In this video I discuss what is glycogen, some of the functions of glycogen, and how many carbs to fill glycogen stores. I also discuss where glycogen storage takes place and how much glycogen is stored in the body. Transcript What is glycogen? To answer this, we are going to start with carbohydrates. When we eat carbs, our body breaks them down into what is called glucose. Glucose is the main source of energy, or fuel for cells. When the cells are full of fuel, the body takes this extra energy and converts it to glycogen. So, glycogen is a form of energy storage in the body. It is estimated that the body stores about 2000 calories worth of energy as glycogen. It gets stored in mainly 2 places, in muscles, and in the liver. Glycogen that is stored in the liver can be used by other organs and cells in the body. Glycogen that is stored in muscles is not shared, so it is used only by muscle cells. It is estimated that The liver will store about 400 calories of energy, and muscles will store about 1600 calories of energy. Now we are going take a basic look at how this works. Lets say that jack here is about to eat. His liver glycogen tank is ¾ full, and his muscle glycogen tank is 3/4 full. Jack eats his meal, and the carbs are broken down into glucose. Some of this glucose is sent by the liver, into the bloodstream to cells throughout his body. The liver takes the extra glucose and converts it to glycogen and stores it for later use, filling up his liver glycogen tank. In between meals when energy is needed, the liver breaks the glycogen down into glucose and releases it into the bloodstream, as you can see the glycogen tank starts to empty until jack eats again. One note here, fat can also be converted to energy to be used, and I will cover that in another video. The process will be similar in the muscles. Jacks muscle glycogen tank was ¾ full before his meal. After his meal, the tank is full. In between meals, jack is moving around, causing his muscle glycogen tank to become depleted.
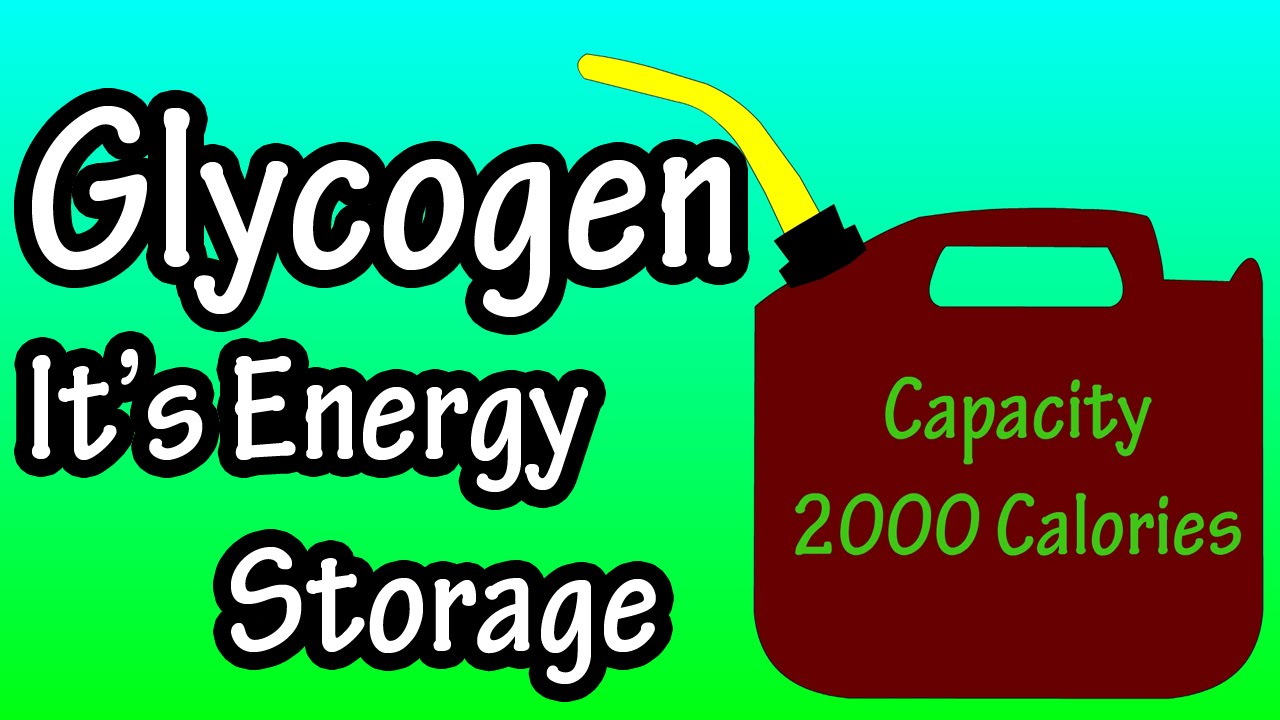
Glycogen – What Is Glycogen?
- Post author:
- Post published:May 27, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

MONDAY: Complete CHEST WORKOUT! (Hindi / Punjabi)

How To: Good Mornings

Things you must know before taking Glutamine Supplements | HINDI

What is ENDOCRINE SYSTEM? What does ENDOCRINE SYSTEM mean? ENDOCRINE SYSTEM meaning & explanation
ECG

Bodybuilding Nutrition, Diet Recipes & Workout – 43

Side plank-6

Reeshape Natural

Are multivitamin supplements necessary during breast feeding?

How to pronounce pantoprazole (Protonix) (Memorizing Pharmacology Flashcard)

Goodmorning-3
Arthritis

What body type are you?

Best exercises for osteoporosis

The Human Body Video – 2
Back Exercise Swiss-Ball Reverse Hyperextension Exercise

Testosterone & Androgenic Effects Video – 44

My Favorite Carbohydrate Sources | Tiger Fitness

What is a Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) and why is it important to know when trying to lose weight.
Erectile Dysfunction: Treatment Options for Erectile Dysfunction
Anatomy & Physiology Online – Cardiac conduction system and its relationship with ECG
Understanding Thyroid Function Tests

Crazy 400m sprint

Human growth hormone bodybuilding
Glucagon and its Functions in HINDI

Zumba Cooldown Perfect by Ed Sheeran || ZumbaFitJessica

Bodybuilding Nutrition, Diet Recipes & Workout – 36

HOW TO MAKE SIMPLE FOOD SWAPS FOR A LOW CHOLESTEROL DIET

How Often Should I Train? | Volume, Intensity & Overtraining

URINE BILIRUBIN TEST

Alcoholism Liver Damage

3 Exercises for Strength Endurance and Conditioning

Keto Diet, Keto Foods, Keto Recipes Video – 19

Foods Rich in Antioxidants – 5 Superfoods with Antioxidants

Speech of Definition – Fitness
3D. ANGIO.BRAIN.mpg
Electrocardiogram – What Is an ECG – Performing an EKG Video.flv

EZ Bar Lying Triceps Extension to Nose
9 Signs & Symptoms Of Kidney Failure | 90% Peoples Are Not Aware

Squat-2

Health And Fitness Video – 7

