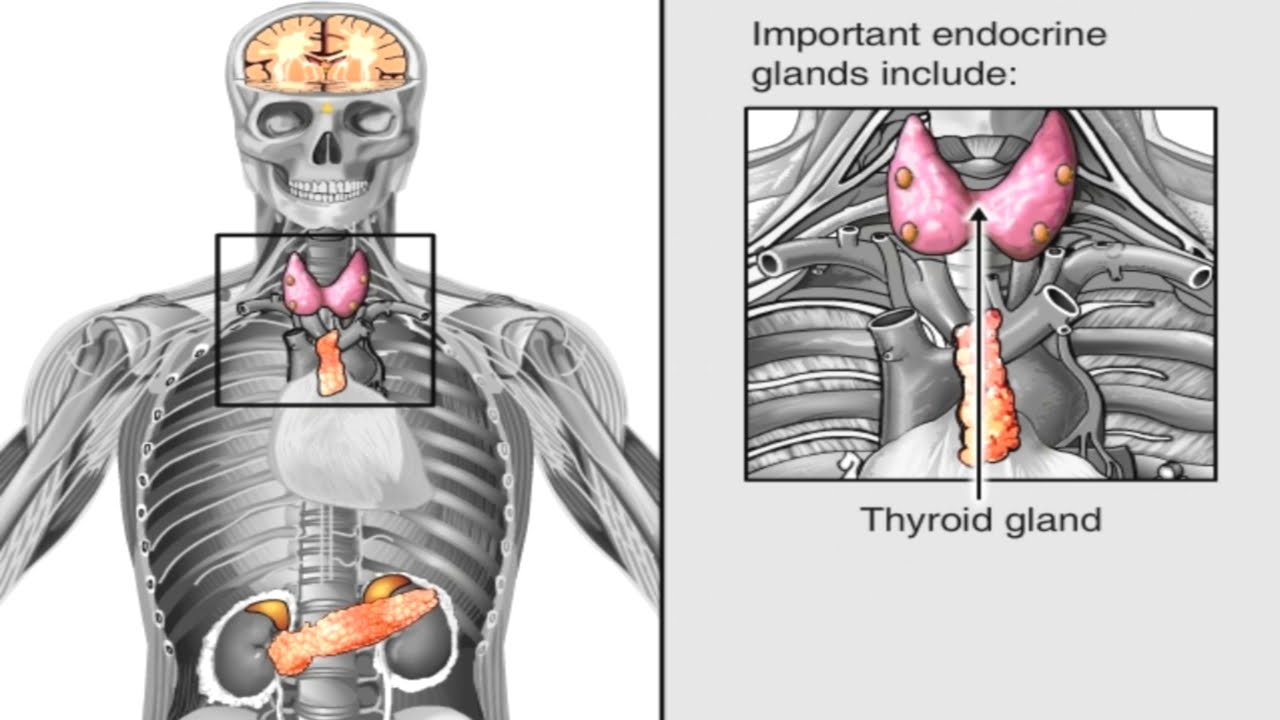
The endocrine system is primarily composed of glands that produce chemical messengers called hormones. Glands of the endocrine system include the pituitary gland, the thyroid gland, the parathyroid glands, the thymus, and the adrenal glands. Other glands are also included within the endocrine system since they contain endocrine tissue that secretes hormones. These include the pancreas, ovaries and testes. The endocrine and nervous systems work very closely together. The brain continuously sends instructions to the endocrine system, and in return receives feedback from the endocrine glands. Because of this intimate relationship, the nervous and endocrine systems are referred to as the neuroendocrine system. The hypothalamus is known as the master switchboard because it’s the part of the brain that controls the endocrine system. The pituitary gland, which hangs by a thin stalk from the hypothalamus, is called the master gland of the body because it regulates the activity of the endocrine glands. The hypothalamus detects the rising level of the target organ’s hormones then sends either hormonal or electrical messages to the pituitary gland. In response, the pituitary gland releases hormones, which travel through the bloodstream to a target endocrine gland, instructing it to stop producing its hormones. Here’s how the endocrine system keeps itself in check: eventually, the hypothalamus detects the rising level of the target organ’s hormones, and sends a message to the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland then stops releasing certain hormones, causing the target organ to stop producing its hormones. The endocrine system constantly adjusts hormone levels so that the body can function normally. This process is called homeostasis. The endocrine system is the collection of glands of an organism that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried towards distant target organs. In humans, the major endocrine glands include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, and adrenal glands. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems. The field of study dealing with the endocrine system and its disorders is endocrinology, a branch of internal medicine. Special features of endocrine glands are, in general, their ductless nature, their vascularity, and commonly the presence of intracellular vacuoles or granules that store their hormones. In contrast, exocrine glands, such as salivary glands, sweat glands, and glands within the gastrointestinal tract, tend to be much less vascular and have ducts or a hollow lumen. A number of glands that signal each other in sequence are usually referred to as an axis, for example, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. In addition to the specialized endocrine organs mentioned above, many other organs that are part of other body systems, such as bone, kidney, liver, heart and gonads, have secondary endocrine functions. For example, the kidney secretes endocrine hormones such as erythropoietin and renin. Hormones can consist of either amino acid complexes, steroids, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, or prostaglandins. The endocrine system is in contrast to the exocrine system, which secretes its hormones to the outside of the body using ducts. As opposed to endocrine factors that travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system, other signaling molecules, such as paracrine factors involved in paracrine signalling diffuse over a relatively short distance. The human endocrine system consists of several systems that operate via feedback loops. Several important feedback systems are mediated via the hypothalamus and pituitary. TRH – TSH – T3/T4 GnRH – LH/FSH – sex hormones CRH – ACTH – cortisol Renin – angiotensin – aldosterone leptin vs. insulin Endocrine glands are glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into instastial spaces and then absorbed into blood rather than through a duct. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, hypothalamus and adrenal glands. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are neuroendocrine organs. The Hypothalamus Essentials The portion of the brain that maintains the body’s internal balance (homeostasis). The hypothalamus is the link between the endocrine and nervous systems. The hypothalamus produces releasing and inhibiting hormones, which stop and start the production of other hormones throughout the body. Pituitary Gland Essentials: The hormones of the pituitary gland help regulate the functions of other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland has two parts—the anterior lobe and posterior lobe—that have two very separate functions.
How Hormones Work in the Body Animation – Endocrine System Anatomy & Physiology Video – Hypothalamus
- Post author:
- Post published:May 2, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Vitamin Complex that By Itself Can Fix Your Depression

Paneer: The Best Vegetarian Protein Source | BeerBiceps Fitness

Insulin Algorithms. Insulin dosing made easy.

hormone replacement therapy – How to Increase Estrogen Healthy Life Styles
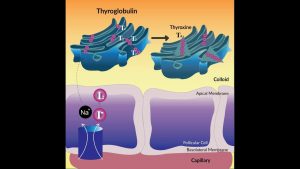
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis

Homicide Psychology/ Psychiatry Video – 1

How to Cool Down and Stretch after a Workout For Dummies

Pre Blended Oils Video – 4

Are BCAAs A Waste Of Money???

I’m Having a Vitamin B Complex!! 2 of 2

Juggernaut Method Squats + Wild Pulls
AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS

Orlistate

Top 9 Foods You Should Avoid While Breastfeeding – The Breastfeeding Diet – Tips for Moms

OMEGA 3 | The “KING” of Bodybuilding SUPPLEMENTS
Molecular Mechanisms in Tuberculosis

Dumbel 1 arm lying triceps extension
Hypertension – High Blood Pressure, Animation

What Is The Definition Of Physiology Medical School Terminology Dictionary

Optometry Video – 3
Bodybuilding Video – 1

15 Foods High in Vitamin D
Surgery Books Video – 1
General Surgery Video – 3
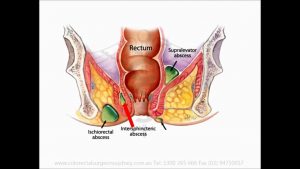
Anal Abscess – English
Hyperextension With ball-10

FOODS THAT LOWER BLOOD PRESSURE CAN CURE HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE

Static Quadriceps Exercise, Correct technique (Isometric Quads)

Close grip tricep extensions supersetted w/ earthquake curls

Best Diet Plan To Lose Belly Fat in 4 Weeks (Top 9 Fat Loss Foods)
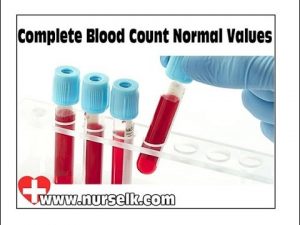
Complete Blood Count with Normal Values

Osteoporosis in 2 mins!

Special Population Exercise Video – 5

Hamstring Stretches to Do at the Desk at Work : Dynamic Exercises

Jay Cutler: What To Eat Pre & Post Workout

Organic Chemistry Food Challenge: Antioxidants

Biomolecules – Amino Acids

Skeletal System

Examples of Low-Impact Aerobic Exercises : General Fitness Tips

★ THE MILITARY DIET – LOSE 6/7 POUNDS per WEEK – The most EFFECTIVE FAT LOSS meal plan EVER★
Workout Supplement and Vitamins (Jeff Cavaliere’s Exact Plan)

