(USMLE topics) Molecular basis of the sliding filament theory (skeletal muscle contraction) – the cross bridge cycle. This video is available for instant download licensing here : https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/all-animations/bones-joints-and-muscles-videos/-/medias/79b11851-3cbe-4df2-921d-3c55818a6c83-muscle-contraction-the-cross-bridge-cycle-narrated-animation Voice by: Sue Stern ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia Muscle contraction is at the basis of all skeletal movements. Skeletal muscles are composed of muscles fibers which in turn are made of repetitive functional units called sarcomeres. Each sarcomere contains many parallel, overlapping thin (actin) and thick (myosin) filaments. The muscle contracts when these filaments slide past each other, resulting in a shortening of the sarcomere and thus the muscle. This is known as the sliding filament theory. Cross-bridge cycling forms the molecular basis for this sliding movement. – Muscle contraction is initiated when muscle fibers are stimulated by a nerve impulse and calcium ions are released. – To trigger muscular contraction, the troponin units on the actin myofilaments are bound by calcium ions. The binding displaces tropomyosin along the myofilaments, which in turn (and) exposes the myosin binding sites. – At this stage, the head of each myosin unit is bound to an ADP and a phosphate molecule remaining from the previous muscular contraction. – Now, the myosin heads release these phosphates and bind to the actin myofilaments via the newly exposed myosin binding sites. – In this way, the actin and myosin myofilaments are cross-linked. – The two myofilaments glide past one another, propelled by a head-first movement of the myosin units powered by the chemical energy stored in their heads. As the units move, they release the ADP molecules bound to their heads. – The gliding motion is halted when ATP molecules bind to the myosin heads, thus severing the bonds between myosin and actin. – The ATP molecules bound to myosin are now decomposed into ADP and phosphate, with the energy released by this reaction stored in the myosin heads, ready to be used in the next cycle of movement. – Having been unbound from actin, the myosin heads resume their starting positions along the actin myofilament, and can now begin a new sequence of actin binding. – Thus, the presence of further calcium ions will trigger a new contraction cycle
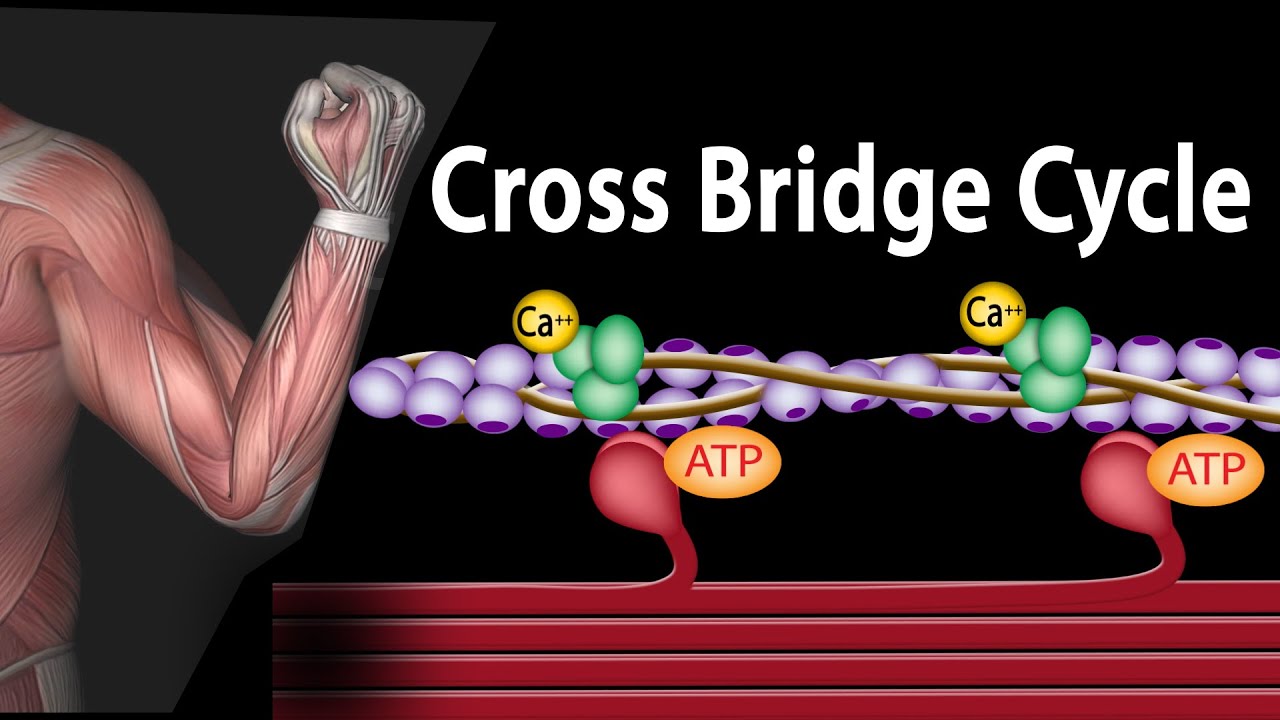
Muscle Contraction – Cross Bridge Cycle, Animation.
- Post author:
- Post published:June 14, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

How to Do a Dumbbell Row | Back Workout

Neurodevelopmental Disorder Video – 4

Alcoholic Liver Disease – For Medical Students

KOREAN BODYBUILDERS : The best Genetics in the WORLD?
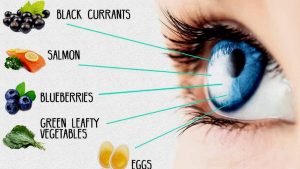
8 Foods To Improve Eyesight, Prevent Cataracts, Glaucoma & Diabetic Eye Problems

What is cardiovascular exercise — Definition of cardiovascular endurance
What Visceral Fat Does To The Body (The Doctors)

World’s Best Multivitamins at CHEMIST SHOP | Cheapest | Guaranteed Results

Triceps Pulley Extension-5

Erector Spinae Back Extension-19

What does isotretinoin mean?

Muscle Building Workout & Squats Video – 12

You Don’t Need Statin Drugs!
How To: Side Oblique Crunch

Good or Bad Vitamin Supplements Medical Course

Dr Ramakrishna tells about the diet in Jaundice | Online Health Tips

Urology Video – 4
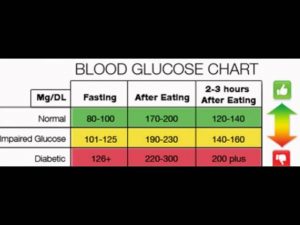
Normal Blood Sugar Level

Keto Diet, Keto Foods, Keto Recipes Video – 25
How does Creatine work? | Axis Labs

Anabolic Steroids – History, Definition, Use & Abuse Video – 20

Testosterone & Androgenic Effects Video – 18

Human Body, Body Building Muscle Building Anatomy Physiology Video – 16

Pediatric Surgery Video – 2

What Is Type 1 Diabetes? | 2 Minute Guide | Diabetes UK

21 Inner thigh Exercises – Adductor Variations

Diabetes Type 1 Cure? – A-Level (A2) Biology

Sports Physiotherapy Video – 2
Testosterone & Androgenic Effects Video – 24

Heart attack (myocardial infarct) medications | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy

Muscle Building Workout & Squats Video – 3

Testosterone & Androgenic Effects Video – 49

Sugar Free, Low Sugar Video – 12

How to hit muscle groups twice a week

CT Angiography at Saifee Hospital Mumbai

WORST Shoulder Exercise for Bigger Shoulders – Upright Rows @hodgetwins
CT Angiography with Dr. Arnder

Emergency Medicine Video – 1
DEXA – Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry

Growth Period Animation WIP 3.

Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) – Explained – Part 1

