medskl.com is a global, free open access medical education (FOAMEd) project covering the fundamentals of clinical medicine with animations, lectures and concise summaries. medskl.com is working with over 170 award-winning medical school professors to provide content in 200+ clinical presentations for use in the classroom and for physician CME. Nephrology – Chronic Kidney Disease Whiteboard Animation Transcript with Steven Cheng, MD https://medskl.com/Module/Index/chronic-kidney-disease Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is caused by a wide variety of pathologic processes, including diabetes, hypertension, and autoimmune diseases. The stages of CKD, from stage 1 to stage 5, reflect progressive loss of function as quantified by the glomerular filtration rate or GFR. GFR is commonly estimated using serum creatinine levels, which increase as renal function falls. In early CKD, patients are frequently asymptomatic due to the large amount of “backup function” in the kidneys. However, as more function is lost, this ability to compensate is overwhelmed. Fluids, electrolytes, minerals, and acids, which are usually flushed out of the body, begin to accumulate, and patients develop anemia and bone/mineral disorders. While we cannot undo this damage, we can prevent the complications of chronic kidney disease. Dietary restrictions to lower sodium and potassium intake can prevent electrolyte abnormalities and diuretics can remove excess fluid. We can also prevent progressive damage from hypertension and proteinuria, using medications that target the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone axis. In some, GFR may continue to fall despite intervention, especially when the underlying disease is poorly controlled or chronic damage is extensive. Patients subsequently develop symptoms of uremia, including persistent fatigue, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, and confusion. Treatment includes dialysis – through a variety of methods – to remove toxins and prolong life. However, the best option for uremic patients is renal transplantation. With a carefully supervised anti-rejection regimen, these patients can again enjoy life with a new kidney.
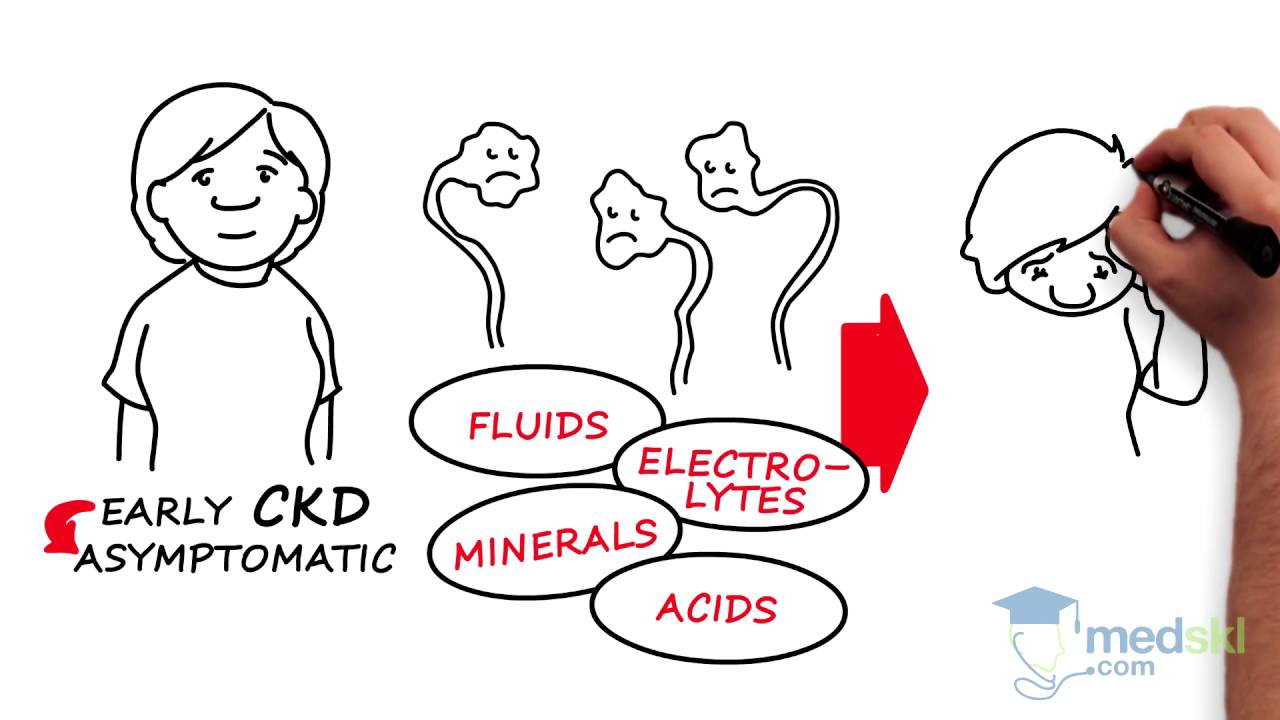
Nephrology – Chronic Kidney Disease: By Steven Cheng M.D.
- Post author:
- Post published:May 24, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like
Understanding Blood Pressure | Human Anatomy and Physiology video 3D animation | elearnin

How To Boost Your Metabolism And Burn More Fat | 3 Simple Tips

Exercises To Increase BMR

Healthy Diet During First Trimester – Onlymyhealth.com
ENT Surgery Video – 5

Crunches-4

Chest Exercises: Push Up

Chemistry in Everyday life part 13 (Food additives) CBSE class 12 XII

Sugar Free, Low Sugar Video – 1

When You Burn Fat, Where Does it Go?

How to Do Back Extensions

Tip of the Day! Target the lower pecs without an official Decline Bench!

Lat Pull Down-10

Overhead Press Dumbbells-10

Swiss Ball Twisting Reverse Back Extension

Child And Adolescent Psychiatry Video – 1

Creatine and Kidney Damage ?

Protein Shake on Non Workout Days

Anabolic Steroids – History, Definition, Use & Abuse Video – 18

… 12 07 2014 – Birmingham – Definition Fitness Centre – Anita CK …

SETS AND REPS

The best and only licensed medicine for weight loss -orlistat

Aroma Therapy Video – 1

BioDomino: The human digestive system in 6,300 dominoes
Erectile Dysfunction and Lower Back Pain

Alcoholic Liver Disease – For Medical Students

Alternating hammer curls (standing with dumbbells)

Seated Rows for THICK BACK MUSCLES! (Hindi / Punjabi)

Fat Loss, Weight Loss Video – 24

6 Packs Abs Video – 5

One Arm Row Dumbbell-4

TRICEPS: Skull Crushers & Close Grip Tricep Press Superset

Latissimus Dorsi Bent Over Row-6

Leg Presses Without Machines : Simple & Effective Exercises
Human Body – Anat & Physio

Meal Prep Shopping List for Fat Loss

Kizen Bench Program|245lbs 8×3|Week 1 day 1

Pranayama Video – 6

Home Remedies To Cure ANEMIA Fast – Treat Iron Deficiency Anemia Naturally | Best Foods For Anemia

Stability ball back extensions

What are Anabolic Steroids?

