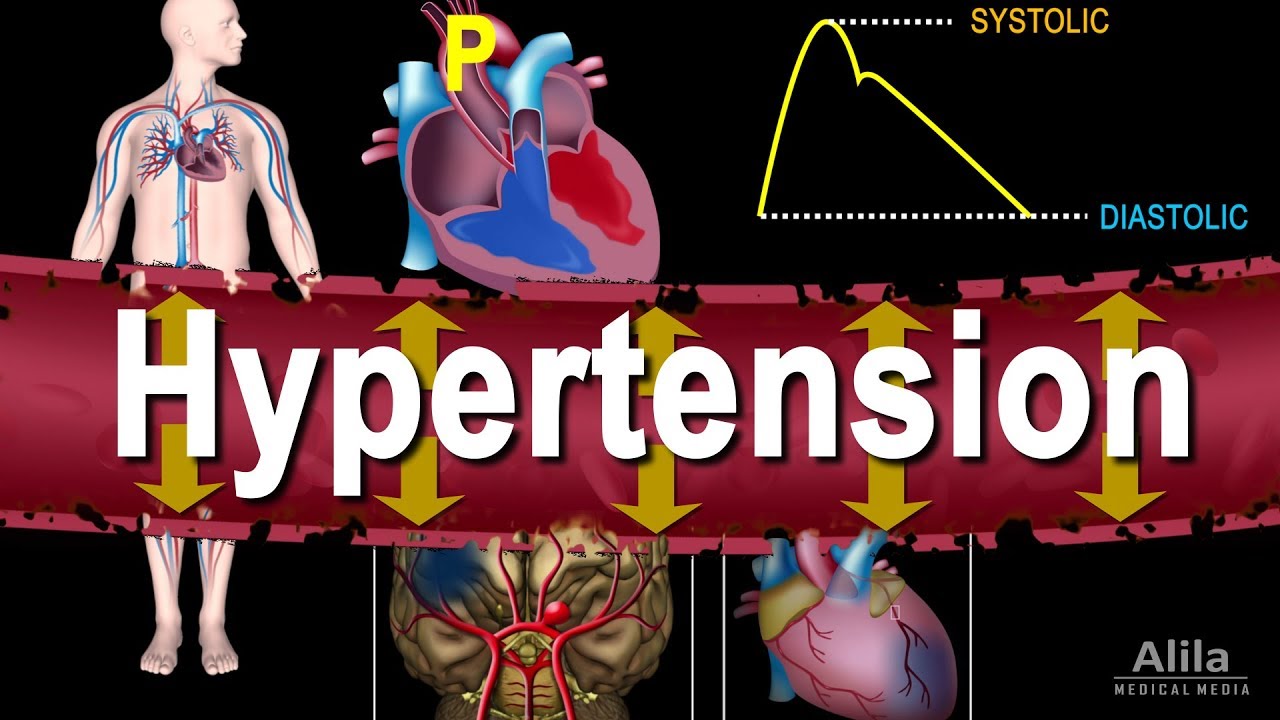
(USMLE topics, cardiology) Blood pressure: systolic and diastolic; hypertension: guidelines, causes, risk factors, complications, treatment, antihypertensive drugs. This video is available for instant download licensing here: https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/hypertensioncholesterol/-/medias/d8cadc84-432b-4925-8e36-16ceeb86ffe0-hypertension-narrated-animation ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Voice by: Sue Stern. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Blood pressure is the force the circulating blood EXERTS on the walls of blood vessels. It is different in different types of vessels, but the term ”blood pressure”, when not specified otherwise, refers to ARTERIAL pressure in the SYSTEMIC circulation. When the heart contracts and pumps blood into the aorta, during systole, the aortic pressure RISES, and so does the systemic arterial pressure. The maximum pressure following an ejection is called the SYSTOLIC pressure. In between heart beats, when the ventricles refill, blood pressure FALLS to its lowest value called the DIASTOLIC pressure. THESE are the 2 numbers on a blood pressure reading. Blood pressure normally shows a daily pattern and is usually lower at night. During day-time, it fluctuates with physical activities and emotional states. Hypertension refers to a PERSISTENT HIGH blood pressure. In the US, high blood pressure used to be defined as greater than 140/90, but recent guidelines have changed these values to 130/80 to better prevent and treat the condition. Normal blood pressure is BELOW 120/80. In practice, blood pressure is considered TOO low ONLY if it produces symptoms. Hypertension does NOT cause symptoms on its own, but it slowly DAMAGES blood vessels, and in the long-term, is a MAJOR risk factor for a variety of cardiovascular diseases such as stroke, aneurysm and heart attack; as well as end organ damage such as renal failure or vision loss. For this reason, hypertension is known as the “SILENT killer”. Hypertension can be classified as primary or secondary, with the former being responsible for over 90% of cases. Primary hypertension has NO apparent cause and may develop as a result of old age, obesity, high-salt diet, lack of exercise, smoking and drinking. Most commonly, the blood vessels are hardened with age or unhealthy diets, making it harder for blood to flow. Secondary hypertension, on the other hand, is caused by an underlying condition. Many conditions and factors can cause hypertension; most notable are kidney problems and endocrine disturbances. Regardless of the cause, the INcrease in blood pressure is produced by EITHER an INcrease in vascular resistance – narrower or stiffer blood vessels; OR an INcrease in cardiac output – larger volume of blood pumped out by the heart. These 2 factors are the targets of antihypertensive drugs. Treatments must start with life style changes such as healthy, low-sodium diets, physical exercise and stress management. On top of that, antihypertensive agents may be used to control hypertension. These include: – Vasodilators: these drugs DILATE blood vessels, thereby DEcreasing vascular resistance and reducing blood pressure. – Diuretics: diuretics promote sodium and water removal by the kidneys and thereby DEcrease blood volume. – Drugs that DEcrease cardiac output by decreasing heart rate or contractility, may also be used to treat hypertension.
Hypertension – High Blood Pressure, Animation
- Post author:
- Post published:May 18, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like
Minerals – Mineral Resources

My New Supplement Stack (Using India’s Cheapest Whey Protein)

The Sublingual Route

Branches of Physiotherapy Video – 28

How long can you live on dialysis with kidney failure ?

Deamination Meaning

Estrogen | Reproductive system physiology | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy

Iron Deficiency Causes

Andrology Video – 5
Pharmacology: Drug binding

Physiotherapy in Obstetrics Video – 9

Lat Pulldown with Band : Best Back Exercises ( Lat exercises )

Crunches-7

Work Out Meal Plan Prep (GOOD, FAST, CHEAP!)

Top 5 Best Amino Acids Supplements 2016 First Half | MassiveJoes.com | Intra-Workout Acid
How fat loss works in your body – the suprising truth

Dr Oz’s Recommendation on Vitamins
Surgery Books Video – 1

Massage Spa Video – 4

Side plank-5

Sugar Free, Low Sugar Video – 17

Resistance Training – ARC-NRG Muscle Group Highlight

HGH, Growth Hormones & Plant Hormones Video – 23

Steroids Side Effects: Wactch this Before Using Steroids

Goodmorning-2

Insulin and glucagon | Chemical Processes | MCAT | Khan Academy

How to test your blood glucose (sugar) levels

What Is Endurance? – Whiteboard Wednesday

Thyroid Disorders Nutrition Video – 1
Ayurvedic lifestyle to deal Epilepsy | – Dr. Advait Kulkarni | Doctors’ Circle

Abhyanga – Ayurved Video – 3

The Iodine-Estrogen Connection: MUST WATCH! Dr.Berg

Deficiency & Malnutrition Video – 1

Top 10 fruits to eat while Breastfeeding

AEROBIC vs ANAEROBIC DIFFERENCE
How Does The Digestive System Work?
How The Body Reacts To Tuberculosis

10 Foods to Avoid During Breastfeeding
Angioplasty Procedure Animation Video.

Is It Safe To Drink Your Urine?

Chicken Breast & Weight Loss – Healthy Fat & Weight Loss Diet

