Insulin is the hormone that drives glucose out of the bloodstream and into cells, and diabetes is the loss of the ability to control blood glucose levels. Yet insulin is so much more than a hormone that controls glucose. For one, it’s highly anabolic, which means it’s critical for building muscle. Insulin also has a dark side, because it can increase fat storage. The challenge is to learn how to spike insulin to optimally recover from workouts and grow, while also blunting it to stay lean. Do you know all the facts about insulin and how to use it to your advantage? Don’t be so sure. If not, my insulin information will teach you how. 642 Jim Stoppani, Ph.D. Jim Stoppani, Ph.D. July 15, 2016 • 8 min read Years ago, insulin was only discussed in reference to diabetes. Insulin is the hormone that drives glucose out of the bloodstream and into cells, and diabetes is the loss of the ability to control blood glucose levels. Yet insulin is so much more than a hormone that controls glucose. For one, it’s highly anabolic, which means it’s critical for building muscle. Insulin also has a dark side, because it can increase fat storage. The challenge is to learn how to spike insulin to optimally recover from workouts and grow, while also blunting it to stay lean. Do you know all the facts about insulin and how to use it to your advantage? Don’t be so sure. If not, my insulin guide will teach you how. Insulin And Muscle Insulin is actually a protein, and it is produced and released by the pancreas whenever you eat carbs, protein, or both. (That is, if the pancreas is working properly). Yet unlike the proteins that are the physical building blocks of muscle, this is a functional protein, much like growth hormone. Like all other proteins, insulin is a chain of amino acids strung together. But the way this protein chain is folded makes it act more like a signaling mechanism than a building block. From the pancreas, insulin enters the blood stream and travels to various tissues, including muscle tissue. The muscle fibers (or cells) are lined with insulin receptors, similar to a docking station. Once the insulin molecule docks onto the receptor, it signals the muscle cell to open up gates. This allows allow glucose, amino acids, and creatine to enter the muscles. This process is a major reason why insulin is so important for building muscle. Another reason is that when insulin docks onto the muscle cells, it instigates biochemical reactions in the muscle that increase protein synthesis, which is the building of muscle out of the amino acids that are entering the muscle cells. In addition, insulin also decreases muscle breakdown, which further enhances muscle growth. Insulin also indirectly aids in muscle development by causing the blood vessels to relax and dilate, allowing greater blood flow to the muscles. By increasing blood flow, insulin can help get even more nutrients like glucose and amino acids to the muscles. This is why you’ll see bodybuilders pounding simple carbs on contest day. Not only does the corresponding spike in insulin drive the carbs into the muscles to keep them full, it also boosts vascularity. Insulin And Fat Insulin’s release from the pancreas signals the body that it has just been fed. Since the body is always trying to spare energy, it halts the body’s burning of stored fat, instead turning to the nutrients that have just been ingested. Meanwhile, insulin also works on fat cells similar to how it works on muscle cells, signaling the gates to open and nutrient storage to commence. An increase in the uptake of glucose and fats causes the body to store more body fat. More fat is stored, less is burned—you can see how spiking insulin levels throughout the day would lead to fat gain over time. As long as those insulin receptors work as designed, a spike in insulin levels clears out the majority of the glucose in the blood, pushing it into muscle and fat cells. This lowers blood glucose levels in an orderly fashion, if someone has a healthy glucose metabolism, but it can also lead to a crash—either because the person’s glucose tolerance is impaired, or too many simple carbs were consumed at once. The low blood sugar that results from a crash is known as hypoglycemia. A crash will make you feel like your energy levels have been zapped. Not only is this bad for your general well-being, but it’s bad for your physique. What’s more, when your energy crashes, your hunger soars. This often causes people to over-eat. For most of us, this means reaching for simple carbs—which can lead to another crash.

INSULIN For Bodybuilding |Muscle Building Messenger
- Post author:
- Post published:May 31, 2021
- Post category:Uncategorized
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Eating Disorders Video – 1

Bodybuilding Nutrition, Diet Recipes & Workout – 41
The scientific truth about steroids

How to make: Lactation Smoothie

Equestrian Video – 3
What Is Arthritis | What Causes Arthritis | Why Arthritis Causes Pain

What is an antioxidant?

Debunking The Myth Of Vitamin Supplements

How To Do TRICEPS BENCH DIPS EXERCISE

Propranolol information burst
Quick review of thyroid hormone synthesis.

flexibility and stretching

Yoga Diet Video – 2

Calculate your own body mass index | Miscellaneous | Heatlh & Medicine | Khan Academy

Anorectal Surgeries Video – 2

MLS Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate

Define Diabetes

Stability Ball Hyperextension – HASfit Low Back Exercises – Lower Back Exercise

Sports Physiology Video – 4
Back Extension

BMR to CMOP

Best Weight Loss Pills | Natural vs Pharmaceutical

Sports Physiology Video – 5

General Practice Video – 4

Bodybuilding Nutrition, Diet Recipes & Workout – 29

How to Do a Lat Pulldown | Back Workout

Fat Burning Cardio Workout – 37 Minute Fitness Blender Cardio Workout at Home

How do vitamins work? – Ginnie Trinh Nguyen
INTERNAL ORGANS
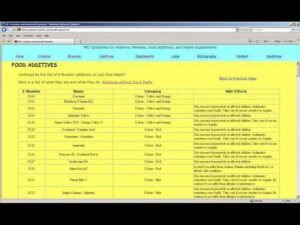
Vitamins and Mineral Sources
what is renal failure / Symptoms of kidney failure / chronic & acute kidney failure

Chest Supported Incline Shrug

Biceps Exercises: Barbell Curls

The Best Pre-Workout Meal for Muscle Gain

Weight Training Video – 6

Muscle Building Workout & Squats Video – 39

How to Use Whey Protein to Build Muscle | Bodybuilding Diet

Bodybuilding Tip Importance of Water & Staying Hydrated When Trying To Build Muscle @hodgetwins

Steroids and Kidney
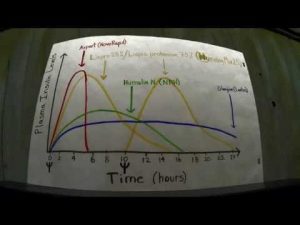
Insulin Action Times

DRES: Clothing for your Body Shape

