Watch more How to Understand Obesity videos: http://www.howcast.com/videos/511330-How-the-Body-Stores-Fat-Obesity When you eat food, all food has calories. Calorie is a unit of energy, so when you eat food digestion begins in your stomach and then your intestines, and your body absorbs the nutrients that it needs in to your bloodstream. Throughout the day, your body will use those calories to help everyday functions of your heart, your lung, your brain, and even just going about your daily life. Whatever excess calories are not used can then be stored as fat. One place that the body stores fat is in your liver. So if you’ve ever had an ultrasound or a CAT scan, someone might have told you that you have a fatty liver. Another place that your body stores fat is just centrally, in your abdomen. This is called the omentum, that’s the fat that encases our organs. We all have that, but people have different amounts of fat depending on how much weight they’re carrying, and that’s actually the dangerous kind of fat, the kind that’s found centrally. Other people store their fat, maybe lower in their bodies, in their hips, in their thighs. This is referred to as gynecoid obesity. So while there’s different ways that the body stores fat, in order to determine if the amount of fat that you’re storing is excessive and that it puts you at increased health risk, you might want to calculate your BMI or your body mass index. And that’s the number that takes your weight and your height and forms a ratio, and helps you decide if you fall in to the obese category. A BMI of 30 or greater is considered obese and puts you at increased health risks. So these are just a few ways of how your body stores excess fat.
How the Body Stores Fat | Obesity
- Post author:
- Post published:May 27, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like
Blood Group Test Experiment Harib Diagnostic Lab

Strong abs exercises: Plank

How Do You Know If You Have Diabetes – Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms

Crunches-3
Uterus and vagina (preview) – Human Anatomy | Kenhub

Human Body, Body Building Muscle Building Anatomy Physiology Video – 1

Steroids Side Effects: Wactch this Before Using Steroids
3 Phase Tablet

How to Do a Dumbbell Shoulder Press

Food Antioxidants, Stroke, and Heart Disease

Sport Meaning

How to Calculate Body Mass Index – Body Mass Index Explained

Is BCCA Good For Your Body? | BeerBiceps BCAA 101

Surya Namaskar – Kalari Version – Part 1

Advantages Of Yoga Video – 2

How to Do a Dumbbell Tricep Extension | Arm Workout

One arm cable triceps extension – Triceps workout / Exercício para Braços – Tríceps

What Is The Definition Of Basal metabolic rate Medical Dictionary Free Online

Endocrine System Diabetes And Asanas Video – 4

Killer bench dips + 400 lbs.I Triceps Exercise I Farid Berlin

Calorie Myth – Why Low Calories Does Not Equal Weight Loss – Dr.Berg

Exercises for Lower Back Extension Based Pain
Sports Medicine Video – 1
How Accutane Works for You
Prostate Enlargement: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia – BPH Causes, Symptoms, Treatment Animation Video

AEROBIC vs ANAEROBIC DIFFERENCE
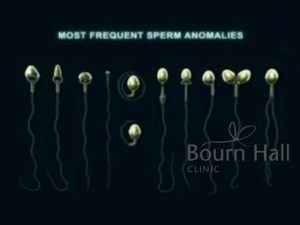
Azoospermia Treatment | Semen Analysis at Bournhall Clinic India

What Is Aerobic Respiration? | Physiology | Biology | FuseSchool

FitPro Nutrition Coach

Testosterone & Androgenic Effects Video – 20

एक दिन में कितना प्रोटीन लेना चाहिए? How much protein in a day

Before and after using the HGH

Which Vitamin B12 Supplement Should We Take? Dr Michael Greger

Forearm Training Tips
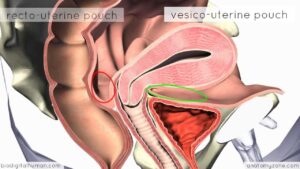
Introduction to Female Reproductive Anatomy – 3D Anatomy Tutorial

Plyometrics – Circuit Training Ideas

What Muscle Groups Do Walking Lunges Work? : Dynamic Exercises
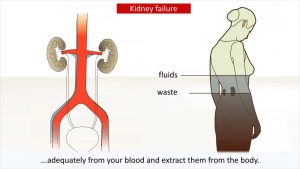
Kidney disease – Causes and treatment of kidney failure

Phil Heath’s Cable Hammer | Bicep Exercise #3

Aerobic Exercise Jogging

Atenolol (Tenormin) Nursing Pharmacology Considerations