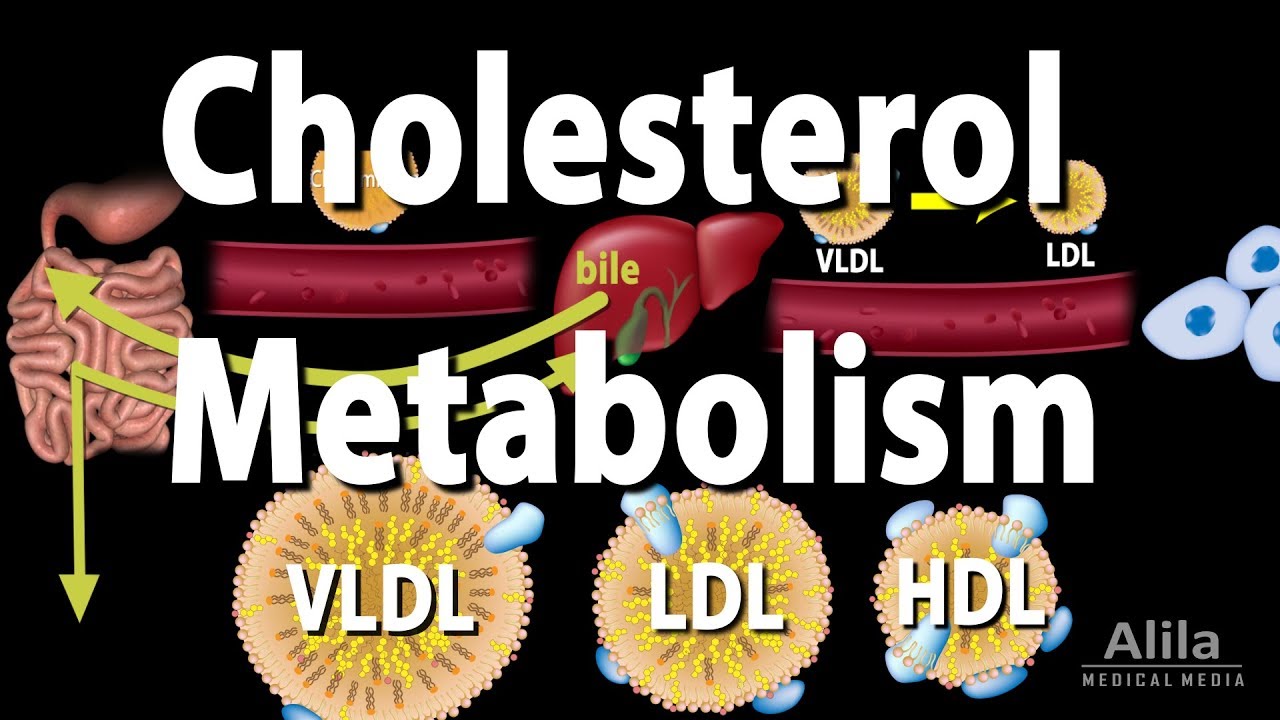
(USMLE topics) The science behind the GOOD and BAD cholesterol. Cholesterol transport and pathways, drugs used for treatment of atherosclerosis. This video is available for instant download licensing here: https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/hypertensioncholesterol/-/medias/47f9fe8c-8be2-4c09-a87b-a2cddc501d29-cholesterol-metabolism-narrated-animation ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Voice by Vicky Prizmic Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Despite having a BAD reputation as a high-risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, cholesterol is an ESSENTIAL component of all animal cells. It is an INTEGRAL part of the cell membrane, providing membrane FLUIDITY and participating in a number of cellular processes. Cholesterol also serves as a PRECURSOR for production of bile, steroid hormones, and vitamin D. While the body can obtain cholesterol from food, many cells SYNTHESIZE their own ENDOGENOUS cholesterol. Cellular production of cholesterol is under NEGATIVE FEEDBACK control. LOW levels of intracellular cholesterol INDUCE its own production, while HIGH cholesterol levels INHIBIT it. Cholesterol, together with other lipids, is transported in blood plasma within large particles known as LIPOPROTEINS. A lipoprotein is an assembly of lipids and proteins. Lipoproteins are classified based on their DENSITY. Because lipids are LIGHTER than proteins, particles that contain MORE lipids are LARGER in size but have LOWER density. Different types of lipoproteins have different sets of proteins on their surface. These proteins serve as “ADDRESS tags”, determining the DESTINATION, and hence FUNCTION, of each lipoprotein. For example, LOW-density lipoprotein, LDL, carries cholesterol FROM the liver to other tissues, while HIGH-density lipoprotein, HDL, RETURNS excess cholesterol TO the liver. Major events in cholesterol metabolism include: – Dietary cholesterol ABSORBED in the intestine and carried in chylomicron to the liver. – The liver PACKAGES its cholesterol pool – a combination of endogenous and dietary – together with triglycerides, another type of lipid, into particles of VERY-LOW-density lipoprotein, VLDL. – VLDL travels in bloodstream to other organs. During circulation, muscle and adipose tissues EXTRACT triglycerides from VLDL, turning it into LOW-density lipoprotein, LDL. – Peripheral cells TAKE UP LDL by endocytosis, using LDL receptor. Cholesterol is used in cell membrane and other functions. – EXCESS cholesterol is exported from the cells and delivered to HIGH-density lipoprotein, HDL, to be RETURNED to the liver in a process called REVERSE cholesterol transport. – The liver uses cholesterol to produce BILE; bile is secreted to the intestine, where it helps break down fats. Part of this bile is EXCRETED in feces; the rest is RECYCLED back to the liver. LDL has the highest cholesterol content and is the MAJOR carrier of cholesterol in the blood. High levels of LDL in the blood are associated with cholesterol plaque build-up and cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. For this reason, LDL is known as “BAD” cholesterol. On the other hand, HDL is called “GOOD” cholesterol, because it REMOVES EXCESS cholesterol from tissues and bloodstream. Common drugs used to LOWER cholesterol include: INHIBITORS of endogenous cholesterol PRODUCTION; INHIBITORS of intestinal cholesterol ABSORPTION; and INHIBITORS of bile reuptake.
Cholesterol Metabolism, LDL, HDL and other Lipoproteins, Animation
- Post author:admin
- Post published:October 7, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

“Skinny Fat” Body Type: Should You Bulk Or Cut First? Info by Guru Mann

Sprinter’s Step Up With Bar

Oestrogen regulation of transcription

10 Foods For Diarrhea – Best Foods For Diarrhea

If White Rice is Linked to Diabetes, What About China?

BCAA Side Effects Dangers You Should Be Aware Of!
Half Life T1/2

Best Foods for Weight Loss – Blueberries for Weight Loss

How To: Cable Rear Delt Fly Exercise

20 Killer Ab Exercises

5 ways to get pregnant fast with Clomid

First Aid Video – 1

Supplement Spotlight Silymarin

Decline Dumbbell Bench Press – Chest Exercise

Cardiologist Discusses Nutrition Changes to Reduce Risk of Heart Disease
Difference Between 2d,3d,4d and Latest 5d ultrasound – Enterprise Ultrasound
How The Body Reacts To Tuberculosis

Health And Fitness Video – 2
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate ( ESR)
Female Reproductive Cycle Made Easy: Hormones
Body composition analyzer testing video

Supplements For Beginners | Complete Supplement Guide For Beginners

What is EXERCISE? What does EXERCISE mean? EXERCISE meaning – How to pronounce EXERCISE?
Oxidants and Antioxidants

First Aid Video – 3
Overweight & Obesity Video – 10

Repetition Meaning

Neurobion Forte benefits | Vitamin B Complex- Uses, Side-effects, Precaution | Doctors Review

What causes fever vomiting and diarrhea ? | Health For All

Watch Miguel Angel Jimenez’s Unique Warm-Up Routine | Golf Monthly

What does anatomy mean?

Stretching Exercise For Calf Muscles In Pregnancy

One Simple Movement To Get V-shaped Abs
Diabetes: Metformin medication
Leg Raises-3
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Laproscopic Surgeries Video – 3

The Difference Between Sperm & Semen – Episode 20

#Adjustment#Flexibility Motivational Cartoon video

Global Mental Health Video – 1
T3 in Bodybuilding Safe or Not | For Educational Purpose Only

