This video is available for instant download licensing here https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/ekgecg/-/medias/4f63a6a7-94c6-463e-8c85-7117e48f5d23-atrial-fibrillation-narrated-animation ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Atrial fibrillation is the most common type of cardiac arrhythmia. In a healthy heart, the sinoatrial node or SA node initiates all electrical impulses in the atria. In atrial fibrillation, electrical impulses are initiated randomly from many other sites called ectopic sites in and around the atria, commonly near the roots of pulmonary veins. These un-synchronized, chaotic electrical signals cause the atria to quiver or fibrillate rather than contract. Although the atrial rate during atrial fibrillation can be extremely high, most of the electrical impulses do not pass through the atrioventricular – the AV – node to the ventricles. This is due to refractory properties of the cells of the AV node. Those do come through are irregular. Ventricular rate or heart rate is therefore irregular and can range from slow – less than 60 – to rapid -more than 100 – beats per minute. On an ECG (EKG), atrial fibrillation is characterized by absence of P-waves and irregular narrow QRS complexes. Reminder: P-wave represents electrical activity of the SA node that is now obscured by activities of multiple ectopic sites. The baseline may appear undulating or totally flat depending on the number of ectopic sites in the atria. In general, larger number of ectopic sites results in flatter baseline. As the atria do not function properly, the heart puts out less blood, and heart failure may occur. The most common complication of atrial fibrillation, however, is the formation of blood clots in the atria. As the atria do not empty completely into the ventricles, the blood may stagnate inside the atria and blood clots may form. These clots may then pass into the bloodstream, get stuck in small arteries and block them. When a blood clot blocks an artery in the brain, a stroke may result.
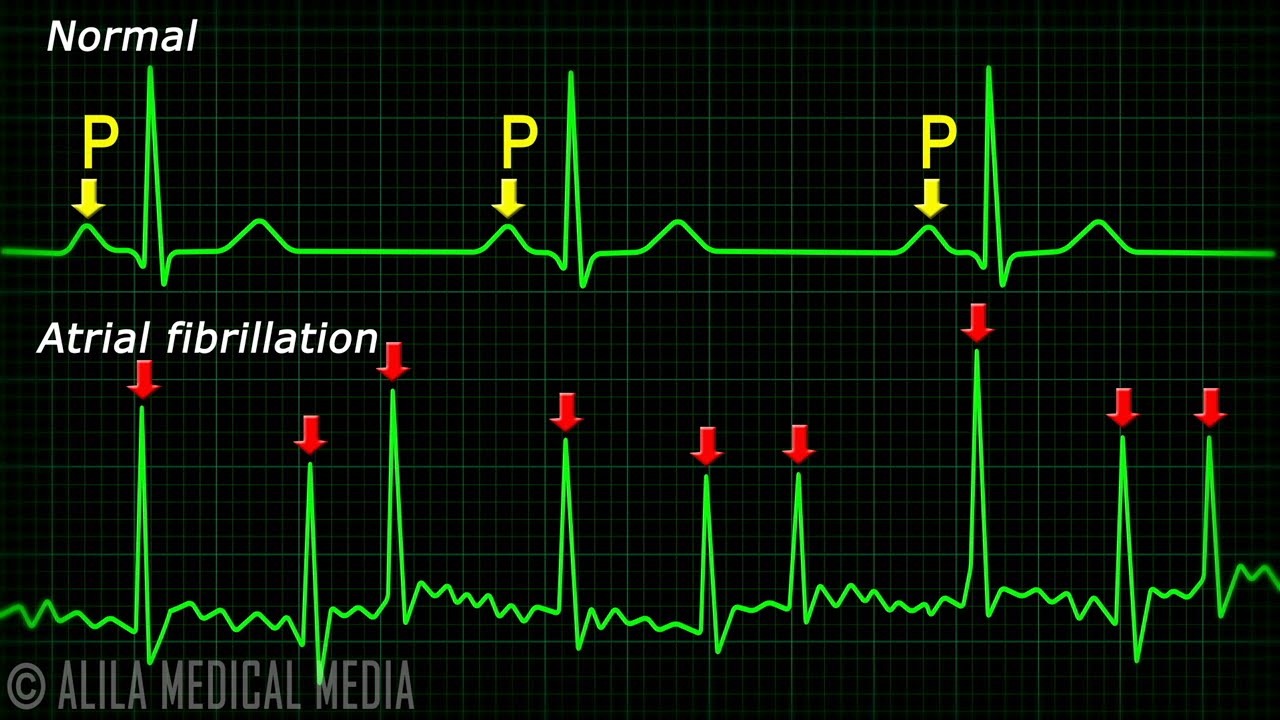
Atrial Fibrillation Anatomy, ECG and Stroke, Animation.
- Post author:
- Post published:June 5, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

You Don’t Need Carbs Pre Workout – do this instead…

BUILD SHIRT STRECHING BACK WITH UPPER TRAPEZIUS-ROPE SHRUGS WORKOUT.

health education on ethinylestradiol and diazepam

Burn Fat | Lower Back and Waist Slimmer Workout
Back Exercise Swiss-Ball Reverse Hyperextension Exercise

Why You Should Warm Up and Cool Down
Chapter 11 propranolol

Amazing!!!! Weight loss Transformations From Fat To Strong FIT Muscular Body

2D Echocardiogram – Testing for Heart Health

Cardiac surgery Video – 4

BMI Body Mass Index Gone Wrong! and Aspire Higher

DECLINE BENCH PRESS | TUTORIAL VIDEO
Fat Loss Diet – Weight Converter

Floor Back Extension

What To Eat Before & After A Gym Workout

Better Running and Stretching Tips for New Runners

Pregnancy Exercises Video – 5
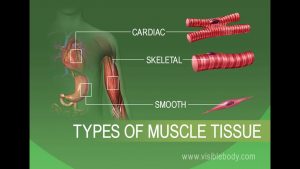
Anatomy and Physiology of Tissues

Shawn Rhoden’s Overhead Dumbbell Tricep Extension

The Magical Chinese Recipe to Lose Weight without any Effort

Benefits Of Human Growth Hormone Releasers

Step Up-3

tablet capsule strip packing

Intermittent Fasting & Fasting Video – 21

Part 1 – Introduction to Pharmacy and its background

Fit over 50 training review – Does fit over 50 training program work ?

Glutamine version- Tokyo Teddy Bear
Put Onion in your socks And This will Happen

Erector Spinae Back Extension-21

Pharmacodynamics: What a Drug Does to the Body Preview

HOME WORKOUT TRAINING – Static & Strength Calisthenics

Chest – Seated Pec Fly

Pain Free diabetic blood sugar testing

Bodybuilding & Water Intake: How Much Do You Need Per Day?

What is Aerobic Exercise- Cardio and aerobics workouts
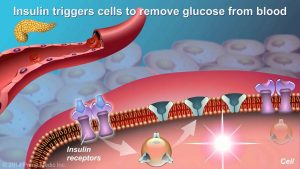
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes

BCAA Supplement/bcaa supplement hindi/bcaa supplement reveiw hindi/bcaa kya he/bcaa sideffect hindi
non surgical lipo animation

Leg Press-6
![Read more about the article SUPPLEMENTS YOU NEED// MUSCLE BUILDING// BCAA// CREATINE [HINDI]](https://videos.drmaheshkumar.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/SUPPLEMENTS-YOU-NEED-MUSCLE-BUILDING-BCAA-CREATINE-HINDI-300x169.jpg)
SUPPLEMENTS YOU NEED// MUSCLE BUILDING// BCAA// CREATINE [HINDI]

What is renal hypertension? – Ask ADC video

