How pacemakers work. Animated explanation of the mechanics of the human heart, and the devices that can assist it Subscribe NOW to The Economist: http://econ.st/1Fsu2Vj Implantable pacemakers and defibrillators are devices that apply electric shocks to maintain the rhythm of the heart and, if necessary, restart it. As the technology improves and the list of treatable conditions grows, the number of devices being implanted is increasing steadily and now exceeds half a million a year. The heart is made up of four chambers; two atria and two ventricles. On each side the atrium is connected to the ventricle by a one-way valve. Blood is pumped as these chambers contract and relax in turn. The beating of a healthy heart is regulated by electrical impulses. The sequence begins as the atria fill with deoxygenated blood from the body on the right and oxygenated blood from the lungs on the left. An electrical signal from the sinoatrial node then causes the atria to contract, forcing blood into the ventricles. The electrical signal is then picked up by the atrioventricular node and directed into the Purkinje fibers in the ventricle walls, causing the ventricles to contract, and the blood is then pumped through the pulmonary valve on the right to the lungs, and the aortic valve on the left to the rest of the body. These valves close and the cycle then restarts. When the sinoatrial node fails to function correctly an artificial pacemaker can be fitted to help regulate the heartbeat with small evenly timed electric shocks. This involves implanting electrodes into one or more of the heart’s chambers, by inserting leads into a vein near the collarbone and implanting a device called the generator just under the skin. For more severe heart conditions an implantable defibrillator or ICD can be used which is also capable of sensing a stopped heart and delivering an electric shock powerful enough to restart it. For some conditions an even more sophisticated device called a CRT ICD can be implanted. This uses a third lead inserted into the left ventricle to resynchronize the ventricles when necessary. However, all these leads can cause problems of their own. Patients with ICDs have a 20% chance of a lead failure within 10 years and replacing leads can require open-heart surgery in about 2% of cases. This has resulted in several efforts to develop new pacemakers that do not depend on leads inside the heart. One design, the subcutaneous ICD, places the lead just outside the heart under the patient’s skin. And wireless designs are now being developed that may eventually do away with the need for leads altogether. Get more The Economist Follow us: https://twitter.com/TheEconomist Like us: https://www.facebook.com/TheEconomist View photos: https://instagram.com/theeconomist/ The Economist videos give authoritative insight and opinion on international news, politics, business, finance, science, technology and the connections between them.
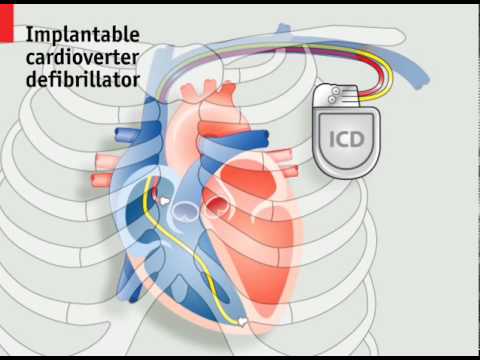
How pacemakers work | The Economist
- Post author:
- Post published:May 24, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Newborn Jaundice

HGH, Growth Hormones & Plant Hormones Video – 5

Digestive System And Asnas Video – 2

Emergency Medicine Video – 1
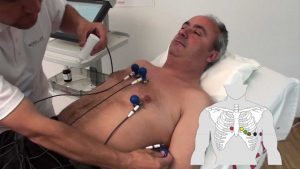
SCHILLER electrode placement for resting ECG with standard electrode set

Dermatology Video – 1

Weightlifting Video – 3

Stability Ball Lower Back Exercises

Donkey Kicks-10

Target INNER Pecs – 3 Flat Dumbbell Chest Exercises

Back Extension…You’re Doing It WRONG

CBC Machine Maintenance
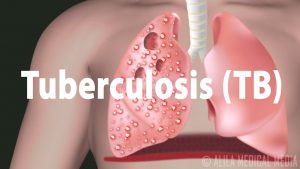
Tuberculosis (TB): Progression of the Disease, Latent and Active Infections.

Sprints: 10 Minute Abs & Cardio Workout for Busy Moms

Chocolate Nutrition Video – 1
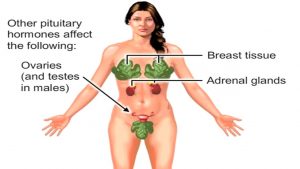
How Does Pituitary Gland Work? Hormones of Hypophysis Functions & Disorders Animation -TSH FSH Video
Neurology Video – 1

What is Hypotension (Low Blood Pressure)? (OUTDATED)

Phase 3 Day 2 A4 – Low Pulley Overhead Triceps Extension with Rope

Types of Stretching

BEST Tricep Exercise for MASS – Close Grip Tricep Press

Strength training for women – Full body workout with dumbbells

Vitamin Supplements Worth Taking

Branched Chain Amino Acid Supplements (BCAA’s)

Nature Made Super B-Complex

GLUTAMINE IS A BOGUS BODYBUILDING SUPPLEMENT @hodgetwins

Drug and Medicine
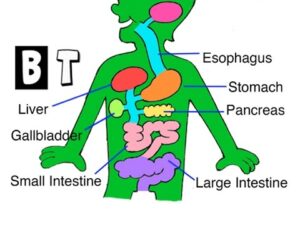
Digestive System for Kids – How Digestion Works – human body parts for children

The Scariest Side Effect of Pregnancy!

Making A Yoga Routine Video – 1

Best Ab Workout Tip Ever (WORKS INSTANTLY!)
Branches Of Medicine Video – 1
Actinic Keratosis Mode of Action Animation

clomid or clomiphene

Cardio-Thoracic Physiotherapy Video – 7

Ballistic Stretching

TREAT FEVER WITHOUT MEDICINES | TREAT FEVER INSTANTLY

What does silymarin mean?

The Side Plank – Core Exercise

Is it normal to get a prescription for propranolol?

What Is a Set? | Gym Workout