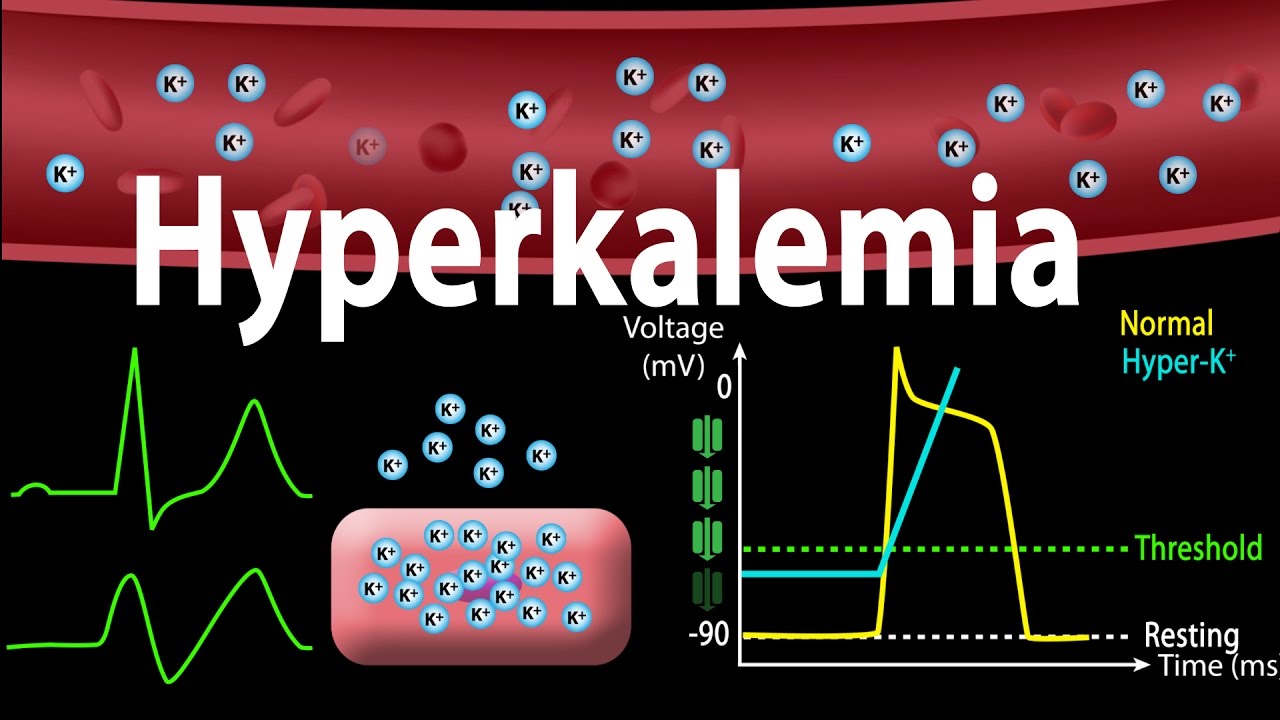
How serum potassium levels affect resting membrane potential and cardiac action potential; ECG (EKG) changes in hyperkalemia. How hyperkalemia causes bradycardia. Electrolytes disorders This video is available for instant download licensing here: https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/ekgecg/-/medias/0e40597c-5219-4950-abbe-aa1583b53ed9-hyperkalemia-narrated-animation ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Voice by: Sue Stern. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Hyperkalemia refers to abnormally high levels of potassium in the blood. The ratio of INTRAcellular to EXTRAcellular potassium is important for generation of action potentials and is essential for normal functions of neurons, skeletal muscles and cardiac muscles. This is why potassium levels in the blood are strictly regulated within a narrow range between 3.5 and 5mmol/L. As the normal daily dietary intake of potassium varies widely and can be as much as 100mmol a day, the body must keep blood potassium levels within the normal limits. This is achieved by 2 mechanisms: – Excretion of potassium through the kidneys and intestines – Shifting of potassium from the extracellular fluid into the cells by the sodium/potassium pump. The pump is mainly regulated by hormones such as insulin and catecholamines. Hyperkalemia is defined as a serum potassium concentration HIGHER than 5mmol/L. Hyperkalemia may result from decreased excretion, excessive intake, or shift of potassium from INSIDE the cells to EXTRA-cellular space. The most common scenario is a RENAL INsufficiency combined with excessive potassium supplements OR administration of certain drugs. Impaired kidney function is most prominent Mild hyperkalemia is often without symptoms, some patients may develop muscle weakness. Slow or chronic increase in potassium levels is less dangerous, as the kidneys eventually adapt by excreting more potassium. Sudden onset and rapid progression of hyperkalemia can be fatal. Primary cause of mortality is the effect of potassium on cardiac functions. As potassium levels INcrease in the EXTRAcellular space, the MAGNITUDE of potassium gradient across the cell membrane is REDUCED, and so is the ABSOLUTE value of the resting membrane potential. Membrane voltage becomes less negative, moving closer to the threshold potential, making it EASIER to initiate an action potential. The effect this has on excitability of myocytes, however, is complex. While initial changes seem to increase myocyte excitability; further rise of potassium has the OPPOSITE effect. This is because the value of membrane potential at the onset of an action potential DETERMINES the number of voltage-gated sodium channels activated during depolarization. As this value becomes less negative in hyperkalemia, the number of available sodium channels DEcreases, resulting in a SLOWER influx of sodium and subsequently SLOWER impulse conduction. ECG changes produced by hyperkalemia follow a typical pattern that correlates with serum potassium levels: peaked T-wave, P wave widens and flattens, PR interval lengthens, QRS complex widens and eventually blends with T-wave. Diagnosis on the basis of ECG alone very difficult. Acute hyperkalemia must be suspected in any patient having new bradycardia or conduction block, especially in those with renal problems. Severe hyperkalemia is treated in 3 steps: – Calcium infusion is given to rapidly REVERSE conduction abnormalities. – Insulin to stimulate the sodium/potassium pump, promoting INTRA-cellular shift – Hemodialysis to remove potassium
Hyperkalemia: Causes, Effects on the Heart, Pathophysiology, Treatment, Animation.
- Post author:
- Post published:May 31, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like
Skeletal System (Part 2)

Androgen Meaning
Amino Acids and Insulin

Top 5 Supplements for Muscle Growth

ARNOLD Training Back

Minerals- What is a Mineral

What is METABOLIC AGE? What does METABOLIC AGE mean? METABOLIC AGE meaning & explanation

Hyperextension With ball-9

Muscle Building Workout & Squats Video – 1

Garlic Nutrition Video – 1

Dumbbell Pullover-7

Estrogen Levels In Women | Her Body

Boxing Video – 3

Dumbbell Bench Press : Chest Exercises

What Colour is Water?

ONE ARM DUMBBELL PREACHER CURLS | TUTORIAL VIDEO

100 % Increase your sperm count in 10 days || Use this Top 5 food for increase Sperm Count.

Buy Alli Weight Loss Aid – How Alli Works
Overweight & Obesity Video – 23
Pharmacology

Atenolol or Tenormin Medication Information (dosing, side effects, patient counseling)

Geriatric Psychiatry Video – 3
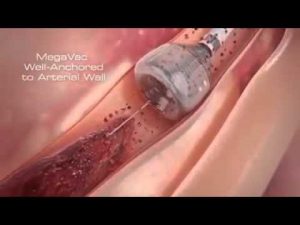
Newest Technology | Heart Stent video (Angioplasty) New Medical Line Video | Heart Attack reasons
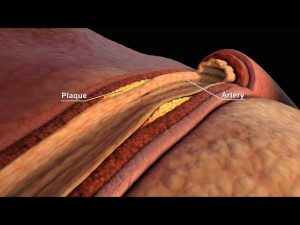
LDL and HDL Cholesterol | Good and Bad Cholesterol | Nucleus Health

Sugar Free, Low Sugar Video – 22

Groin and Adductor Strain Rehabilitation Exercise

Law 8: Fat is Back | 10 Laws Of Muscle-Building

Rear Deltoid-9

Anabolic Steroids – History, Definition, Use & Abuse Video – 7

BICEP EXERCISES FOR STRENGTH & DEFINITION
The10 Best Exercises to Lose Weight
Clinical Psychiatry Video – 1

Dumbbell Pullover-1
Animation exercises level 1

Fish Oil Benefits and Side Effects

Biological Psychiatry Video – 2

Hormones Involved In Birth Control & Fertility Treatment | Biology | FuseSchool
The ABCs of Vitamins | HealthiNation

Flexibility Stretching Video – 6

BCAA Supplements – Are They Necessary? (Branched Chain Amino Acids)

Health & Skill Components of Fitness