(USMLE topics) Alcoholic fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis: Signs and symptoms, risk factors, pathophysiology, complications, diagnosis and treatment. This video is available for instant download licensing here: https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/all-animations/digestive-system-videos/-/medias/012159d6-87f0-425d-bd0d-37b284ff287a-alcoholic-liver-disease-narrated-animation ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Voice by : Marty Henne Support us on Patreon and get early access to videos and free image downloads: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Alcoholic liver disease is liver damage caused by alcohol abuse. The risk of developing liver disease correlates with the amount and duration of alcohol use. Daily drinking poses a higher risk than binge drinking. Other risk factors include gender, genetics, and obesity. Alcoholic liver disease includes 3 disorders that develop in sequence: alcoholic fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Alcoholic fatty liver is accumulation of liver fat as a result of alcohol use. The liver is usually enlarged but not tender. There are often no symptoms and the condition can be reversed if the patient stops drinking. Alcoholic hepatitis is liver inflammation. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include fever, jaundice, fatigue, and a tender, painful and enlarged liver. Cirrhosis is when a large amount of hepatic tissue is permanently replaced with non-functional scar tissue, known as fibrosis. Symptoms range from those of alcoholic hepatitis to those of end-stage liver disease. The liver eventually shrinks. Cirrhosis cannot be reversed. The liver is the major site of alcohol metabolism. Two main pathways are involved: alcohol dehydrogenase, ADH; and cytochrome P-450 2E1, or CYP-2E1. ADH converts alcohol to acetaldehyde. A second enzyme, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, ALDH, then metabolizes acetaldehyde to acetate. People who have low levels of ALDH are more susceptible to toxic effects of acetaldehyde. Both of these reactions convert NAD+ to NADH. An increased NADH/NAD+ ratio promotes fatty liver by inhibiting fatty acid oxidation and stimulating fatty acid synthesis. In addition, acetaldehyde also promotes production of enzymes involved in fatty acid synthesis, and inhibits expression of enzymes implicated in fat oxidation. Alcohol use has also been shown to reduce export of fat from the liver. All these events lead to fat accumulation in hepatic cells. Chronic alcohol use upregulates the CYP-2E1 pathway. This pathway generates harmful reactive oxygen species, which can damage proteins and DNA. The effect is exaggerated in patients who are deficient in antioxidants due to malnutrition. Chronic alcohol exposure also activates hepatic macrophages, triggering inflammation. In addition, acetaldehyde can bind to cellular proteins, forming so-called adducts that are seen as foreign antigens by the immune system, provoking the body’s inflammatory attacks. Chronic inflammation and subsequent attempts at tissue repair lead to formation of scar tissue. As a result, the liver internal structure is disrupted, impairing its functions. Scarring of liver tissue also obstructs blood flow, causing high blood pressure in the portal vein that brings blood from the intestine to the liver. As liver functions decline, toxins that are normally removed by the liver can now reach the general circulation and pass into the brain, producing symptoms such as confusion, drowsiness, tremor, or even coma, in a condition known as hepatic encephalopathy. Portal hypertension may cause variceal bleeding, enlarged spleen, and abdominal distension. Diagnosis is usually based on signs of liver dysfunction, other symptoms related to alcohol use, history of heavy drinking, liver function tests and complete blood count. Abstinence is the best treatment. Supportive care includes good nutrition and vitamin supplements. Corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation but their effectiveness is till debatable. Liver transplantation may be considered for abstinent patients with severe liver damage.
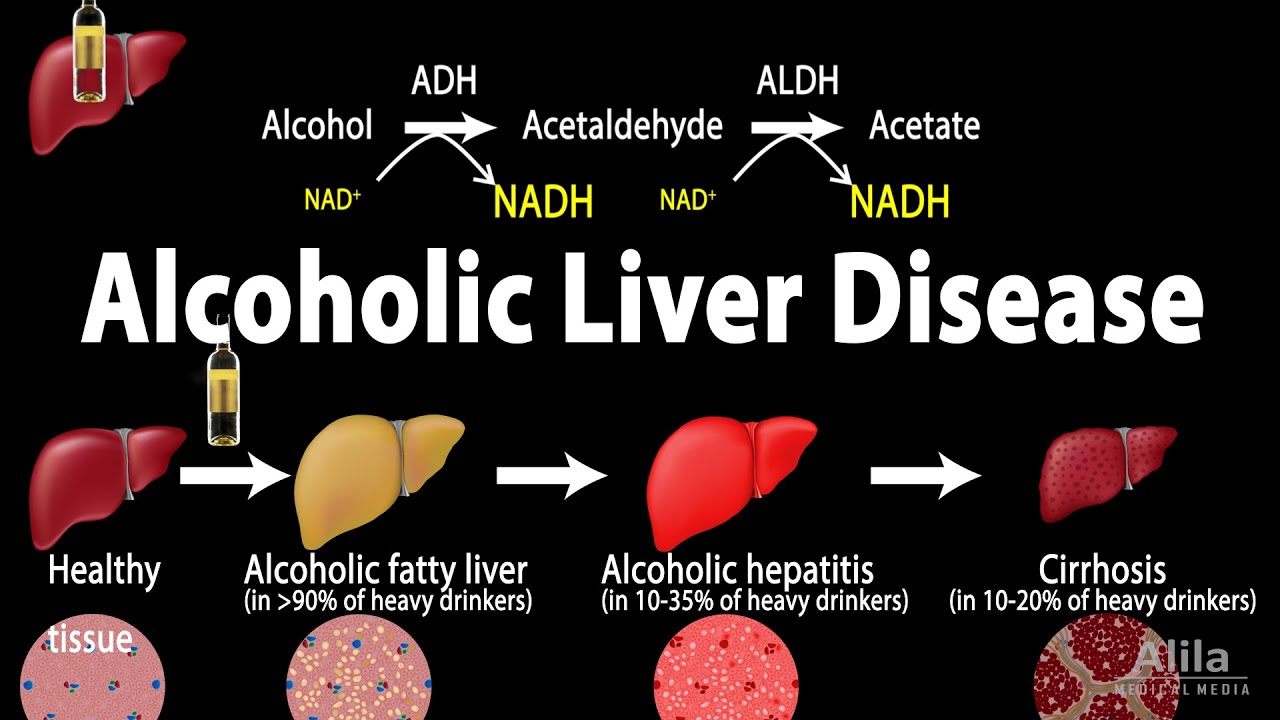
Alcoholic Liver Disease, Animation
- Post author:admin
- Post published:October 11, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Thyroid gland and hormone synthesis
Minerals for Brain Health: Platinum, Indium and Gold

Leg Presses Without Machines : Simple & Effective Exercises

How To Do: Preacher Curl, Good Form vs. Bad Form

Bowen Therapy Video – 2
Fever, tonsils swelling Homeopathic medicines! R1!! uses and symptoms! Inflammation drops

Weightlifting Video – 1

Human Body, Body Building Muscle Building Anatomy Physiology Video – 7

Anemia symptoms and treatments – Signs of being anemic
Complete Blood Count

Flexibility Stretching Video – 1

Aerobics Meaning
Pregnancy swelling (edema)

Zumba Dance Workout for weight loss

Triceps Dips-6
Skeletal System Rap

What is Mineral oil?

Tyrone Bell – How to fix Lagging Muscle Groups | TY-TV

Biological Psychiatry Video – 2

How to Choose a Multivitamin

Testosterone & Androgenic Effects Video – 29

Can You Use Minoxidil on Your Beard? | Eric Bandholz

Stress, hormones and weight gain connection

Hyper Extensions
Hair Growth Animation

What is STEROID SULFATASE? What does STEROID SULFATASE mean? STEROID SULFATASE meaning & explanation
WHICH BODY TYPE ARE YOU? How to Train & Eat for YOUR body type?
Properties of Water

ओमेगा 3 क्या होता है और कैसे इस्तेमाल करे | Omega 3 Fish oil Benefits | In 2019 | In Hindi

One Arm Row Dumbbell-7
Malnutrition & Nutritional Deficiency Diseases Video – 2
ADI STUDIO (Medical Animation) – Alopecia

What Is BMI (Body Mass Index)?

What Are Kidney Stones – Kidney Stone Home Remedies

Flat Bench Fly-3

Muscular Strength Asanas Video – 4

Push UP: Chest workout at home – This excersise can transform your body in 6 weeks
Obstetrics Video – 4

Alternating hammer curls (standing with dumbbells)

Lat Pull Down-7

Best Upper Back Exercise – Dumbbell Row

