This video is available for instant download licensing here: https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/all-animations/respiratory-system-videos/-/medias/63e4494c-bc90-4b5f-a058-dccd2756252e-progression-of-tuberculosis-narrated-animation Voice by: Qudsi Baker. ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Tuberculosis, or TB, is one of the oldest and most common infectious diseases. About one third of the world population is believed to be infected with TB. Fortunately, only about 5% of these infections progress to active disease. The other 95% of infected people are said to have a dormant or latent infection; they do not develop any symptoms, and do not transmit the disease. Tuberculosis is caused by a rod-shaped bacterium, or a bacillus, called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. An infection is initiated following inhalation of mycobacteria present in aerosol droplets discharged into the atmosphere by a person with an active infection. The transmission process is very efficient as these droplets can persist in the atmosphere for several hours and the infectious dose is very low – less than 10 bacilli are needed to start the infection. Once in the lung, the bacteria meet with the body’s first-line defense – the alveolar macrophages. The bacteria are ingested by the macrophages but manage to survive inside. Internalization of the bacilli triggers an inflammatory response that brings other defensive cells to the area. Together, these cells form a mass of tissue, called a granuloma, characteristic of the disease. In its early stage, the granuloma has a core of infected macrophages enclosed by other cells of the immune system. As cellular immunity develops, macrophages loaded with bacteria are killed, resulting in the formation of the caseous center of the granuloma. The bacteria become dormant but may remain alive for decades. This enclosed infection is referred to as latent tuberculosis and may persist throughout a person’s life without causing any symptoms. The strength of the body’s immune response determines whether an infection is arrested here or progresses to the next stage. In healthy people, the infection may be stopped permanently at this point. The granulomas subsequently heal, leaving small calcified lesions. On the other hand, if the immune system is compromised by immunosuppressive drugs, HIV infections, malnutrition, aging, or other factors, the bacteria can be re-activated, replicate, escape from the granuloma and spread to other parts of the lungs causing active pulmonary tuberculosis. This reactivation may occur months or even years after the initial infection. In some cases, the bacteria may also spread to other organs of the body via the lymphatic system or the bloodstream. This widespread form of TB disease, called disseminated TB or miliary TB, occurs most commonly in the very young, the very old and those with HIV infections. Tuberculosis is generally treatable with antibiotics. Several antibiotics are usually prescribed for many months due to the slow growth rate of the bacteria. It’s very important that the patients complete the course of the treatment to prevent development of drug-resistant bacteria and re-occurrence of the disease.
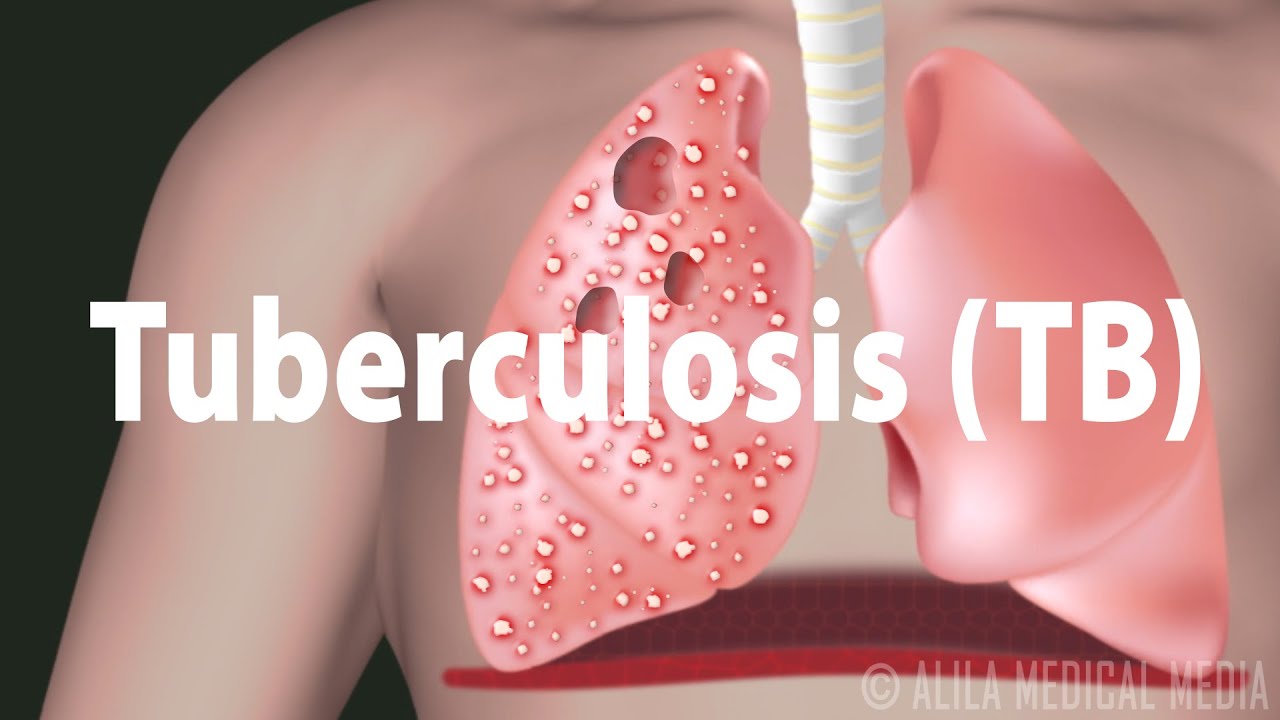
Tuberculosis (TB): Progression of the Disease, Latent and Active Infections.
- Post author:admin
- Post published:October 7, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Fitness Definitions

Hepa Merz L Ornithine; L Aspartate
Diabetes Type 1 and Type 2, Animation.
![Read more about the article Osteoporosis [Bone Disease] | Simple & Effective Natural Home Remedies for Osteoporosis & Arthritis](https://videos.drmaheshkumar.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Osteoporosis-Bone-Disease-Simple-Effective-Natural-Home-Remedies-for-Osteoporosis-Arthritis-300x169.jpg)
Osteoporosis [Bone Disease] | Simple & Effective Natural Home Remedies for Osteoporosis & Arthritis

Stretching Video – 1

What is ANEMIA? What does ANEMIA mean? ANEMIA signs, symptoms, causes & treatment

Muscle Building Workout & Squats Video – 26

How to Tone Your Abs with Donkey Kickbacks | Health

Hyperextension With ball-2

The Magical Chinese Recipe to Lose Weight without any Effort

Aromatic Oils Video – 2

You Don’t Need Statin Drugs!

Post-Workout Cooldown
Vitamin B12 Functions In Our Body |Hindi| Vitamin B12 Source – Supplements

What is SEMEN? What does SEMEN mean? SEMEN meaning, definition, explanation & pronunciation
Major Muscle Groups pt 2

Breaking News: NO Carbohydrates are needed post workout for Bodybuilders.
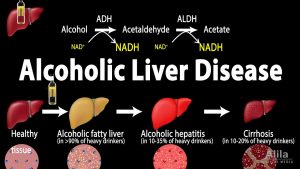
Alcoholic Liver Disease, Animation

Thyroid Diet Plan : How To Lose Weight Fast 10 kgs in 10 Days – Indian Meal Plan For Weight Loss

What’s the Difference between Programing and Coaching?

Geriatric Nutrition Video – 1

Adjusting Your Diet to Your Body Type – Somatotyping

Rheumatology Video – 4

Wild Catt slow descent squats
Laproscopic Surgeries Video – 4

Hot Stone Therapy Video – 3

Bodybuilding Pre-Workout Meal Example
Stretching Types

BEST TIME TO TAKE CREATINE|CREATINE कब लें Pre or Post Workout

10 Best Pre & Post Workout Meals / Snacks

Better Running and Stretching Tips for New Runners

Sprints: 10 Minute Abs & Cardio Workout for Busy Moms

Sleep Medicine Video – 2

Carbohydrate Nutrition Video – 2

Stretch All Deltoid Heads!

How to Eat & Exercise Correctly According to Your Body Type (Ecto, Meso, Endo)

How to do a preacher curl for maximum results!!

What am I eating to BUILD MUSCLES? Full day of eating

It’s time to try new investment options like Mutual Funds.

DYNAMIC STRETCHING / WARM UP ROUTINE FOR SPEED TRAINING / EXERCISE
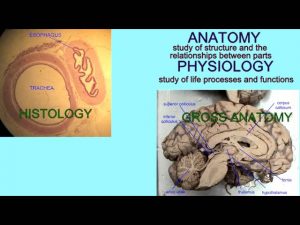
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: DEFINITIONS

