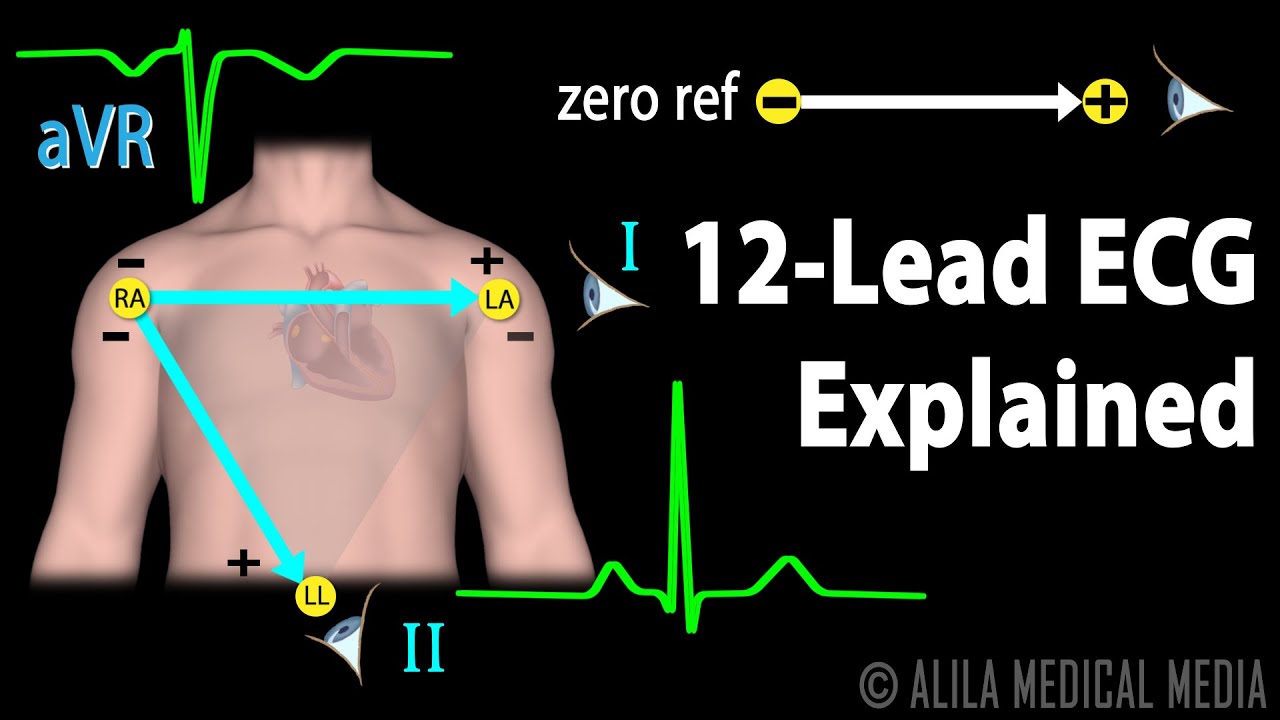
(USMLE topics, cardiology) Understanding the standard 12-lead EKG – Basics of electrocardiography explained. This video is available for instant download licensing here: https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/ekgecg/-/medias/4d57ce72-0d39-4525-b523-329941b9edcf-12-lead-ecg-explained-narrated-animation ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Voice by: Sue Stern. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Electrical activities of the heart can be picked up on the skin via electrodes. An ECG machine records these activities and displays them graphically. The graphs show the heart’s OVERALL electrical potential, or voltage, as it changes over time during a cardiac cycle. The 12 leads of the ECG represent 12 electrical views of the heart from 12 different angles. The conventional 12-lead procedure involves attaching 10 electrodes to the body: one to each limb and six across the chest. There are 6 limb leads and 6 chest leads. The 6 limb leads look at the heart in a vertical plane and are obtained from three electrodes attached to the right arm, left arm, and left leg. The electrode on the right leg is an earth electrode. The measurement of a voltage requires 2 poles: negative and positive. The ECG machine uses the negative pole as zero reference. Thus, the position of the positive pole is the “point of view”, and the line connecting the 2 poles is the “line of sight”. Leads I, II, and III are BI-polar – they measure electrical potential between 2 of the 3 limb electrodes: Lead I represents the voltage between the right arm – negative pole – and the left arm – positive pole, and thus looks at the heart from the left. Lead II sees signal movements between the right arm – negative – and the left leg –positive – forming the INFERIOR LEFT view. Similarly, lead III measures electrical potential between the left arm – negative – and the left leg –positive, looking at the heart from an INFERIOR RIGHT angle. Leads aVR, aVL, and aVF, or “augmented limb leads”, are UNIpolar. They use ONE limb electrode as the positive pole, and take the average of inputs from the OTHER two as the zero reference. Hence, aVR looks at the UPPER RIGHT side of the heart; aVL looks at the UPPER LEFT side of the heart; and aVF looks at the INFERIOR wall of the heart. The chest leads, or precordial leads, view the heart in a HORIZONTAL plane. These are unipolar leads. The corresponding chest electrodes serve as the positive poles. The reference negative value is the same for all chest leads and is calculated as the average of inputs from the three limb electrodes. DE-polarization TOWARD a lead produces a POSITIVE deflection; DE-polarization AWAY from a lead gives a NEGATIVE deflection. The REVERSE is true for RE-polarization. Thus, leads that look at the heart from different angles may have waves pointing in different directions.
12 Lead ECG Explained, Animation
- Post author:
- Post published:June 5, 2021
- Post category:Uncategorized
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Athletics Video – 3

Hematology Video – 1

Insulin and Glucagon | Physiology | Biology | FuseSchool

Epidemiology Video – 1
Fitness Components

Back Exercise – Lat Pulldown Machine for Upper Lats

Is Whey Protein SAFE at Age under 18 | Guru Mann | Health & Fitness

Spa Associations Video – 1
Proper Breathing Exercise to Strengthen Lungs to Keep Healthy – Dr Mandell

Is it safe to eat Jackfruit during Pregnancy, The Side Effects You Should Be Aware Of!

What To Eat Before And After Your Workout To Maximize Fat Loss – With Thomas DeLauer

Build Massive Upper Back and Lats with Sling Shot Rows

Keto Diet, Keto Foods, Keto Recipes Video – 9

Single hand Triceps extension
BCAA (Branched Chain Amino Acids)

This Full Body Exercise Burns Fat Like Crazy – One Exercise Fat Burning Workout – Sixpack Factory

StairMaster HIIT Programming Solutions

Develop Bigger & More Vascular Forearms | Best Exercises

Human Body, Body Building Muscle Building Anatomy Physiology Video – 18

Physiology Of Sports & Sports Medicine Video – 3

Are you Eating EGG WHITES For Weight Gain? (YOU NEED TO WATCH THIS RIGHT NOW!)

6 Pack Diet Plan Disaster (CALORIE CUTTING!)

Pranayama Video – 6

“The 59”: Skull Crushers & Close Grip Bench

Biceps: One Arm Preacher Curl Low Pulley Cable

Use Of Finasteride In Androgenic Alopecia (hairfall)

Urinalysis – OSCE Guide

Making A Yoga Routine Video – 3
How your baby become male or female ?!!
ProGuide™ Chronic Dialysis Catheters Animation

Hockey Video – 4
Body Composition

Cognitive Psychology Video – 1

Leg Curl Machine by Fitness Model Julia

TDEE & BMR

Dumbbell One Arm Overhead Tricep Extension Technique

DYNAMIC STRETCHING / WARM UP ROUTINE FOR SPEED TRAINING / EXERCISE

Sex Psychiatry Video – 2

What is WATER VAPOR? What does WATER VAPOR mean? WATER VAPOR meaning & explanation

How To: Overhead Front Raise (With Plate)

How to Use Egg Protein to Build Muscle | Bodybuilding Diet

