This video and more updated versions of similar videos are available for instant download licensing https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/diabetes ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Diabetes refers to a group of conditions characterized by a high level of blood glucose, commonly referred to as blood sugar. Too much sugar in the blood can cause serious, sometimes life-threatening health problems. There are two types of chronic diabetic conditions: type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Pregnant women may acquire a transient form of the disease called “gestational diabetes” which usually resolves after the birth of baby. Pre-diabetes is when the blood sugar level is at the borderline: higher than normal, but lower than in diabetics. Prediabetes may or may not progress to diabetes. During food digestion, carbohydrates – or carb – break down into glucose which is carried by the bloodstream to various organs of the body. Here, it is either consumed as an energy source – in muscles for example – or is stored for later use in the liver. Insulin is a hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreas and is necessary for glucose intake by target cells. In other words, when insulin is deficient, muscle or liver cells are unable to use or store glucose, and as a result, glucose accumulates in the blood. In healthy people, beta cells of the pancreas produce insulin; insulin binds to its receptor on target cells and induces glucose intake. In type 1 diabetes, beta cells of the pancreas are destroyed by the immune system by mistake. The reason why this happens is unclear, but genetic factors are believed to play a major role. Insulin production is reduced; less insulin binds to its receptor on target cells; less glucose is taken into the cells, more glucose stays in the blood. Type 1 is characterized by early onset, symptoms commonly start suddenly and before the age of 20. Type 1 diabetes is normally managed with insulin injection. Type 1 diabetics are therefore “insulin dependent”. In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas produces enough insulin but something goes wrong either with receptor binding or insulin signaling inside the target cells. The cells are not responsive to insulin and therefore cannot import glucose; glucose stays in the blood. In other words, type 2 diabetics are “insulin resistant”. Here again, genetic factors predispose susceptibility to the disease, but it is believed that lifestyle plays a very important role in type 2. Typically, obesity, inactive lifestyle, and unhealthy diet are associated with higher risk of type 2 diabetes. Type 2 is characterized by adult onset; symptoms usually appear gradually and start after the age of 30. Type 2 diabetes accounts for about 80 to 90% of all diabetics. Management focuses on weight loss and includes a low-carb diet.
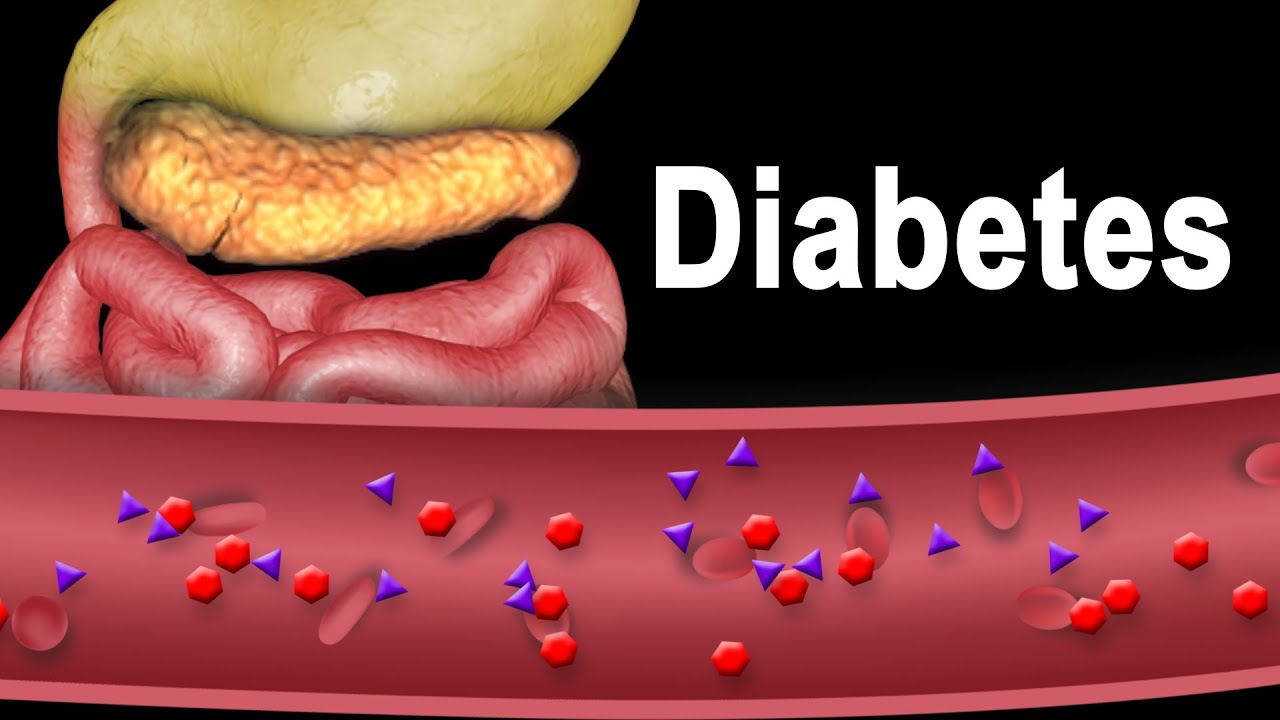
Diabetes Type 1 and Type 2, Animation.
- Post author:admin
- Post published:October 8, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Plant-Based Bodybuilding

Urology Video -3
Human Body Systems Video – 6

Physiology Of Sports & Sports Medicine Video – 1

Powerful All Natural ANTIOXIDANT & HEALTHY JOINTS!

Keto Diet, Keto Foods, Keto Recipes Video – 28

(CC) How to Pronounce ondansetron (Zofran) Backbuilding Pharmacology

How To: Donkey Kicks
How to check man sperm count for fertility at home
Awareness Telmisartan Price

Growth Hormone – HGH Energizer

6 Packs Abs Video – 4

Crunch elbow towards knee – alternated

How to Get Rid of Fever Fast | by Onion | Health Tips

Understanding semen analysis – Dr. Teena S Thomas

Healthy foods for osteoarthritis patients, You must know them
![Read more about the article Top 10 Foods High In Protein [HD]](https://videos.drmaheshkumar.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Top-10-Foods-High-In-Protein-HD-5-300x169.jpg)
Top 10 Foods High In Protein [HD]

3 Best Home Remedies For FOOD POISONING TREATMENT

Static neck exercises 5 kinds.avi

Seated Calf Raise-5

Amino Acid Supplement Review – Empyrean Nutrition Peptibolic
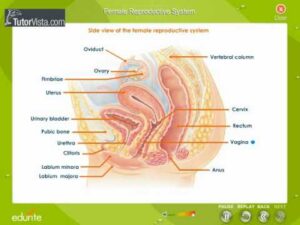
Female reproductive System Part2

Weightlifting Video – 3

Pregnancy Exercises Video – 3
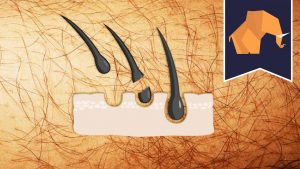
Does hair grow back THICKER if you shave or pluck?

Type 1 vs. Type 2 Diabetes

Light Weights Vs Heavy Weights

Chocolate Peanut Butter Protein Smoothie – Meal Replacement, Pre and Post Workout Shake

Gastrointestinal Surgery Video – 3
What is the Best Way to Treat Acne?

Spiking Insulin For Muscle Growth
Vitamin B Complex – What and Why?

Hyperextension With Machine-3

Military Psychiatry Video – 2

What does basal metabolic rate mean?

Badminton Video – 3
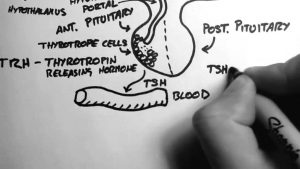
Thyroid Hormone 1 – Control

Overweight & Obesity Video – 16

How To Do A Crunch Properly | Beginners Tutorial

Purus Labs AminoD Essential Amino Acid Supplement – MassiveJoes.com RAW REVIEW D Puruslabs Australia
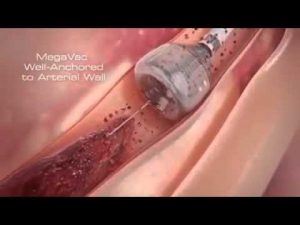
Newest Technology | Heart Stent video (Angioplasty) New Medical Line Video | Heart Attack reasons

