewhere in the body. Most commonly, this happens in patients with atrial fibrillation, a heart condition in which the heart does not pump properly, blood stagnates in its chambers and this facilitates blood clotting. The clots may then pass into the bloodstream, get stuck in smaller arteries of the brain and block them. Hemorrhagic stroke, on the other hand, occurs when an artery leaks or ruptures. This can result from high blood pressure, overuse of blood-thinners/anticoagulant drugs, or abnormal formations of blood vessels such as aneurysms and AVMs. As a hemorrhage takes place, brain tissues located BEYOND the site of bleeding are deprived of blood supply. Bleeding also induces contraction of blood vessels, narrowing them and thus further limiting blood flow. Stroke symptoms may include one or more of the following: – Paralysis of muscles of the face, arms or legs: inability to smile, raise an arm, or difficulty walking. – Slurred speech or inability to understand simple speech. – Sudden and severe headache, vomiting, dizziness or reduced consciousness. Cerebral stroke is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention. It is essential to determine if a stroke is ischemic or hemorrhagic before attempting treatment. This is because certain drugs used for treatment of ischemic strokes, such as blood thinners, may CRITICALLY aggravate bleeding in hemorrhagic strokes. – For ischemic strokes, emergency treatment aims to restore blood flow by removing blood clots. Medication, such as aspirin and tissue plasminogen activator, TPA, are usually the first options. TPA may be given intravenously, or, in the case the symptoms have advanced, delivered directly to the brain via a catheter inserted through an artery at the groin. Blood clots may also be removed mechanically by a special device delivered through a catheter. – Emergency treatment for hemorrhagic strokes, on the other hand, aims to stop bleeding, reduce blood pressure, and prevent vasospasm and seizures. These goals are usually achieved by a variety of drugs. If the bleeding is significant, surgery may be required to drain the blood and reduce intracranial pressure. Preventive treatments for strokes include: – Removal of cholesterol plaques in carotid arteries that supply the brain – Widening of narrowed carotid arteries with a balloon, and sometimes, a stent. This is usually done with a catheter inserted at the groin. – Various procedures to prevent rupturing of brain aneurysms, such as clipping and embolization. – Removal or embolization of vascular malformations – Bypassing the problematic artery
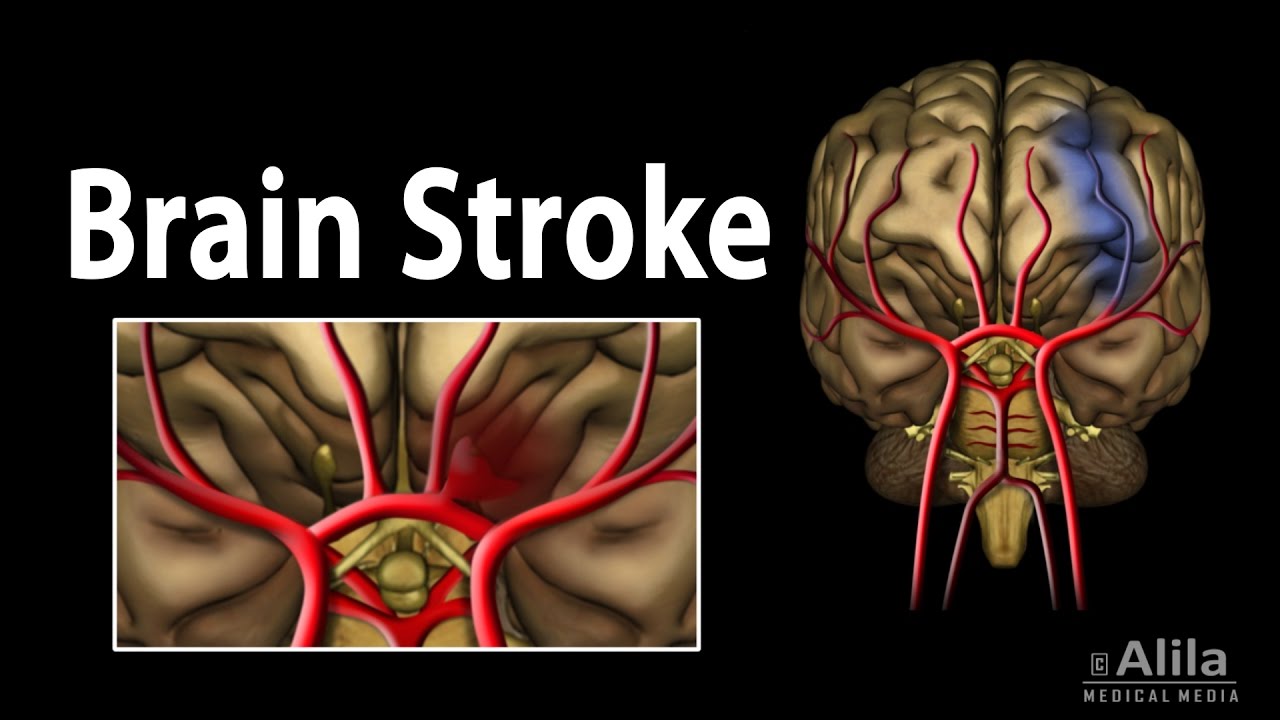
Brain Stroke, Types of, Causes, Pathology, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention, Animation.
- Post author:
- Post published:May 23, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

What is STEROID HORMONE? What does STEROID HORMONE mean? STEROID HORMONE meaning & explanation

Are shrugs the best exercise to develop your Upper Traps / Trapezius? Here’s some great alternatives

9 Nutrition Rules for Building Muscle | Jim Stoppani’s Shortcut to Strength

Sex Psychiatry Video – 1

How to do a proper leg extension

How to hit muscle groups twice a week

Diazepam: Psychotropic Drug to Treat Anxiety, Seizures, and Muscle spasm
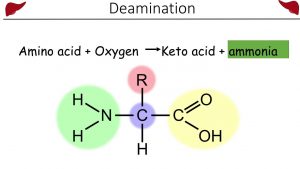
Urea and the Ornithine cycle

How to Read Nutrition Facts | Food Labels Made Easy

What body type are you?

Donkey Kicks-8
Brain Damage

Honey Nutrition Video – 2
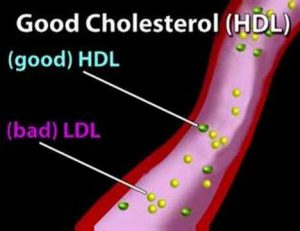
Understanding Cholesterol (Cholesterol #1)

Using DIM For High Androgen to Help Facial Hair, Cystic Acne & Alopecia | Dr.Berg

Leg Extension-2

Post-Workout Cooldown
Catabolism

The 6 Fat Burning Hormones Triggers Explained By Dr.Berg

Pharmacy/drug animation (Commercial Work)

Love Psychology Video – 4

Foundation Training Anchored Extension

Lipid profile in psoriasis patients – Video abstract: 32539

Best Vegetables For Weight Loss, Healthiest Vegetables List

Trunk strengthening exercises

Gynecology Video – 2

Dumbbell Pullover-8

Aura Reading Video – 1

Preservatives Video – 1

Best Low Carb Food List for Weight Loss – No Carb Diet Plan for weight loss
STRETCH MECHANICS by Mirabai Holland

Diet in Liver disease (Fatty liver, Liver cirrhosis, Hepatomegaly, Jaundice & Hepatitis)

Llenado del tubo de Wintrobe

What Is Circuit Training? | Gym Workout

Muscle Building Workout & Squats Video – 34

HAMMER CURLS- 5 DIFFERENT TYPES- Rich Piana
Blood glucose measurement – OSCE Guide

Part 2 – People – the internal organs – Important words with sound and the picture – Learn French
Understanding Cholesterol and its Effects
Anatomy and Physiology of Metabolism Nutrition
WHICH BODY TYPE ARE YOU? How to Train & Eat for YOUR body type?

