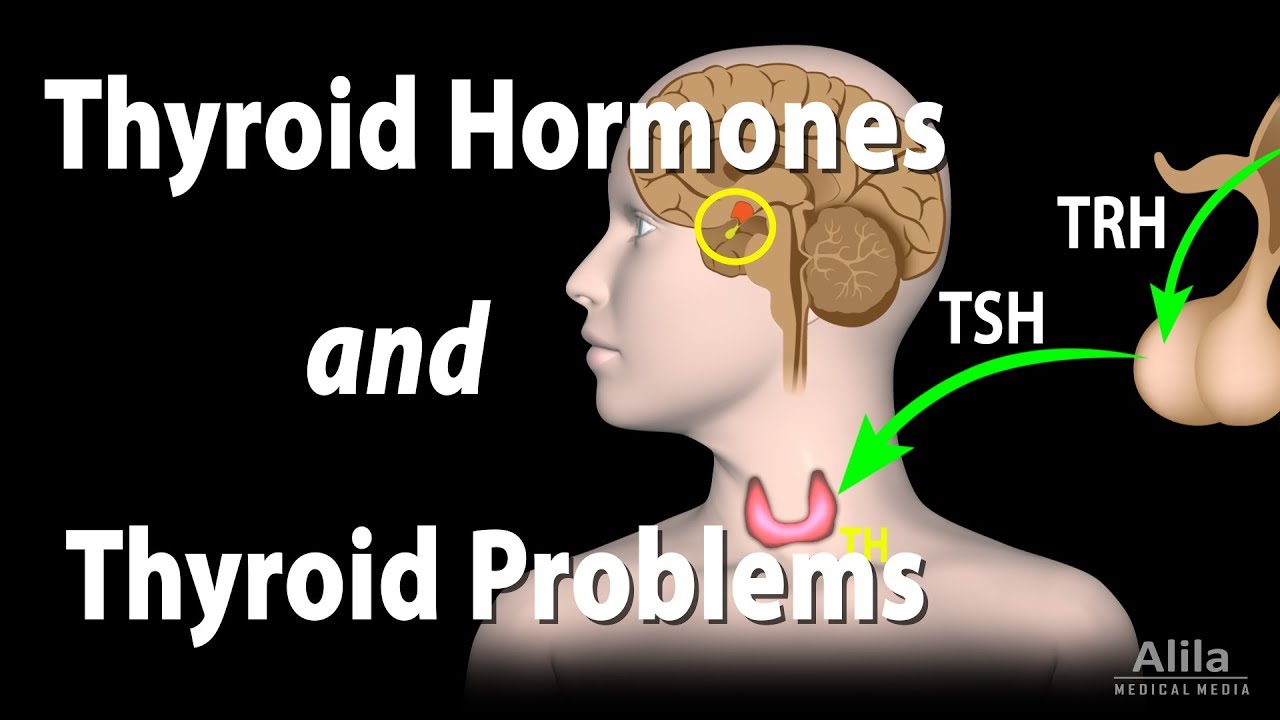
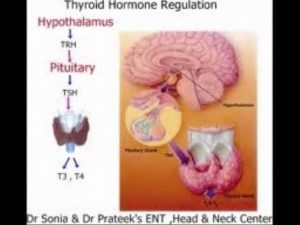
(USMLE topics, endocrinology) Regulation of thyroid hormone, hyper- and hypothyroidism: causes, symptoms and treatment, goiter. This video is available for instant download licensing here https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/endocrinology-basics/-/medias/db2b8c0b-5e34-4dfa-9ea9-3ce376ef52c4-thyroid-gland-hormones-and-problems-narrated-animation Voice by: Sue Stern ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped ENDOCRINE gland located in the neck. It is wrapped around the trachea, just below the thyroid cartilage –the Adam’s apple. The two major hormones of the thyroid are triiodothyronine, T3 and thyroxine, T4. The numbers 3 and 4 indicate the number of iodine atoms present in a molecule of each hormone. T3 and T4 are collectively referred to as THYROID hormones. Thyroid hormone secretion is under control of thyroid-stimulating hormone, TSH, from the anterior pituitary. TSH, in turn, is induced by thyrotropin-releasing hormone, TRH, produced by the hypothalamus. The amount of circulating thyroid hormones is regulated by a negative feedback loop: when their levels are too high, they SUPPRESS the production of TSH and TRH, consequently INHIBITING their own production. Thyroid hormones act to INCREASE the body’s metabolic rate. They stimulate appetite, digestion, breakdown of nutrients and absorption. They also increase oxygen consumption, raise the breathing rate, heart rate and contraction strength. As a result, the body’s HEAT production is INCREASED. Thyroid hormone secretion usually rises in winter months to keep the body warm. Thyroid hormones are also important for bone growth and fetal brain development. There are 2 major groups of thyroid problems: HYPOthyroidism: when the thyroid does NOT produce ENOUGH hormones, resulting in a LOW metabolic rate, combined with SLOW respiratory and cardiovascular activities. Common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain despite poor appetite, cold intolerance, slow heart rate, heavy menstrual bleeding and constipation. Iodine deficiency and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis are the most common causes. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed by the body’s own immune system. Hypothyroidism, especially when caused by iodine deficiency, may lead to swelling of the thyroid gland, known as GOITER. In an attempt to fix the low levels of thyroid hormones, the pituitary produces MORE TSH to further stimulate the thyroid gland. The thyroid, while UNable to make hormones WITHOUT iodine, responds to TSH by GROWING in size. Hypothyroidism is managed with thyroxine hormone replacement. HYPERthyroidism: when the thyroid gland produces TOO MUCH hormones, resulting in a TOO ACTIVE metabolism, together with respiratory and cardiovascular rates that are HIGHER than necessary. Common symptoms include irritability, insomnia, weight loss despite good appetite, heat intolerance, heart racing and diarrhea. Hyperthyroidism is most commonly caused by Graves’ disease, another autoimmune disorder characterized by presence of an antibody, called thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin, TSI. TSI, similar to TSH, stimulates the thyroid gland to produce hormones. Unlike TSH, however, TSI is NOT regulated by negative feedback mechanisms, leading to UNcontrolled production of thyroid hormones. TSI also stimulates the thyroid gland to grow, which MAY lead to formation of a goiter. Hyperthyroidism may be managed with drugs that suppress thyroid function, radioactive iodine that selectively destroys the thyroid gland, or surgery that removes part of the gland.
Thyroid Gland, Hormones and Thyroid Problems, Animation
- Post author:
- Post published:June 2, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Developmental Psychology Video – 2

Echo Tech (Echocardiographic Technician) interview questions
Anatomical Position And Directional Terms – Anatomical Terms – Directional Terms Anatomy

Echocardiogram: An ultrasound for your heart

Cholesterol Medicine Information – Different Ways to Lower Your Cholesterol Levels

What is TB? | Infectious diseases | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy

Cable Front Raise Exercise
Testosterone & Androgenic Effects Video – 24

Decline Bench Press-1
Difference Between Adverse Effect and Side Effect

What is Fish Oil? Omega-3 Benefits & Side Effects Review by Guru Mann

Pharmacokinetics: Vd, Clearance, Half-life: Calculation Drug Distribution, Elimination, Rate
Starting Insulin Early For Type 2 Diabetes
ENT Surgery Video – 5

Acne explained

Deficiency & Malnutrition Video – 2

Intermittent Fasting & Fasting Video – 23

Radiology Video – 4

Dip Tutorial – Chest or Tricep

Overweight & Obesity Video – 22

How To Do TRICEPS BENCH DIPS EXERCISE
FLUORIDE : Thyroid Hormones 8 / 20

Oxygen, Antioxidants, and Free Radicals

Hip Flexor Stretch – Done Correctly

Chemistry CBC Blood Test | Life Extension

Fruits NOT for Pregnant Women
Anatomy & Physiology Online – Cardiac conduction system and its relationship with ECG

What’s Your Body Type – Endomorph Workout
Yoga Counciling Video – 4
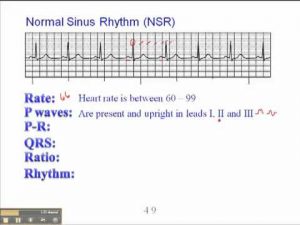
ECG: Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)

Dermatology Video – 2

CCQ 25 Tablets Review | Clomifene Citrate & Ubidecarenone Tablets Uses, Side Effects, Precautions

How Statins Work to Reduce Cholesterol

Bodybuilding Nutrition, Diet Recipes & Workout – 1

Sugar Free, Low Sugar Video – 12

Human Body Video – 5

Back Extension Machine

5 Components of Fitness

Spot Jogging

WHAT IS FITNESS | EARN YOUR SWOOB

Brandon Williams Uses 150lb Dumbbells for Chest Press

