This video is available for instant download licensing here: https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/all-animations/respiratory-system-videos/-/medias/63e4494c-bc90-4b5f-a058-dccd2756252e-progression-of-tuberculosis-narrated-animation Voice by: Qudsi Baker. ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Tuberculosis, or TB, is one of the oldest and most common infectious diseases. About one third of the world population is believed to be infected with TB. Fortunately, only about 5% of these infections progress to active disease. The other 95% of infected people are said to have a dormant or latent infection; they do not develop any symptoms, and do not transmit the disease. Tuberculosis is caused by a rod-shaped bacterium, or a bacillus, called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. An infection is initiated following inhalation of mycobacteria present in aerosol droplets discharged into the atmosphere by a person with an active infection. The transmission process is very efficient as these droplets can persist in the atmosphere for several hours and the infectious dose is very low – less than 10 bacilli are needed to start the infection. Once in the lung, the bacteria meet with the body’s first-line defense – the alveolar macrophages. The bacteria are ingested by the macrophages but manage to survive inside. Internalization of the bacilli triggers an inflammatory response that brings other defensive cells to the area. Together, these cells form a mass of tissue, called a granuloma, characteristic of the disease. In its early stage, the granuloma has a core of infected macrophages enclosed by other cells of the immune system. As cellular immunity develops, macrophages loaded with bacteria are killed, resulting in the formation of the caseous center of the granuloma. The bacteria become dormant but may remain alive for decades. This enclosed infection is referred to as latent tuberculosis and may persist throughout a person’s life without causing any symptoms. The strength of the body’s immune response determines whether an infection is arrested here or progresses to the next stage. In healthy people, the infection may be stopped permanently at this point. The granulomas subsequently heal, leaving small calcified lesions. On the other hand, if the immune system is compromised by immunosuppressive drugs, HIV infections, malnutrition, aging, or other factors, the bacteria can be re-activated, replicate, escape from the granuloma and spread to other parts of the lungs causing active pulmonary tuberculosis. This reactivation may occur months or even years after the initial infection. In some cases, the bacteria may also spread to other organs of the body via the lymphatic system or the bloodstream. This widespread form of TB disease, called disseminated TB or miliary TB, occurs most commonly in the very young, the very old and those with HIV infections. Tuberculosis is generally treatable with antibiotics. Several antibiotics are usually prescribed for many months due to the slow growth rate of the bacteria. It’s very important that the patients complete the course of the treatment to prevent development of drug-resistant bacteria and re-occurrence of the disease.
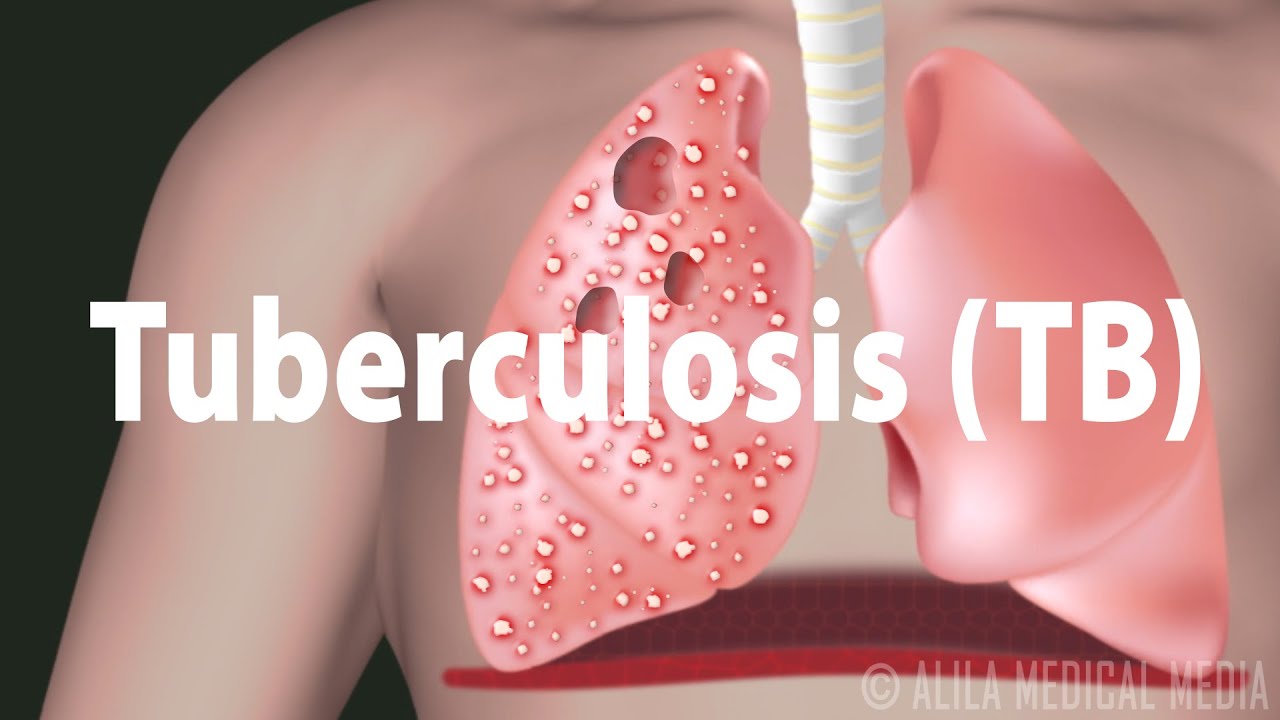
Tuberculosis (TB): Progression of the Disease, Latent and Active Infections.
- Post author:admin
- Post published:October 7, 2021
- Post category:Uncategorized
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Yoga Industry And Advantages Video – 4
What is Normal Body Temperature? What is a Fever?

Legal Psychology Video – 5
The Role of Estrogen in Pregnancy
Human Physiology – Functional Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System

Thyroid Disorders Nutrition Video – 2

Muscle Building Workout & Squats Video – 24

Sperm and Eggs Cells | Cells | Biology | FuseSchool
The Role of Insulin in the Human Body
MINOXIDIL WORK ON TEMPLES IN JUST 2 MONTHS??!

Should you use Glutamine

How to Do Lateral Raise

How to Do a Barbell Lat Pullover | Back Workout
Latissimus Dorsi Bent Over Row-7

Sprinting Running Video – 1

Obstetrics Video – 2

Dumbbell Supinated Press – HASfit Shoulder Exercise Demonstration – Anterior Deltoid Exercises

Best Chest Exercise – Incline Bench Press tips & techniques, Hindi, India – Fitness Rockers

MAX CONTRACTION – 4 – MAXIMUM MUSCLE GROWTH!!!!
Male Hormones
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?

Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR or sed rate) Test

GLUCOSE MONITORING with the HELO

Maximum Intensity Full Body Workout
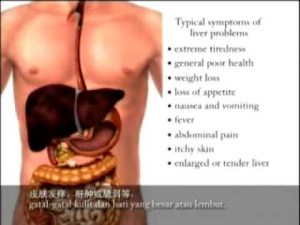
How Milk Thistle and Dandelion helps liver cells?

Branches Of Medicine Video – 3

What is BMR and why you should know your BMR | Rajelakshmi Mohan
Erectile Dysfunction Nerve Inflammation
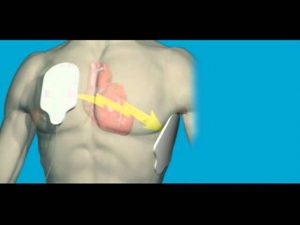
What is Cardiac Arrest

Healthy Pregnancy Diet | Parents

Your Brain On Thyroid Hormone

Close Grip Triceps Extension-3
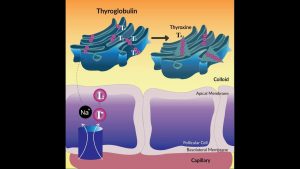
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis
Newest Technology | Heart Stent video (Angioplasty) New Medical Line Video | Heart Attack reasons
Human body composition

Advanced Hammer Curl Tip – For Bigger Arms
Uses of Cheapest Vitamin B Complex with B12 NEUROBION FORTE

Dip Tutorial – Chest or Tricep

Is clomiphene a safe option to plan pregnancy? – Dr. Karamjit Kaur

What is Osteoporosis?

How To: Hanging Leg-Lift

