Bilirubin is produced from the destruction of Red Blood Cells. It is a highly toxic molecule and there is 0.2 – 0.3g of it produced every day in the body. Yet, a normal Bilirubin level is maintained at 0.2- 1.2mg/dl. If this level increases, it’s called hyperbilirubinemia. Jaundice is the yellow discoloration of skin, mucus membrane and sclera (Icterus) due to increase in Bil in blood to more than 2mg/dl. Jaundice itself is not a disease, but rather a sign of some abnormaility in the body associated with metabolism of bilirubin. Based on reason for occurance, Jaundice is of three types: Prehepatic, Hepatic, and post Hepatic. “Hepatic” is a word of Greek origin, meaning Liver. Prehepatic: Excess Hb Breakdown producing more Unconjugated Bilirubin than Liver can Handle. Or Problem in uptake of this Bilirubin by Liver. ~Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia. eg: It can also happen in sickle cell anemia, spherocytosis, Thalassemia Ectopic Pregnancy. Hepatic: Problem in Conjugation of Bilirubin. ~Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia. eg: Physiological Jaundice of Newborn: In the womb, the RBC of fetus has a different Hb than adults. Soon after birth, this Hb is rapidly broken down to make way for Adult Hemoglobin. The Unconjugated bilirubin thus formed is more than the newborn’s liver can handle. It takes 2 weeks for the liver to become capable of conjugating that much bilirubin. Hence, for a week or so, the newborn has this harmless jaundice. Other causes are Gilbert’s Syndrome or its more severe form, Criggler Najjar disease. Hepatitis (Inflammation of Liver) by Viruses like Hepatitis A,B,C,D,E. Hepatocellular damage causes both conjugated and Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia. (Part 2: 37:00) Alanine Transaminase and Aspartate transaminase enzymes of liver spill into blood circulation in liver damage. If AST & ALT both increased, but AST=2*ALT, Alcoholic injury Post Hepatic: Problem in transport of Conjugated Bilirubin out of Liver so it goes back the direction it came from. ~Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia. ALP, Gamma glutamyl Transferase, 5 nucleotidases spill into blood

Jaundice and Neonatal Jaundice Explained- What is it and How do babies get Jaundice?
- Post author:
- Post published:June 12, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

How To: Close-Grip Barbell Bench Press

Low Pulley Biceps Curl

Lat Pull Down-13
What Is Semen
Pre Surgery Video – 1

Silymarin – Rejuvenate your Liver

Insulin vs Glucagon

Equate Whey protein review

Flat Bench Press Dumbbell-6
MUSCULAR SYSTEM CONTRACTION AND RELAXATION CYCLE

What Is Puberty (Puberty Explained)
Half Life (T 1/2) – Pharmacology

Rheumatology Video – 2

70 Bodyweight Cardio Exercises
Triceps Exercises

One Hand Trice Extension-5
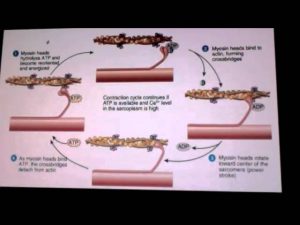
MUSCULAR SYSTEM CONTRACTION AND RELAXATION CYCLE

Top 10 Resistance Band Exercises (You can do anywhere)

3 Lat Pulldown Variations

Jogging on Spot

Back Flexibility Video

Metabolism, Anabolism, and Catabolism

DEFINITION FITNESS

Anemia – Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & More…

Branches of Physiotherapy Video – 20
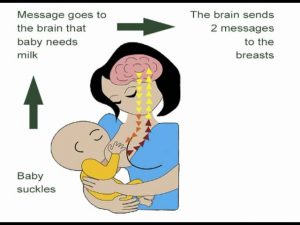
Lactation Animation

HGH, Growth Hormones & Plant Hormones Video – 20

Lat Pull Down-4
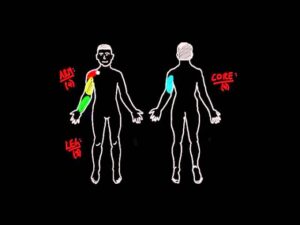
11 major muscle groups

Instructional Fitness – Rear Pull Downs

How to Decrease Your Metabolism

Pulmonology Video – 4

Zumba Cooldown Perfect by Ed Sheeran || ZumbaFitJessica

Cardio with a BARBELL – 2 Muscle Building Cardio Exercises

Lat Pull Down-11
Running

Human Body, Body Building Muscle Building Anatomy Physiology Video – 44

Thyroid Gland: Thyroid Hormone Function

Strength of Materials (Part 1: Stress and Strain)
Branches of Physiotherapy Video – 25

Seated Bent Over Rear Delt Raise – Shoulder Exercise – Bodybuilding.com

