Ear Anatomy | Inside the ear | 3D Human Ear animation video | Biology | Elearnin Ear is that part of the human body that detects sound from the environment and delivers it to the brain. With the help of a ear, humans have the ability to locate the sources of sound. Apart from just being a receiver of sound, it also plays a major role in maintaining a proper balance and position of the body. So as per the laws of science, sound is actually caused when the air molecules are set into vibration and one can hear the sound when the ear picks up or feels these vibrations or sound waves. There are nine main parts of the ear that include the pinna, the ear canal, the ear drum, the hammer, anvil, stirrup, cochlea , Eustachian tube and the auditory nerve. The pinna, also known as the auricle, is the visible portion of the ear that is externally seen. This helps in locating sound sources and directs the sound into it. This does not play any role in maintaining the balance of sound that is heard. The ear canal is a tube like pipeline, that connects the outside of the ear to the ear drum. The ear drum is in the middle ear, which vibrates on receiving sound waves. The hammer on receiving the vibrations from the eardrum, sends them to the anvil that inturn passes them to the stirrup and these are then passed to the inner ear. The inner ear consists of the cochlea and a liquid. The cochlea is a shell-like structure. The Eustachian tube controls the amount of pressure in the ear. The auditory nerve carries the sound to the brain and it is the brain that interprets the sound. The ear together with the brain , controls the balance of the body. All the movements are controlled by this balance and also with the help of muscles. The liquid in the inner ear that we mentioned earlier, is actually responsible for the balance. The liquid in the ear moves along in sync with the physical movement of the body and thus, sending information to the brain on how the body is actually moving at any given instance. The earlobe is the soft lower part of the external ear and this does not have any firmness nor any elasticity. It contains a cartilage and has a large amount of blood supply that provides warmth to the ears and hence aids in the overall balance process.
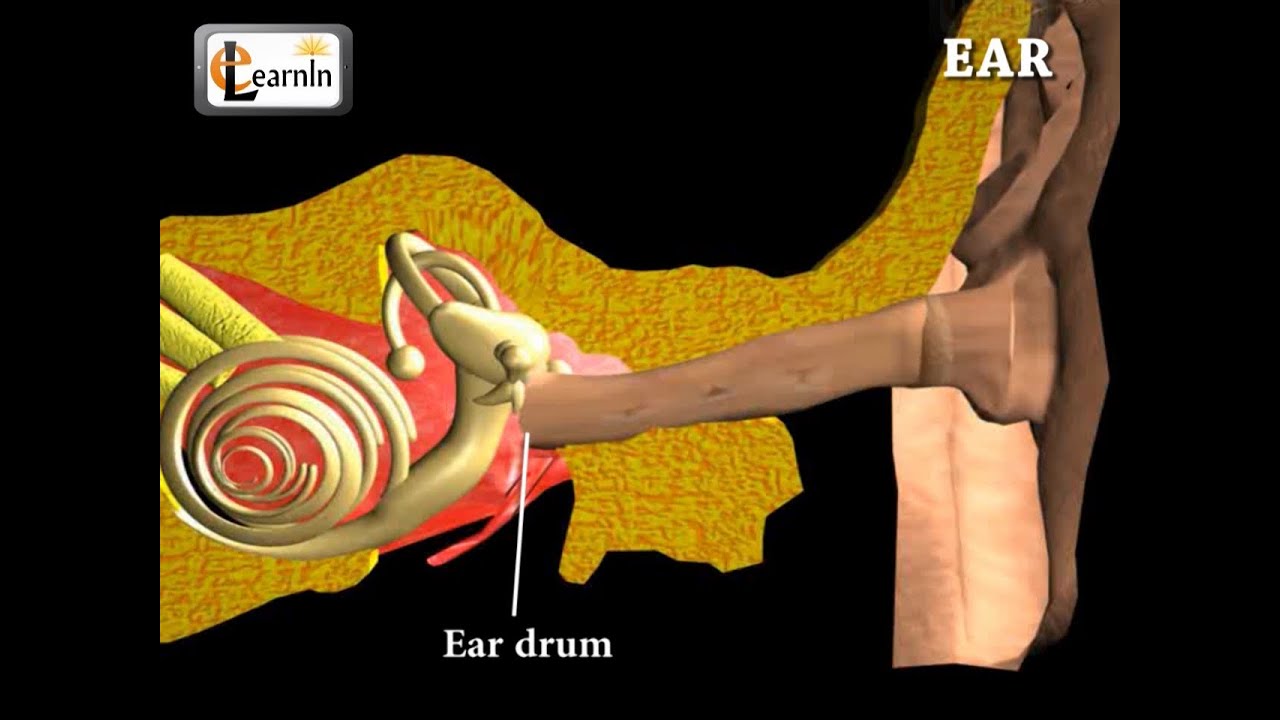
Ear Anatomy | Inside the ear | 3D Human Ear animation video | Biology | Elearnin
- Post author:
- Post published:May 10, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like
ICSE Science class 6 demo ROCKS AND MINERALS TYPES OF ROCKS
Hypertension

Top 8 Plant Based Protein Sources

One Arm Dumbbell Row – Back Exercise – Bodybuilding.com

Gynecomastia Treatment – Is There Any Medical Treatment?

Nutrition Physiology Video – 2

DRES: Clothing for your Body Shape

Arm Workout Tips | Hammer Curls | Biceps Workout

ECG in Dextrocardia

The Sprinter Bodyweight Cardio Drill

Cardio VS. Strength Training (Part 1) (THE BIGGEST FITNESS MYTH)

Alternating hammer curls (standing with dumbbells)

Female reproductive hormones and its function
Patient Education Video: Low Testosterone
Orthopedic Physiotherapy Video – 9
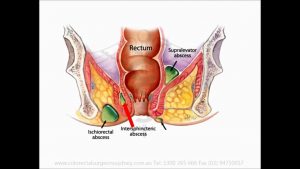
Anal Abscess – English

Are Supplements Bad For Your Liver?

Aroma Oils Video – 1

Sugar Free, Low Sugar Video – 22

Abdominal Exercises : Roman Chair Hyper-extension Abs Exercise

Varicocele: STOP Toxic Blood Pooling!

Massage Spa Video – 4

Urology Surgery Video – 3

TUESDAY Shoulders 9 1 song is attention

Side Effects of Cholesterol Drugs (Lipitor) & Safe Natural Alternatives

shrug exercise

Intermittent Fasting & Fasting Video – 21

Shawn Rhoden’s Overhead Dumbbell Tricep Extension

Physiotherapy in Rehabilitation Video – 16
Brain Protective Drugs Alprazolam

Nutrients in Avocado | Benefits of Avocado | Weight loss or Weight gain!

(Baby hairs?!) Minoxidil Personal Science Test Using Rogaine 5% Day 39

Preacher Curls – 7 Important Preacher Curl Tips

Anaerobically Meaning
Orthopedic Physiotherapy Video – 2
The Main Causes of High Liver Enzymes & Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease – Dr.Berg

Patient Information 2: TB Drugs and Treatment

Internal Medicine Video – 1

How Do Bodybuilders Get Lean Before Competition?
01 Liver Video

THE ONLY 2 MAJOR WAYS TO INCREASE YOUR METABOLISM (The Truth)

