For the related metabolic process, see anabolism. Catabolism (from Greek κατά kata, “downward” and βάλλειν ballein, “to throw”) is the set of metabolic pathways that breaks down molecules into smaller units to release energy. Catabolism breaks down large molecules (such as polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids and proteins) into smaller units (such as monosaccharides, fatty acids, nucleotides, and amino acids, respectively). As molecules such as polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids comprise long chains of these small monomer units (mono = one + mer = part), the large molecules are called polymers (poly = many). This video is targeted to blind users. Attribution: Article text available under CC-BY-SA Creative Commons image source in video

Catabolism
- Post author:
- Post published:June 14, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Instructional Fitness – Shrugs Behind The Back

Pharmacokinetics: Vd, Clearance, Half-life: Calculation Drug Distribution, Elimination, Rate

Female Body Types And Body Shapes Different Body Types Women Have

Cadbury Bournville – The perfect way to end your day (20 sec)

Ornithine transcarbamylase OTC deficiency arabic MEANING

Beginner’s Biceps Training: Perfect the High-Cable Curl Exercise

One Hand Triceps Extension-12

Intermittent Fasting & Fasting Video – 30

How to Get Toned Abs (IN ANY LIGHTING!)

Nutrition for Muscles building Video – 1

Module-Minute-The-Five-Health-Related-Fitness-Components

Flat Bench Fly-3
Cellular structure of bone | Muscular-skeletal system physiology | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy

Routes of drug entry | Processing the Environment | MCAT | Khan Academy

BEARD GROWTH UPDATE (DAY 13) BIOTIN OVERDOSING + SIDE EFFECTS + TIPS Advice Guide to a Thicker Beard

Are you Eating EGG WHITES For Weight Gain? (YOU NEED TO WATCH THIS RIGHT NOW!)

How To: High Cable Chest Fly

Yoga Exercises for Lungs

Neurological Physiotherapy Video – 12

Addiction Psychiatry Video – 3

URINE BILIRUBIN TEST
How to Give Someone an Insulin Injection
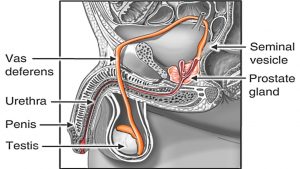
How Sperm Travels through Male Reproductive System Animation – Sperm Release Pathway -Function Video

HOW TO SUMO DEADLIFT ft. Larry

Muscle Building Workout & Squats Video – 42

Sports Psychiatry Video – 2

Physiology Of Sports & Sports Medicine Video – 4

Top 5 Best Whey Protein Powder Supplements 2016 First Half | MassiveJoes.com | Isolate Shakes

Physiotherapy in Rehabilitation Video – 16
The Human Body Video – 5
Vitamin B Complex – What and Why?
Most Beneficial Herb Known Produces HGH

What body type are you?
Diabetes Basics: What Is Diabetes?
Swedish Massage Video – 1

Basketball Video – 4

How to do Decline bench Press Correctly | Chest Exercise | Do It Yourself
Obstetrics Video – 1

Fitness Exercises : Side Crunches on Stability Ball Exercise

Understanding semen analysis – Dr. Teena S Thomas
Laproscopic Surgeries Video – 1

