To better understand GERD, it’s important to know what happens in the normal digestive process. As you chew your food and swallow, food particles travel from your mouth to the esophagus. The esophagus is a muscular tube that contracts and relaxes in a wave-like motion to help move food and liquids down toward your stomach. This is called “peristalsis.” Just before the esophagus gets to the stomach, it travels through your diaphragm. The diaphragm is a broad muscle that separates your stomach from your chest cavity. The opening in the diaphragm where the esophagus travels through, is called the “hiatus.” You’ll hear more about the hiatus, and how it can be associated with GERD, a little later. The esophagus then joins the stomach at the “lower esophageal sphincter,” also called the “LES.” This sphincter acts as a doorway between the esophagus and the stomach. After you swallow, it opens to let food into the stomach. Then, the sphincter closes to keep food and stomach juices from going back up into the esophagus. The hiatus also helps close off the entryway to the stomach. Inside your stomach, strong acids and enzymes make up the stomach juices that break down your food. Your stomach has special mechanisms that help protect it from these strong juices. But your esophagus doesn’t have these same defenses, so it’s important for the LES to close off the stomach opening to keep the juices in the stomach. Sometimes, the acidic contents of the stomach do go back up, or reflux, into the esophagus, and some reflux is normal. Much of the time, this never causes any problems because the esophagus also has some ways to protect itself. For example, the saliva in your esophagus can help neutralize stomach acid, and gravity and peristalsis help to wash the saliva and stomach juices back down into the stomach. But other times, reflux can cause the burning, pressure, or pain in your chest or throat that most people call heartburn or acid indigestion.
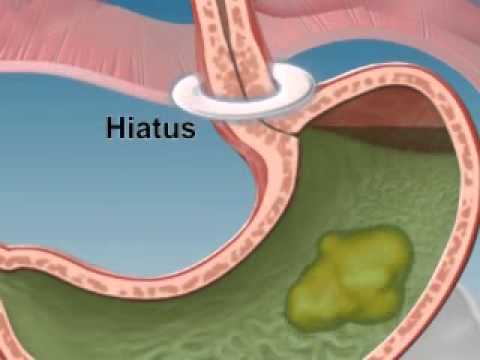
How Does My Stomach Work?
- Post author:
- Post published:May 27, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Vitamins – What are Vitamins – Types Of Vitamins – Fat Soluble Vitamins – Water Soluble Vitamins

Bodybuilding Nutrition, Diet Recipes & Workout – 32

Anabolic Steroids – History, Definition, Use & Abuse Video – 18

Treadmill High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) Workout | Part 1
what is diabetes type 2?
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) – Causes, symptoms and treatment modalities
Body Types

The Ultimate Thyroid Home Test with Dr. Rob

Supradyn multivitamin tablet : Uses, benefits & side-effects & precautions | Detail review in hindi

The BIG difference between T3 and T4

Best body building exercise

How to STOP Prediabetes Going Into Diabetes

Back Extensions On Ball, New Path Chiropractic Jupiter,Fl

Hot Stone Therapy Video – 2
Synthesis and Regulation of Thyroid Hormone
Teen gets tummy tuck to remove ‘hang’

Leg Curl-6

How To Increase Sperm Count Fast & Naturally ?
Free Radicals, Glutathione, Superoxide NADPH Oxidase N Acetylcysteine CGD MPO CCl4

7 Habits That Make You Gain Weight

Leg Extension-5

Muscle Building Workout & Squats Video – 32

Human Body, Body Building Muscle Building Anatomy Physiology Video – 47

Top 10 Foods That Help Lose Belly Fat – Tips To Burn Belly Fat

Alexander Technique Video – 1

Blood Pooling: Cardiovascular Physiology

Glycemic Index Load – Low glycemic index foods list diets
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes

Sports Injuries Video – 6

Chest Workout: Push-Ups

Exercise Anatomy Video – 3

High Intensity Training Video – 5
Strength

Archery Video – 4

Incline Bench Press-3

Chest Supported Incline Shrug

Anesthesiology Video – 2
Surgery Video – 1

Health Related Components of Fitness

The Estrogen Receptor (II): Molecular & Cellular Mechanisms
Hormones and Gender Transition

