In this video I discuss what is glycogen, some of the functions of glycogen, and how many carbs to fill glycogen stores. I also discuss where glycogen storage takes place and how much glycogen is stored in the body. Transcript What is glycogen? To answer this, we are going to start with carbohydrates. When we eat carbs, our body breaks them down into what is called glucose. Glucose is the main source of energy, or fuel for cells. When the cells are full of fuel, the body takes this extra energy and converts it to glycogen. So, glycogen is a form of energy storage in the body. It is estimated that the body stores about 2000 calories worth of energy as glycogen. It gets stored in mainly 2 places, in muscles, and in the liver. Glycogen that is stored in the liver can be used by other organs and cells in the body. Glycogen that is stored in muscles is not shared, so it is used only by muscle cells. It is estimated that The liver will store about 400 calories of energy, and muscles will store about 1600 calories of energy. Now we are going take a basic look at how this works. Lets say that jack here is about to eat. His liver glycogen tank is ¾ full, and his muscle glycogen tank is 3/4 full. Jack eats his meal, and the carbs are broken down into glucose. Some of this glucose is sent by the liver, into the bloodstream to cells throughout his body. The liver takes the extra glucose and converts it to glycogen and stores it for later use, filling up his liver glycogen tank. In between meals when energy is needed, the liver breaks the glycogen down into glucose and releases it into the bloodstream, as you can see the glycogen tank starts to empty until jack eats again. One note here, fat can also be converted to energy to be used, and I will cover that in another video. The process will be similar in the muscles. Jacks muscle glycogen tank was ¾ full before his meal. After his meal, the tank is full. In between meals, jack is moving around, causing his muscle glycogen tank to become depleted.
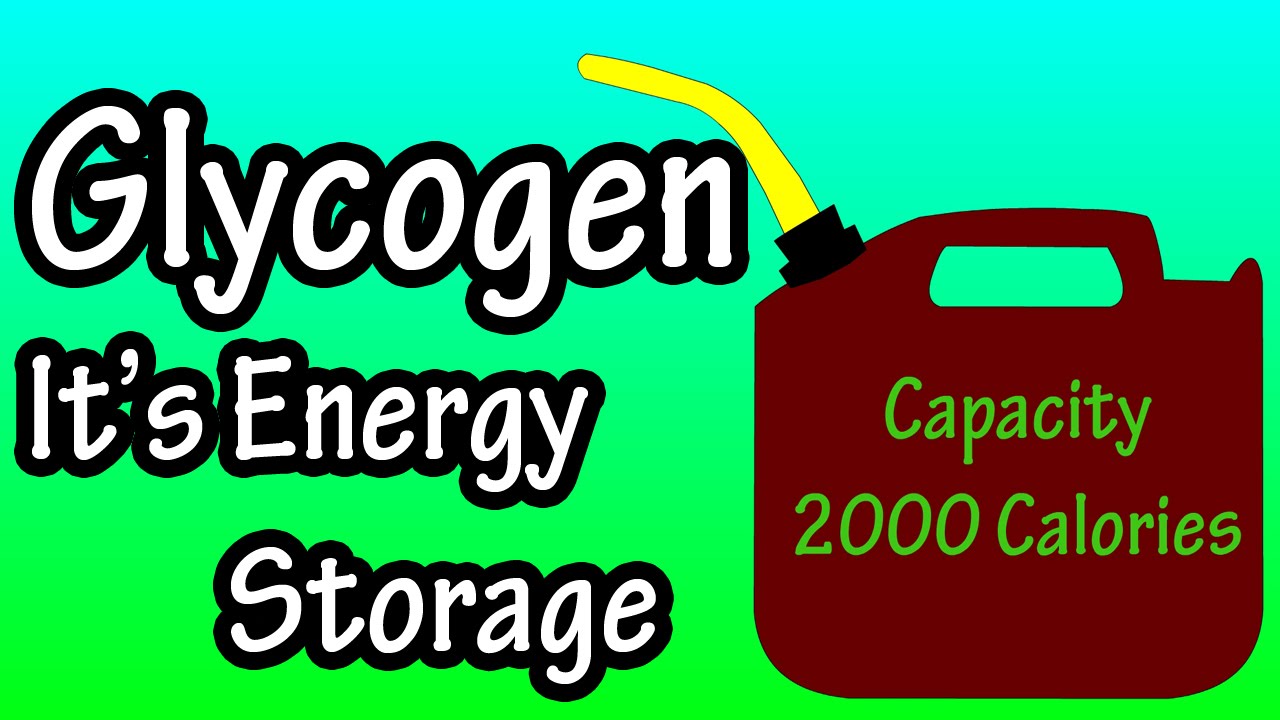
Glycogen – What Is Glycogen?
- Post author:
- Post published:May 24, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Trap Bar Deadlift with Shrug

Propranolol

Do These 3 Things EVERY Morning!

Vitamins Minerals For Health Video – 1
Why BMI is BS
Exercise and Insulin Stimulated Glucose Uptake by Skeletal Muscle

What Causes Hair Loss | What Causes Alopecia Areata | Cure To Baldness
Names and Functions of Organs
CT Angiography with Dr. Arnder

How to Do Barbell Lying Triceps Extensions for Best Results!

What is Renal Hypertension & Renal Stenosis with its management? – Dr. Pallavi Patri

Anatomical Terms: Directional Terms (Anatomy)

Medication Onset of Action & Peak Effect
Know which body type you have !

What is Perfect Age to start Workout? | Guru Mann | Health and Fitness HD

5 Foods High in Vitamin B12

Exercises With Cones : Fitness Training Exercises

Allah Explains Semen Production! (Fun Islamic Fact #16)

What I Eat Before A Workout // Easy Vegan Meal & Snack Ideas

Pediatric Physiotherapy Video – 13

Forensic Psychiatry Video – 3
What is a Protein? Learn about the 3D shape and function of macromolecules
Stretching Exercises

HBP 005- How stress causes High Blood Pressure

Dr Ramakrishna tells about the diet in Jaundice | Online Health Tips

Master the Chest Fly Press – Best Chest Training – BPI Sports

Andrology Video – 2
ISO Lateral Decline Press Exercises for a Fuller Chest
Know Your Body Types

Drink Amazing Drink for Weight Loss

How to Calculate the Daily Calorie Deficit for Maximum Fat Loss : Nutrition Advice

Andropause: Treating Male Hormone Imbalance Naturally (Male Menopause)
Liver Protective Medicine Ornithine

Clinical Psychology Video – 4

Donkey Kicks-6

Flexibility and Gymnastics Skills. Flexibility Stretches. Professional contortion. yoga flexibility

Endocrine System

What is Nutrition?। Definition and importance of Nutrition by Anshika Mam। Bsc Nursing, GNM Students

Health Benefits of Fish Oil Omega-3 Fatty Acids | GuruMann

Military Press – Dumbbells

Lateral Raises-16

