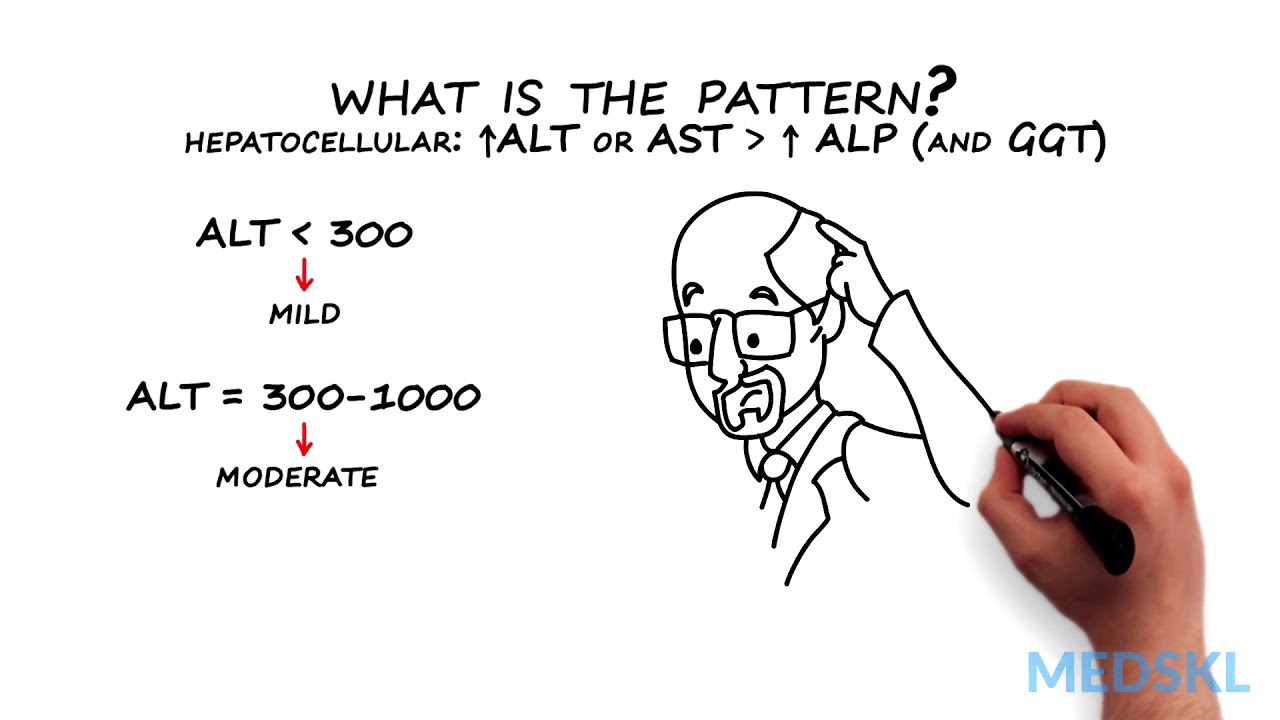
Abnormal liver tests occur frequently. Liver enzymes are frequently confused with liver function tests. This module will help distinguish the two. It is important to be able to assess the test results in light of the patient’s presenting complaint, risk factors and condition. This module will also cover an approach to patients with abnormal liver test results. medskl.com is a global, free open access medical education (FOAMEd) project covering the fundamentals of clinical medicine with animations, lectures and concise summaries. medskl.com is working with over 170 award-winning medical school professors to provide content in 200+ clinical presentations for use in the classroom and for physician CME. Gastroenterology – Abnormal Liver Tests Whiteboard Animation Transcript with Kelly Burak, MD https://medskl.com/module/index/abnormal-liver-tests INTRODUCTION Liver tests or liver enzymes, sometimes incorrectly call liver “function” tests, refer to AST, ALT, ALP, and may include GGT. Abnormal values are often found on routine blood tests and indicate liver injury. Bilirubin, albumin and prothrombin time (or INR) are better tests of the function of the liver and are the LFTs. How to Interpret Abnormal Liver Tests A patient with abnormal liver tests can present in a number of different ways or can be completely asymptomatic.1,2,3 While a clinical assessment focused on risk factors and stigmata of liver disease remains key, the pattern of liver enzyme elevation will guide the differential and workup. 1. Take a look at which enzymes are elevated. A rise in ALT and/or AST that is proportionally higher than ALP indicates a hepatocellular pattern of injury,1 while A rise in ALP, confirmed to be from liver by an abnormal GGT, indicates a cholestatic pattern.1 2. What is the pattern? If the pattern of injury is cholestatic – that is the ALP (and GGT) rise > ALT or AST – you will need to obtain a dedicated ultrasound of the liver and biliary tree to look at the bile ducts Dilated bile duct indicate extrahepatic cholestasis and an ERCP may be needed for diagnosis and therapy Normal bile ducts indicate intrahepatic cholestasis, and a liver biopsy may be required if the cause is not identified by history or other investigations, such as an anti-mitochondrial antibody or MRCP If the pattern of injury is hepatocellular – that is the ALT or AST rise is greater than ALP (and GGT) – determine severity using the ALT level An ALT of <300 is mild and 300-1000 correspond to moderate liver disease.1 These can be acute or chronic and unfortunately the differential diagnosis is broad Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the most common cause of mild elevation4,5 Alcoholic liver disease is associated with an AST that is often 2-3 times higher than the ALT, but alcohol or NAFLD rarely cause the ALT to be <3001,4,5 Further evaluation and testing will be guided by your history and clinical suspicion If ALT >1000 there is SEVERE liver injury which is always acute and symptomatic. These patients are at high risk of acute liver failure.1,3 If you see these values, think and test for the following: Drugs – especially acetaminophen overdose; Viruses – Hepatitis A through E, HSV, CMV, VZV; Ischemia from Budd-Chiari Syndrome or shock; Autoimmune Hepatitis; Wilson’s Disease; and if the patient is pregnant or recently postpartum, HELLP syndrome or acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP)1,3 Quick recognition and diagnosis can guide appropriate management in these patients
Gastroenterology – Abnormal Liver Tests: By Kelly Burak M.D.
- Post author:
- Post published:June 6, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Floor Back Extension

Neurological Physiotherapy Video – 5

General Surgery Video – 2

Industrial Chemicals By Krishna Antioxidants Pvt Ltd, Mumbai
Which Body Type Are YOU? (3 Tips For Each!)

Patient Information 2: TB Drugs and Treatment

How To Do Leg Raises Exercise For Beginners Lower Core And Abs

Muscle Building Workout & Squats Video – 37
Multivitamin with Vitamin B Complex Forte & Vitamin C BECOSULES

Free T3, Free T4, Reverse T3

One Arm Row Dumbbell-7

How to warm up before exercise

Sports Physiotherapy Video – 4
The Role of Insulin in the Human Body

The ATHLEAN-X Channel (SUBSCRIBE!)
How carbohydrates lead to fat gain: Glucose

Physiological Benefits of Meditation
How to use an Insulin pen (Hindi)

What Is Puberty (Puberty Explained)

How to Use Whey Protein to Build Muscle | Bodybuilding Diet

What to Eat Before Gym and What to Eat After Gym Workout

What are lipids?
Brain Parts & Functions video for Kids from www.makemegenius.com

Additional Psychiatry Video – 3

5 KILLER Chest Exercises With NO BENCH (GRUUUUESOME!!)

The Best Pre-Workout Meal for Muscle Gain
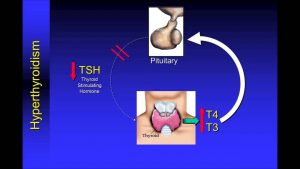
Understanding Thyroid Function Tests

Omega 3 Fatty acids | mechanism of action and health benifits

How to do a donkey kick/ fire hydrant variation (cycling core exercises demo)

Ornithine transcarbamylase OTC deficiency arabic MEANING

Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology: Crash Course A&P #1
How your heart works – Cardiac Cycle

ESR XC A30 for Greiner tube 标清
How to Reach the Antioxidant RDA
![Read more about the article Top 10 Foods High In Protein [HD]](https://videos.drmaheshkumar.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Top-10-Foods-High-In-Protein-HD-4-300x169.jpg)
Top 10 Foods High In Protein [HD]

WHAT TO EAT BEFORE AND AFTER WORKOUT | AMIT PANGHAL | PANGHAL FITNESS

Chicken Breast & Weight Loss – Healthy Fat & Weight Loss Diet

Gastrointestinal Surgery Video – 3
Anabolic vs Catabolic is KEY to FAT LOSS
Ultrashape 3D positioning system body fat reduction machine principle of weight loss therapy

Red Blood Cell Count Abnormal

