Grab our free cheatsheet covering the 63 Must Know Labs for nurses right here: http://www.NURSING.com/labs Listen to all the episodes at: https://www.NURSING.com/labspodcast/ View this post on our blog: https://www.NURSING.com/erythrocyte-sedimentation-rate-esr/ Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Normal: 0-20 mm/h Indications: Identifies inflammation which assists in diagnosing: o Cancer o Infection o Autoimmune diseases Description: The Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) test measures sedimentation of Red Blood Cells (RBCs). The inflammatory process affects proteins in the blood which causes RBCs to stick together and settle out of liquid. Normal blood has very little settling, but during the inflammatory process the ESR is elevated. What would cause increased levels? Anemia Chronic Renal Failure Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Infection Tuberculosis Pregnancy Polymyalgia Rheumatica Multiple myeloma Medications: o Oral contraceptives o Theophylline o Vitamin A What would cause decreased levels? Sickle cell anemia Polycythemia Vera Leukocytosis Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Medications: o Aspirin o Cortisone o Quinine

Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate ESR Nursing Considerations, Normal Range, Nursing Care
- Post author:
- Post published:June 5, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Medicine Advantages Of Xenical Orlistat
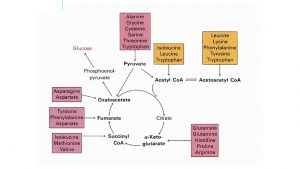
Bridge between Anabolic and Catabolic Pathways

Tone Up Exercises for Women in Their 40s : Body Sculpting Basics for Women

How to Use the Back Extension Machine for the Obliques : Shaping Up

What Should A Diabetic ‘Mom To Be’ Eat? – Pregnancy Tips

Endocrine system anatomy and physiology | Endocrine system lecture 1

How to Do Basic Sitting Stretches | Taekwondo Training

History Of Surgery Video – 6

operating a full blood count machine

Global Mental Health Video – 2

Human Body, Body Building Muscle Building Anatomy Physiology Video – 49

Zumba Cooldown / Stretch – Let me Love you (Remix)
Gastroenterology Video – 1
BMI vs Body fat %

How to Do a Barbell Lat Pullover | Back Workout

Sky Jumping Video – 2

Branches of Physiotherapy Video – 1

Anabolic Steroids – History, Definition, Use & Abuse Video – 27

Cardio and Aerobic Exercising : How to Burn Calories Through Walking & Jogging
Heart Attack-What Can Cause a Heart To Stop Beating?

Dumbbell Chest Workout At Home!

Different Types of Protein | HealthiNation

Lying Triceps Extension-6

WHEY PROTEIN or MASS GAINER? (Tips for Beginner)

Hydrolysis of fats

How to hit muscle groups twice a week

How to Perform Abdominal Crunches for Sculpted Abs
Body Types

How to warm up before exercise

How to warm up before exercise

BUTTERFLY WORKOUT FOR CHEST

Health & Skill Components of Fitness

Echo, What Is It?

Keto Diet, Keto Foods, Keto Recipes Video – 30

Surya Namaskar Video – 6

How I Hit My Upper Chest Without Any Incline Presses

Cheap Bodybuilding Foods (Bodybuilding On A Budget)

A Beginners Guide To Walking Fitness
Surgery for Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy

Digestive System Song
Early Warning Signs Of Liver Disease

