EmpoweRN.com For more ARBS NCLEX questions, go here: http://empowern.com/2015/06/arbs/ ARBs are a relatively new type of antihypertensive drugs, which were developed to cover the shortcomings of ACE inhibitors. For instance, for patients who are sensitive to the side effects of ACE inhibitors, the treatment can be done using ARB drugs instead of ACE inhibitors. Mechanism of action: Human body contains several mechanisms which help protect it against severe conditions. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is one of those mechanisms. When blood pressure decreases due to blood loss or other reasons, RAAS is activated to reverse the reaction and prevent cardiovascular collapse. However, prolonged or inappropriate activity of RAAS can lead to hypertension, which can damage vital organs of the body such as blood vessels, heart, kidneys and the brain. In one step of the RAAS mechanism, angiotensin I is converted into angiotensin II which then binds to a receptor. There are two types of Angiotensin II receptors: AT1 and AT2. Angiotensin II AT1 receptor acts as an intermediary for all the effects of angiotensin II on the cardiovascular system, such as vasoconstriction, sympathetic activation, aldosterone discharge and other impacts that may be a health risk. The function of angiotensin II AT2 receptor is still unknown. ARB drugs work by preventing the potential substance angiotensin II from binding to the AT1 receptor. This blocks the activity of angiotensin II and causes blood vessels to relax and decreases reabsorption of water and sodium in the kidney. Hence, causing a drop in blood pressure. Some ARB drugs that are available in the United States include: V – Valsartan (Diovan) O – Olmesarta (Benicar) C – Candesarta (Atacand) I – Irbesartan (Avapro) T – Telmisartan (Micardis) E – Eprosarta (Teveten) L – Losartan (Cozaar) ARBs that are combined with hydrochlorothiazide or other anti-hypertensive are also available, these include: A – Amlodipine and valsartan (exforge) I – Irbesartan-hydrochlorothiazide (avalide) L – Losartan potassium-hydrochlorothiazide (hyzaar) V – Valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide (diovan HCT) Medical Use: ARBs can be used alone as well as along with other anti-hypertensive drugs. They are also used to treat congestive heart failure, to prevent diabetes and kidney failure associated with high blood pressure, and to reduce risks of stroke in patients with hypertension or an enlarged heart. Side effects and contraindication: ARBs may cause following side effects: Low blood pressure High blood potassium level Drowsiness Headache Dizziness Nausea Vomiting Cough Nasal congestion Diarrhea Rash Bone or Muscle pain Associated with sexual dysfunction
ARBS Angiotensin Receptor Blockers
- Post author:
- Post published:May 28, 2021
- Post category:Uncategorized
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

CLOTHES for the “BODY TYPES”

Biologia: Insulina e glucagon – ENEM
How Tuberculosis Begins

How to Calculate the Daily Calorie Deficit for Maximum Fat Loss : Nutrition Advice

Chest Workout: Push-Ups

Protein Requirements to Build Muscle & Lean Mass

Human Body, Body Building Muscle Building Anatomy Physiology Video – 16

Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR or sed rate) Test
How To: Seated Low Row (LF Cable)
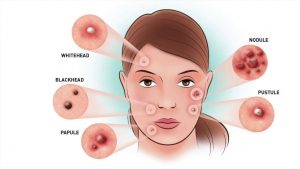
6 Different Types Of Pimples That You Should Know

BMR & BMI

What is Infertility

Close Grip Tricep Push Downs
Patients Can Test Blood Sugar Via Smartphones

Red Blood Cell Count Abnormal

Advantages Of Yoga Video – 1

FAT LOSS VEGETARIAN Diet Plan for Women (Hindi) | How to Lose Weight Fast 10kgs | Indian Meal Plan
MECHANISM OF HORMONE ACTION

What medications are safe to take during pregnancy? – Dr. Shefali Tyagi
Holistic Spa Video – 1
Lomy Lomy Massage Video – 2

Hormones and Men’s Health

Can A Brain Injury Make You A Genius?

Crazy 400m sprint
Low Pulley Bicep Curl

B Complex Supplements Video – 1

V Position Exercise-1
Metformin Part 2: How Does it Work?

How To: Incline Chest Press (Hammer Strength)

Clinical Psychiatry Video – 1

Weight Training Video – 3

Developmental Psychology Video – 4

What Are Carbohydrates ? What Is Carbohydrates?
Bone scan

30 Foods for Arthritis: Arthritis foods

Sports Physiotherapy Video – 1

Bodybuilding Nutrition, Diet Recipes & Workout – 21

Atenolol For High Blood Pressure, Chest Pain and Survival After Heart Attacks – Overview

Tricep Dips

Herbal Nutrition Video – 2

