Structure of Bone|Anatomy of Bone|3D Animation|Biology It is important for bones to be strong to support our body weight and in some cases provide protection such as the skull and ribs. However, they must also be light enough to make movement possible. A long bone consists of several sections: Diaphysis: This is the long central shaft Epiphysis: Forms the larger rounded ends of long bones Metaphysis: Area betweent the diaphysis and epiphysis at both ends of the bone Epiphyseal Plates: Plates of cartilage, also known as growth plates which allow the long bones to grow in length during childhood. Once we stop growing, between 18 and 25 years of age the cartilage plates stop producing cartilage cells and are gradually replaced by bone. Covering the ends of bones, where they form a joint with another bone, is a layer of hyaline cartiage. This is a firm but elastic type of cartilage which provides shock absorbtion to the joint and has no neural or vascular supply. Bone Anatomy If you were to cut a cross-section through a bone, you would first come across a thin layer of dense connective tissue known as Periosteum. This can be divided into two layers, an outer ‘fibrous layer’ containing mainly fibroblasts and an inner ‘cambium layer’, containing progenitor cells which develop into osteoblasts (the cells responsible for bone formation). The periosteum provides a good blood supply to the bone and a point for muscular attachment. Formation and remodelling of bone Bone formation is an essential process in the development of the human body. It starts during the development of the foetus, and continues throughout childhood and adolescence as the skeleton grows. Bone remodelling meanwhile is a life-long process, consisting of resorption (the breaking down of old bone) and ossification (formation of new bone), and is key to shaping the skeleton and to the repair of bone fractures. There are three types of cell present in bone that are of particular interest – osteoblasts, osteocytes and osteoclasts, which are respectively responsible for the production, maintenance and resorption of bone. Osteoblasts Mononucleated “bone-forming” cells found near the surface of bones. They are responsible for making osteoid, which consists mainly of collagen. The osteoblasts then secrete alkaline phosphatase to create sites for calcium and phosphate deposition, which allows crystals of bone mineral to grow at these sites. The osteoid becomes mineralised, thus forming bone. Osteocytes These are osteoblasts that are no longer on the surface of the bone, but are instead found in lacunae between the lamellae in bone. Their main role is homeostasis – maintaining the correct oxygen and mineral levels in the bone. Osteoclasts Multinucleated cells responsible for bone resorption. They travel to specific sites on the surface of bone and secrete acid phosphatase, which unfixes the calcium in mineralised bone to break it down. During foetal development there are two mechanisms for creating bone tissue: Endochondral ossification Intramembranous ossification Intramembranous ossification occurs in the formation of flat bones such as those in the skull, and will not be covered further here. More information can be found through the Going Further page. Endochondral ossification This involves bone growth from an underlying cartilage model, and is seen in the formation and growth of long bones such as the femur. The initial step involves the development of a cartilage model, which has the rough shape of the bone being formed. In the middle of the shaft is the primary ossification centre, where osteoblasts lay down osteoid on the shaft to form a bone collar. The osteoid calcifies, and blood vessels grow into cavities within the matrix. Osteoblasts then use the calcified matrix as a support structure to lay down more osteoid and form trabeculae within the bone. Meanwhile osteoclasts break down spongy bone to create the medullary cavity, which contains bone marrow.
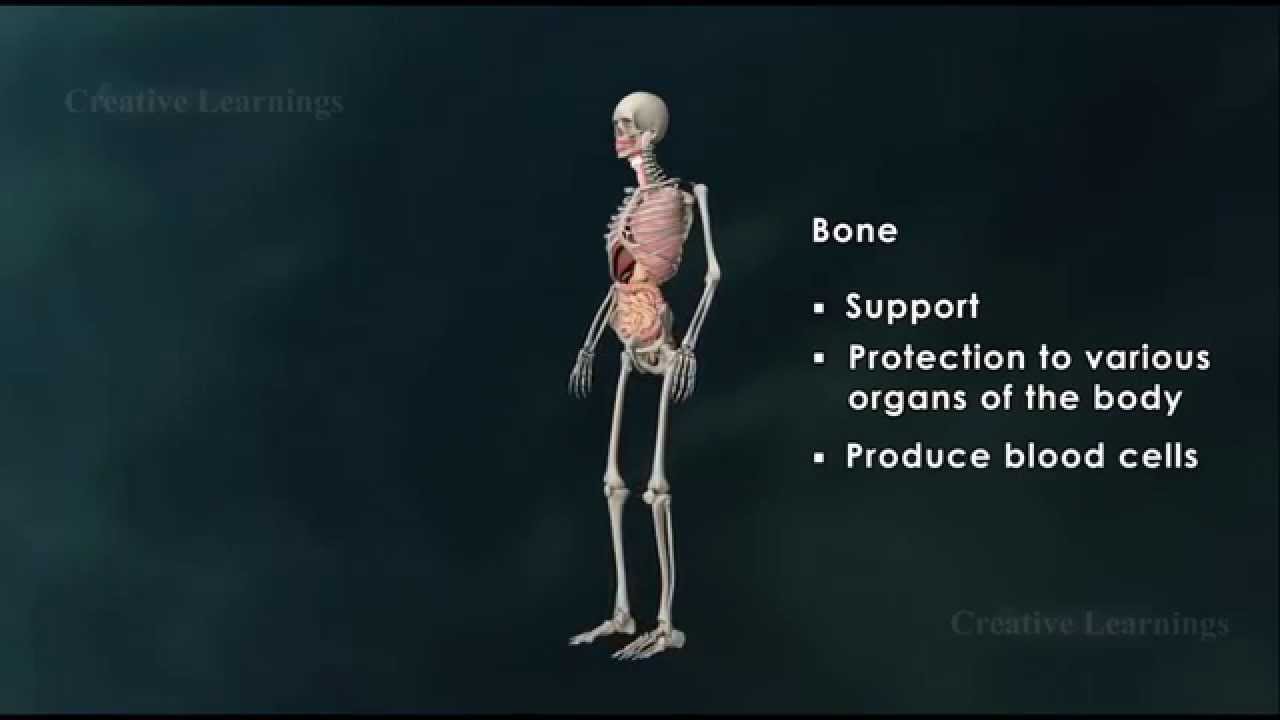
Structure of Bone|Anatomy of Bone|3D Animation|Biology
- Post author:
- Post published:May 10, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like
How To Get your Hormones Into “Weight-Loss” Mode And Melt Away Fat | ALL ABOUT YOUR HEALTH
How Does Exercise Impact Weight Loss?

Pre Workout Meal Example For Breakfast

Jaundice | When to Worry | Parents

Prone Back Extension

Hammer Curl-3

Special Population Exercise Video – 2
Circuit Training

How to Aqua Jog

Lemme H.I.I.T. That – Sprints

When You Burn Fat, Where Does it Go?

The Rock’s CHEST WORKOUT ROUTINE

Wrestling Video – 1

Community Psychiatry Video – 3
How Monthly Rhythms Affect Cortisol & Female Hormones?

Best Weight Loss Pills | Natural vs Pharmaceutical

Anabolic Steroids – History, Definition, Use & Abuse Video – 7

Super crazy wild 1-Leg Squats on Aeromat Pad by Ryan Muetzel

What is Trans Fat? Is Trans Fat Bad for You?
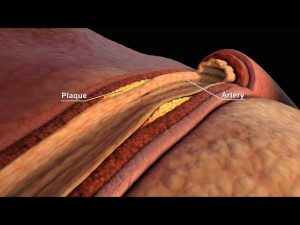
LDL and HDL Cholesterol | Good and Bad Cholesterol | Nucleus Health

Lateral Raises-8

What is Nutrition?। Definition and importance of Nutrition by Anshika Mam। Bsc Nursing, GNM Students
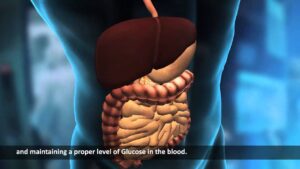
Human Body Video – 6

Health Videos: 12 best Foods to increase metabolism

Overweight & Obesity Video – 13

Ophthalmology Video – 2

fast metabolism diet-fat burning diet-fat burning foods-fat loss diet-metabolism boosting foods
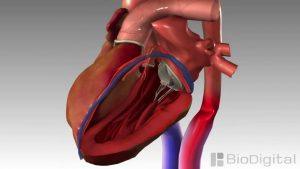
3D Medical Animation – Congestive Heart Failure
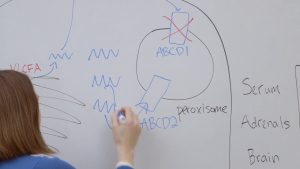
Thyroid hormone based strategy for correcting abnormality in X-ALD

BMI Protocol Video

Psychosomatic Medicine Video – 2

Intermittent Fasting & Fasting Video – 16
Blood glucose control and diabetes

CBC Machine Maintenance

Introduction To Anatomy Physiology: Homeostasis & Health (01:05)

BCAA Benefits Burn Fat, Lose Weight, Lower Sugar!

Does CREATINE Damage the KIDNEY | Myth or Truth? Deep Explanation by Guru Mann

Work Out Meal Plan Prep (GOOD, FAST, CHEAP!)

5 Drinks to Help You Lose Weight

Do You NEED Vitamin Supplements | Earth Lab

The Side Plank – Core Exercise

