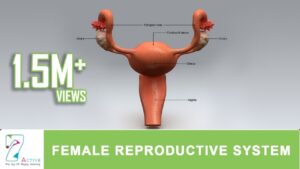
Follow us at: https://plus.google.com/+tutorvista/ Check us out at http://www.tutorvista.com/content/biology/biology-iv/reproduction-in-animals/hormonal-control-menstrual-cycle.php Menstrual Cycle The menstrual cycle is a cycle of physiological changes that can occur in fertile females. Overt menstruation (where there is blood flow from the uterus through the vagina) occurs primarily in humans and close evolutionary relatives such as chimpanzees. Females of other species of placental mammal undergo estrous cycles, in which the endometrium is completely reabsorbed by the animal (covert menstruation) at the end of its reproductive cycle. This article focuses on the human menstrual cycle. The menstrual cycle, under the control of the endocrine system, is necessary for reproduction. It is commonly divided into three phases: the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase; although some sources use a different set of phases: menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase. The length of each phase varies from woman to woman and cycle to cycle, though the average menstrual cycle is 28 days. Menstrual cycles are counted from the first day of menstrual bleeding. Hormonal contraception interferes with the normal hormonal changes with the aim of preventing reproduction. Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, menses slow then stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles atrophy and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 2436 hours after the Luteinizing Hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovum, or egg in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the egg only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the endometrium (uterine lining) changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. These hormone drops cause the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. In the menstrual cycle, changes occur in the female reproductive system as well as other systems (which lead to breast tenderness or mood changes, for example). A woman’s first menstruation is termed menarche, and occurs typically around age 12. The end of a woman’s reproductive phase is called the menopause, which commonly occurs somewhere between the ages of 45 and 55. Please like our facebook page http://www.facebook.com/tutorvista
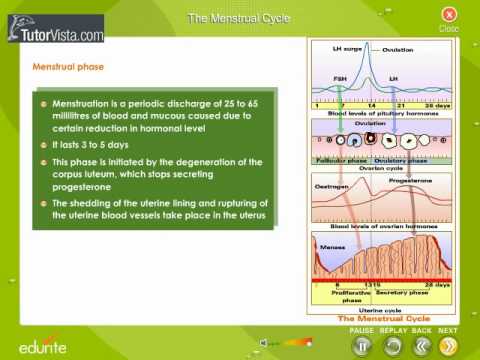
The Menstrual Cycle
- Post author:
- Post published:May 6, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

THE BAR CROSSFIT BACK EXTENSION ON THE FLOOR
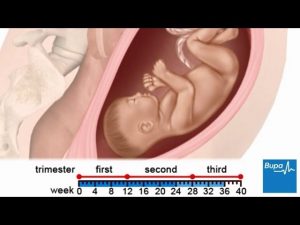
How a baby develops during pregnancy

What is Metabolism, Types Of Metabolism and Metabolic Rate In Hindi

What am I eating to BUILD MUSCLES? Full day of eating
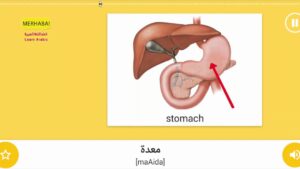
Part 7 – Internal organs – Vocabulary of People – important words – Learn Arabic – تعلم العربية

How to Do a Squat | Gym Workout

Geriatric Physiotherapy Video – 13

What natural ways to lower high cholesterol & triglycerides levels? – Ms. Ranjani Raman

Sports Injuries Video – 1
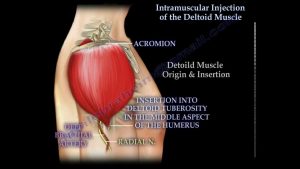
Intramuscular injection of the deltoid muscle – Everything You Need To Know – Dr. Nabil Ebraheim

What is ANTIOXIDANT? What does ANTIOXIDANT mean? ANTIOXIDANT meaning, definition & explanation

Dead Lift-4
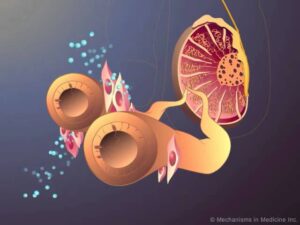
Testosterone Production

Complete 20 Min ABS Workout – Gym Body Motivation
Pediatric Surgery Video – 3

HEALTH BENEFITS OF FISH OIL

Newborn Jaundice

How To Workout Hammer Strength Back Routine with Chris R. Rea from ReaShape

Muscle Actions- Functional Groups

Prevent Osteoporosis by Dr. John Westerdahl

Bodybuilding Nutrition, Diet Recipes & Workout – 48

FAT LOSS 101 FOR MEN (Chest Fat, Belly, Love Handles!)

Opthalmogical/Eye Surgeries Video – 2

Bench Dips for Big Triceps, How to Get Big Triceps

How to Prevent Prediabetes from Turning into Diabetes

Adductor Machine-3

Defined Fitness Farmington NM – Complete Gym Tour

How to Do Barbell Lying Triceps Extensions for Best Results!

Accuracy of Coronary CT Angiogram
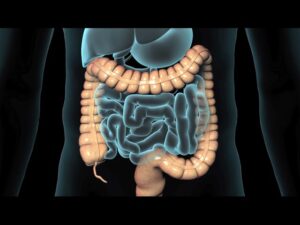
Gastrointestinal Surgery Video – 2

PHARMACODYNAMICS

7 Habits That Make You Gain Weight

Homemade reverse hyper test
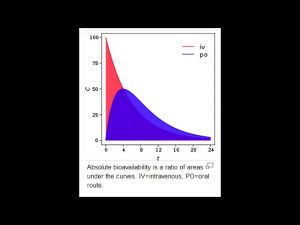
Bioavailability (F) – Pharmacokinetics

Sugar Free, Low Sugar Video – 29

Aroma Oils Video – 3

The Right Way To Squat | Squat Exercise | Fitness Video | How to Squat? I OZiva

Basketball Video – 3

How To: Dumbbell Upright-Row

How to Calculate the Daily Calorie Deficit for Maximum Fat Loss : Nutrition Advice
The Female Reproductive System of Human

