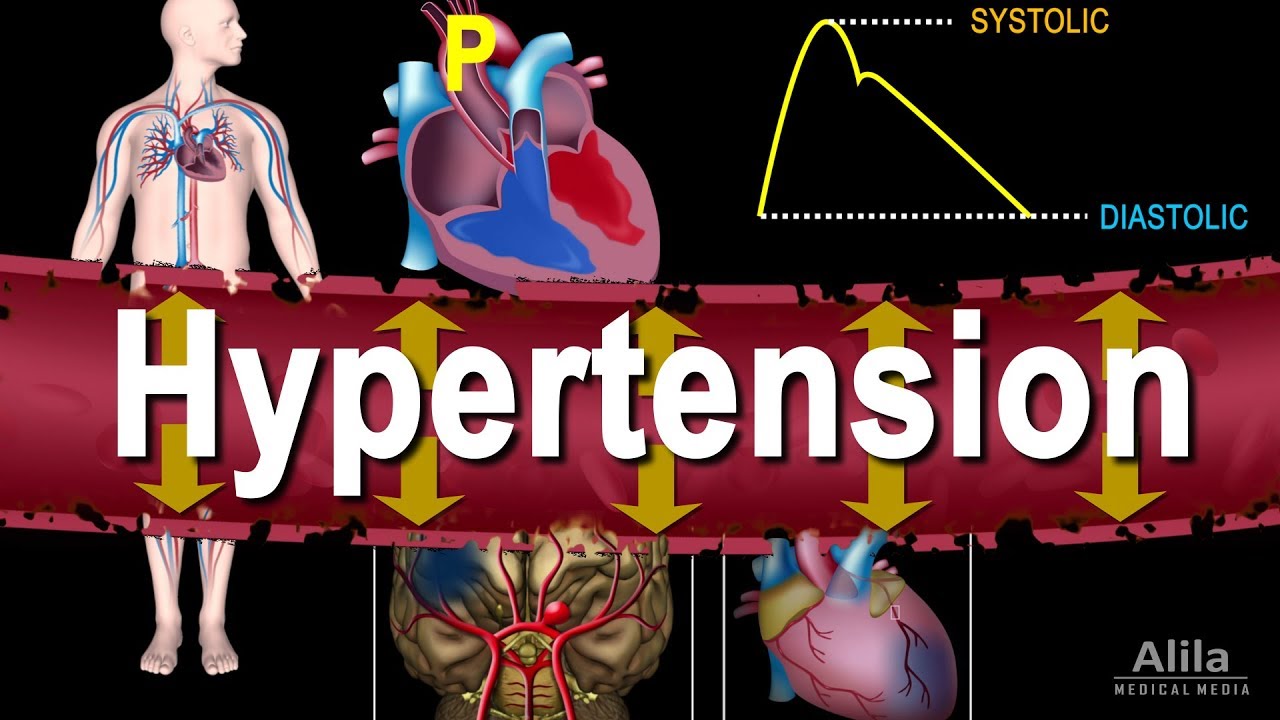
(USMLE topics, cardiology) Blood pressure: systolic and diastolic; hypertension: guidelines, causes, risk factors, complications, treatment, antihypertensive drugs. This video is available for instant download licensing here: https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/hypertensioncholesterol/-/medias/d8cadc84-432b-4925-8e36-16ceeb86ffe0-hypertension-narrated-animation ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Voice by: Sue Stern. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Blood pressure is the force the circulating blood EXERTS on the walls of blood vessels. It is different in different types of vessels, but the term ”blood pressure”, when not specified otherwise, refers to ARTERIAL pressure in the SYSTEMIC circulation. When the heart contracts and pumps blood into the aorta, during systole, the aortic pressure RISES, and so does the systemic arterial pressure. The maximum pressure following an ejection is called the SYSTOLIC pressure. In between heart beats, when the ventricles refill, blood pressure FALLS to its lowest value called the DIASTOLIC pressure. THESE are the 2 numbers on a blood pressure reading. Blood pressure normally shows a daily pattern and is usually lower at night. During day-time, it fluctuates with physical activities and emotional states. Hypertension refers to a PERSISTENT HIGH blood pressure. In the US, high blood pressure used to be defined as greater than 140/90, but recent guidelines have changed these values to 130/80 to better prevent and treat the condition. Normal blood pressure is BELOW 120/80. In practice, blood pressure is considered TOO low ONLY if it produces symptoms. Hypertension does NOT cause symptoms on its own, but it slowly DAMAGES blood vessels, and in the long-term, is a MAJOR risk factor for a variety of cardiovascular diseases such as stroke, aneurysm and heart attack; as well as end organ damage such as renal failure or vision loss. For this reason, hypertension is known as the “SILENT killer”. Hypertension can be classified as primary or secondary, with the former being responsible for over 90% of cases. Primary hypertension has NO apparent cause and may develop as a result of old age, obesity, high-salt diet, lack of exercise, smoking and drinking. Most commonly, the blood vessels are hardened with age or unhealthy diets, making it harder for blood to flow. Secondary hypertension, on the other hand, is caused by an underlying condition. Many conditions and factors can cause hypertension; most notable are kidney problems and endocrine disturbances. Regardless of the cause, the INcrease in blood pressure is produced by EITHER an INcrease in vascular resistance – narrower or stiffer blood vessels; OR an INcrease in cardiac output – larger volume of blood pumped out by the heart. These 2 factors are the targets of antihypertensive drugs. Treatments must start with life style changes such as healthy, low-sodium diets, physical exercise and stress management. On top of that, antihypertensive agents may be used to control hypertension. These include: – Vasodilators: these drugs DILATE blood vessels, thereby DEcreasing vascular resistance and reducing blood pressure. – Diuretics: diuretics promote sodium and water removal by the kidneys and thereby DEcrease blood volume. – Drugs that DEcrease cardiac output by decreasing heart rate or contractility, may also be used to treat hypertension.
Hypertension – High Blood Pressure, Animation
- Post author:admin
- Post published:October 7, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Testosterone & Androgenic Effects Video – 41

Components of physical fitness
Erectile Dysfunction animation flv

Step Up-4

Physiotherapy in Obstetrics Video – 5

Optometry Video – 2

What is Acne and How Do I Get Rid of it Forever? | Allure

TRX close grip press w/triceps extension

Muscle Growth before interview

Emergency Medicine Video – 3

How to Do a Dumbbell Tricep Extension | Arm Workout

Tips for Pre & Post Workout Meals

How to Do Rear Deltoid Rows
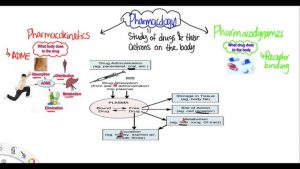
Basics of Pharmacology

Human Body, Body Building Muscle Building Anatomy Physiology Video – 25

Digestion and Absorption of Proteins – Part 1/2

ANEMIA AWARNESS VIDEO
Neurobion fort Tablet of Vitamin B Complex with B12

Bodybuilding Nutrition, Diet Recipes & Workout – 1
Pregnancy swelling (edema)

World’s Best Fish Oil Capsule | WOW Omega – 3 Fish Oil Capsule Supplement Review in Hindi

Bodybuilding Nutrition, Diet Recipes & Workout – 5

Stop Jogging and Start Sprinting! – How to Sprint and Why it’s Better for Your Health

Overhead Triceps Single Hand Extension | Moderate Weight Is Best Weight #shorts #YoFitnessShorts

Vomiting Home Remedies – Instant Relief

How To Burn Body Fat Naturally | Best Fat Burning Tips For Women

How to Warm Up before Sprinting | Sprinting

Spa Marketing Video – 1

Split Stance Bent Over Dumbbell Row

Pulmonology Video – 2
Will This Solve Organ Transplant Rejection Forever?
Shock Wave – Mechanism of Action

Calculate Body Mass Index (BMI)
ESR Test

Spicejet Amex Offer

Branches of Physiotherapy Video – 32

Testosterone & Androgenic Effects Video – 9

Football Psychology Video – 1

Lab Test Lipid Panel Mesa AZ | Blood Sugar Lab Test AZ | Allen Family Medicine (480) 699-2222

Meditation Video – 6

How to Use Your BMR (Basal Metabolic Rate) to Lose Weight – Dr Mandell