This video is available for instant download licensing here : https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/addiction-science/-/medias/64c6e72c-f3af-4b26-aba2-f4dbfad29cca-mechanism-of-drug-addiction-in-the-brain-narrated-animation ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Addiction is a neurological disorder that affects the reward system in the brain. In a healthy person, the reward system reinforces important behaviors that are essential for survival such as eating, drinking, sex, and social interaction. For example, the reward system ensures that you reach for food when you are hungry, because you know that after eating you will feel good. In other words, it makes the activity of eating pleasurable and memorable, so you would want to do it again and again whenever you feel hungry. Drugs of abuse hijack this system, turning the person’s natural needs into drug needs. The brain consists of billions of neurons, or nerve cells, which communicate via chemical messages, or neurotransmitters. When a neuron is sufficiently stimulated, an electrical impulse called an action potential is generated and travels down the axon to the nerve terminal. Here, it triggers the release of a neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft – a space between neurons. The neurotransmitter then binds to a receptor on a neighboring neuron, generating a signal in it, thereby transmitting the information to that neuron. The major reward pathways involve transmission of the neurotransmitter dopamine from the ventral tegmental area – the VTA – of the midbrain to the limbic system and the frontal cortex. Engaging in enjoyable activities generates action potentials in dopamine-producing neurons of the VTA. This causes dopamine release from the neurons into the synaptic space. Dopamine then binds to and stimulates dopamine-receptor on the receiving neuron. This stimulation by dopamine is believed to produce the pleasurable feelings or rewarding effect. Dopamine molecules are then removed from the synaptic space and transported back in to the transmitting neuron by a special protein called dopamine-transporter. Most drugs of abuse increase the level of dopamine in the reward pathway. Some drugs such as alcohol, heroin, and nicotine indirectly excite the dopamine-producing neurons in the VTA so that they generate more action potentials. Cocaine acts at the nerve terminal. It binds to dopamine-transporter and blocks the re-uptake of dopamine. Methamphetamine – a psychostimulant – acts similarly to cocaine in blocking dopamine removal. In addition, it can enter the neuron, into the dopamine-containing vesicles where it triggers dopamine release even in the absence of action potentials. Different drugs act different way but the common outcome is that dopamine builds-up in the synapse to a much greater amount than normal. This causes a continuous stimulation, maybe over-stimulation of receiving neurons and is responsible for prolonged and intense euphoria experienced by drug users. Repeated exposure to dopamine surges caused by drugs eventually de-sensitizes the reward system. The system is no longer responsive to everyday stimuli; the only thing that is rewarding is the drug. That is how drugs change the person’s life priority. After some time, even the drug loses its ability to reward and higher doses are required to achieve the rewarding effect. This ultimately leads to drug overdose.
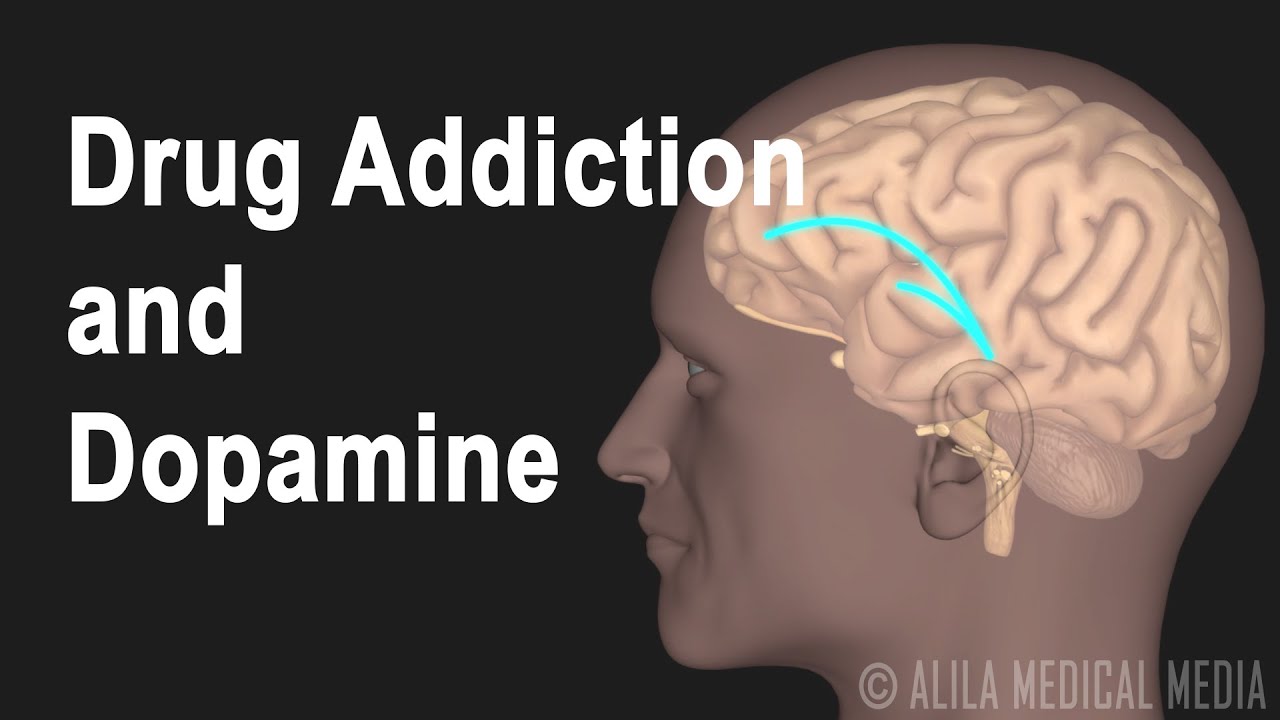
Mechanism of Drug Addiction in the Brain, Animation.
- Post author:
- Post published:May 25, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like
Fat Loss/Obesity Nutrition
Growth Hormone Deficiency
Vitamins, How They Work
What is a Carbuncle? Mr. Popper’s World’s Largest Cysts & Boils

Flexibility Stretching Video – 5

Tennis Video – 1

Low Thyroid Problems
Fat cells inside human body behavior
Gynecomastia Patients Talk About Their Surgery Experience
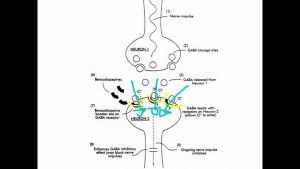
GABA & Benzodiazepenes – VCE U4 Psychology

How To: Dumbbell Bent-Over Raise
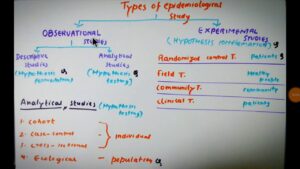
Epidemiology Video – 2

Lipid

Swedish Massage Video – 2
Semen Analysis (Sperm Count)

3 Foods That Help Prevent Heart Disease | Healthy Food

Diabetes Education – Carbohydrates

Metabolism, Anabolism, and Catabolism

Kelly Coffey Meyer’s 30 Minutes to Fitness “Muscle Definition”

Decline Bench Press-3

↓ 5 Important & Clinically Proven Reasons You Should NOT Take Statin Drugs – by Dr Sam Robbins

Clear and Compelling Writing Grammarly
The scientific truth about steroids

Bodybuilding Nutrition, Diet Recipes & Workout – 28
Nuts and Bolts of Cholesterol Lowering

sports meaning and pronunciation
Estrogen Metabolism

Team Wild’s Cable Squats
![Read more about the article Master Human Anatomy And Physiology course book [awesome way to learn] 2013](https://videos.drmaheshkumar.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Master-Human-Anatomy-And-Physiology-course-book-awesome-way-to-learn-2013-300x225.jpg)
Master Human Anatomy And Physiology course book [awesome way to learn] 2013

Light Cardio and Stretching Cool Down Workout – Relaxing Stretches for Flexibility

GYM HACK | Seated Calf Raise | Tiger Fitness

Pre/During/Post Workout Drink || SHREDDED NEXT LEVEL by Guru Mann ||

Full day of Eating – Extreme Fat loss Diet – Lose 10 Kg

How To Do a Close Grip Tricep Bench Press
Skin disease-You may fear of Abscess #TeYouTe

L GLUTAMINE : WHAT DOES GLUTAMINE DO

Pec Fly Machine-3

Cialis & Erectile Dysfunction | Erection Problems

Emergency Psychiatry Video – 3

michalbudzisz – anabolism
ARBS Angiotensin Receptor Blockers

