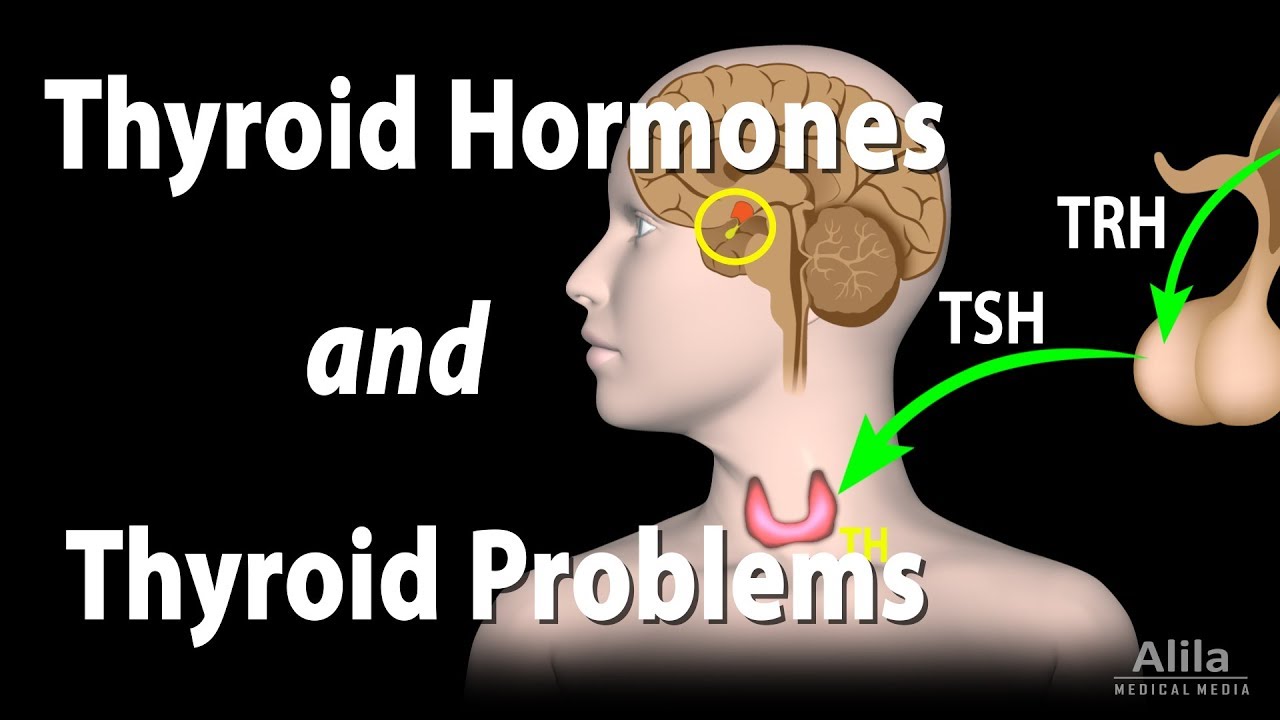
(USMLE topics, endocrinology) Regulation of thyroid hormone, hyper- and hypothyroidism: causes, symptoms and treatment, goiter. This video is available for instant download licensing here https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/endocrinology-basics/-/medias/db2b8c0b-5e34-4dfa-9ea9-3ce376ef52c4-thyroid-gland-hormones-and-problems-narrated-animation Voice by: Sue Stern ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped ENDOCRINE gland located in the neck. It is wrapped around the trachea, just below the thyroid cartilage –the Adam’s apple. The two major hormones of the thyroid are triiodothyronine, T3 and thyroxine, T4. The numbers 3 and 4 indicate the number of iodine atoms present in a molecule of each hormone. T3 and T4 are collectively referred to as THYROID hormones. Thyroid hormone secretion is under control of thyroid-stimulating hormone, TSH, from the anterior pituitary. TSH, in turn, is induced by thyrotropin-releasing hormone, TRH, produced by the hypothalamus. The amount of circulating thyroid hormones is regulated by a negative feedback loop: when their levels are too high, they SUPPRESS the production of TSH and TRH, consequently INHIBITING their own production. Thyroid hormones act to INCREASE the body’s metabolic rate. They stimulate appetite, digestion, breakdown of nutrients and absorption. They also increase oxygen consumption, raise the breathing rate, heart rate and contraction strength. As a result, the body’s HEAT production is INCREASED. Thyroid hormone secretion usually rises in winter months to keep the body warm. Thyroid hormones are also important for bone growth and fetal brain development. There are 2 major groups of thyroid problems: HYPOthyroidism: when the thyroid does NOT produce ENOUGH hormones, resulting in a LOW metabolic rate, combined with SLOW respiratory and cardiovascular activities. Common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain despite poor appetite, cold intolerance, slow heart rate, heavy menstrual bleeding and constipation. Iodine deficiency and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis are the most common causes. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed by the body’s own immune system. Hypothyroidism, especially when caused by iodine deficiency, may lead to swelling of the thyroid gland, known as GOITER. In an attempt to fix the low levels of thyroid hormones, the pituitary produces MORE TSH to further stimulate the thyroid gland. The thyroid, while UNable to make hormones WITHOUT iodine, responds to TSH by GROWING in size. Hypothyroidism is managed with thyroxine hormone replacement. HYPERthyroidism: when the thyroid gland produces TOO MUCH hormones, resulting in a TOO ACTIVE metabolism, together with respiratory and cardiovascular rates that are HIGHER than necessary. Common symptoms include irritability, insomnia, weight loss despite good appetite, heat intolerance, heart racing and diarrhea. Hyperthyroidism is most commonly caused by Graves’ disease, another autoimmune disorder characterized by presence of an antibody, called thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin, TSI. TSI, similar to TSH, stimulates the thyroid gland to produce hormones. Unlike TSH, however, TSI is NOT regulated by negative feedback mechanisms, leading to UNcontrolled production of thyroid hormones. TSI also stimulates the thyroid gland to grow, which MAY lead to formation of a goiter. Hyperthyroidism may be managed with drugs that suppress thyroid function, radioactive iodine that selectively destroys the thyroid gland, or surgery that removes part of the gland.
Thyroid Gland, Hormones and Thyroid Problems, Animation
- Post author:
- Post published:May 22, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like
Organ Transplantation Surgeries Video – 4

6 Exercise for Fat/Obese People to Lose Weight
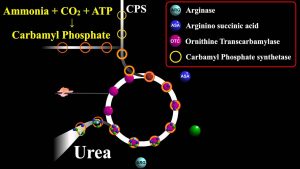
Urea Biosynthesis or Ornithine Cycle
Neurological Physiotherapy Video – 7

Muscleblaze Weight Gainer Review || Gain weight fast
Pip Progressive Muscle Relaxation

Pediatric Physiotherapy Video – 14

Eliminating 90% of Heart Disease Risk

What are the side effects of orlistat?|Effects of Weight Loss Medicine-Dr. Anantharaman Ramakrishnan

Muscle Contraction – Are You Working Out Hard Enough?

How many eggs should I eat a day – For Men and Women – BeerBiceps Diet

7 MIN STRETCHING EXERCISES AFTER WORKOUT ( New) | FULL BODY COOL DOWN FOR RELAXATION & FLEXIBILITY

Fitness motivation – The Aesthetic Era, here to stay

Keto Diet, Keto Foods, Keto Recipes Video – 27

How to Do a Donkey Kick (Exercise)

Beware Of Fake Supplement – How To Identify? | Health and Fitness Tips | Guru Mann

Testosterone & Androgenic Effects Video – 50
Insulin Resistance

How to treat severe acne without using accutane or isotretinoin?

How long can you live on dialysis with kidney failure ?

Sports Injuries Video – 1

Alyaa Gad – Liver Patient Diet
Side plank-4

DYNAMIC STRETCHING / WARM UP ROUTINE FOR SPEED TRAINING / EXERCISE

BICEP EXERCISES FOR STRENGTH & DEFINITION
Is a New Treatment for Diabetes Near?

Community Psychology Video – 1

Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) Explained

One Simple Movement To Get V-shaped Abs

Exercise Anatomy: Abs Workout | Pietro Boselli

Top 5 Fruits That Burn Belly Fat

Mary Did You Know? (Official Music Video) | One Voice Children’s Choir cover

(CC) How to Pronounce propranolol (Inderal) Backbuilding Pharmacology

Pre Blended Oils Video – 1

What are metabolic processes
Top 5 Best Liver Supplements In Amazon India

Easy Home Made Protein Shake Without Protein Powder

Abdominal Crunch and Back Extension Exercise Demonstration

How To Do: Preacher Curl, Good Form vs. Bad Form

Diet Tips: 7 Best Foods To Increase Body Strength

BCAAS & AMINO ACIDS ARE WASTE OF MONEY!!! @hodgetwins

