For more information, log on to- http://shomusbiology.weebly.com/ Download the study materials here- http://shomusbiology.weebly.com/bio-materials.html Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή “metabolē”, “change” or Greek: μεταβολισμός metabolismos, “outthrow”) is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories. Catabolism breaks down organic matter, for example to harvest energy in cellular respiration. Anabolism uses energy to construct components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy and will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. As enzymes act as catalysts they allow these reactions to proceed quickly and efficiently. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell’s environment or signals from other cells. The metabolism of an organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which it will find poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals.[1] The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food. A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species.[2] For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants.[3] These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and being retained because of their efficacy.[4][5] Source of the article published in description is Wikipedia. I am sharing their material. © by original content developers of Wikipedia. Link- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
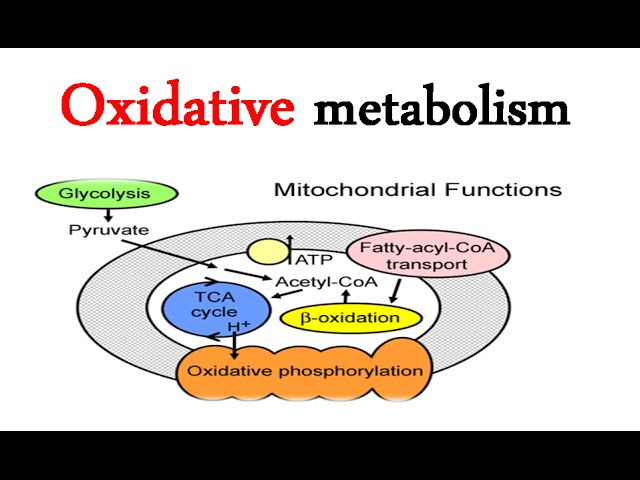
Overview of oxidative fuel metabolism
- Post author:
- Post published:June 15, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Back Extensions On Ball

Carrier Oils Video – 1

nice meditation videos relaxation video
Stretching Exercises

Body Composition Measurement

Shrugs-6

Reading 12-Lead ECG’s – EMTprep.com

Abhyanga – Ayurved Video – 4

What is Whey Protein? (Protein Shake)
Diabetes Protective Medicine Metformin
Running Muscle Groups used
Ultrashape 3D positioning system body fat reduction machine principle of weight loss therapy

BCAA Kya Hai? BCAA Ke Fayde Aur Nuksan | @Fitness Fighters
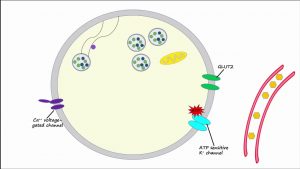
Regulation of Insulin Release and Insulin Action

Anabolic Androgenic Steroid Misused
Liver Damage Symptoms
Understanding Blood Pressure | Human Anatomy and Physiology video 3D animation | elearnin

Hormones and Men’s Health

Anabolic Steroids – History, Definition, Use & Abuse Video – 4

Wexford University Health, Fitness, Nutrition Degrees
Learning How to do ECG

Step Ups…You’re Doing It WRONG

Do Calories Matter in Ketosis: Insulin vs Thermodynamics (With Dr. Anderson)
Female Reproductive Cycle
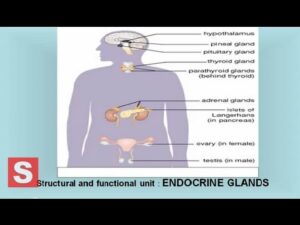
Endocrine system – Control and Coordination CBSE Class X Science ( Biology) Lesson

Clinical Psychology Video – 2

006 Lying Tricep Extensions
How Do You Get Pregnant? | Planned Parenthood Video
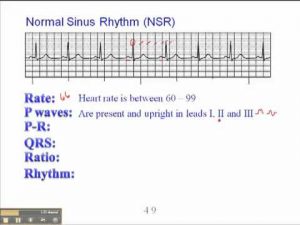
ECG: Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)

Muscle Building Workout & Squats Video – 7

Brain Disorders: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Propranolol

TOP 3 Natural GLUTAMINE Food for Muscle Building & Recovery | Info by Guru Mann

Close Grip Bench Press for Big Triceps

Physiotherapy in Obstetrics Video – 1

Athletic Stretching & Cool-Down Exercise: Danielle Pascente

Anabolic Steroids – History, Definition, Use & Abuse Video – 30

Things you must know before taking Glutamine Supplements | HINDI

Barbell Bench Press – HASfit Chest Exercise Demonstration – Flat Bench Presses Form – Pectoral

Bodybuilding Nutrition, Diet Recipes & Workout – 1

How To: Plank

