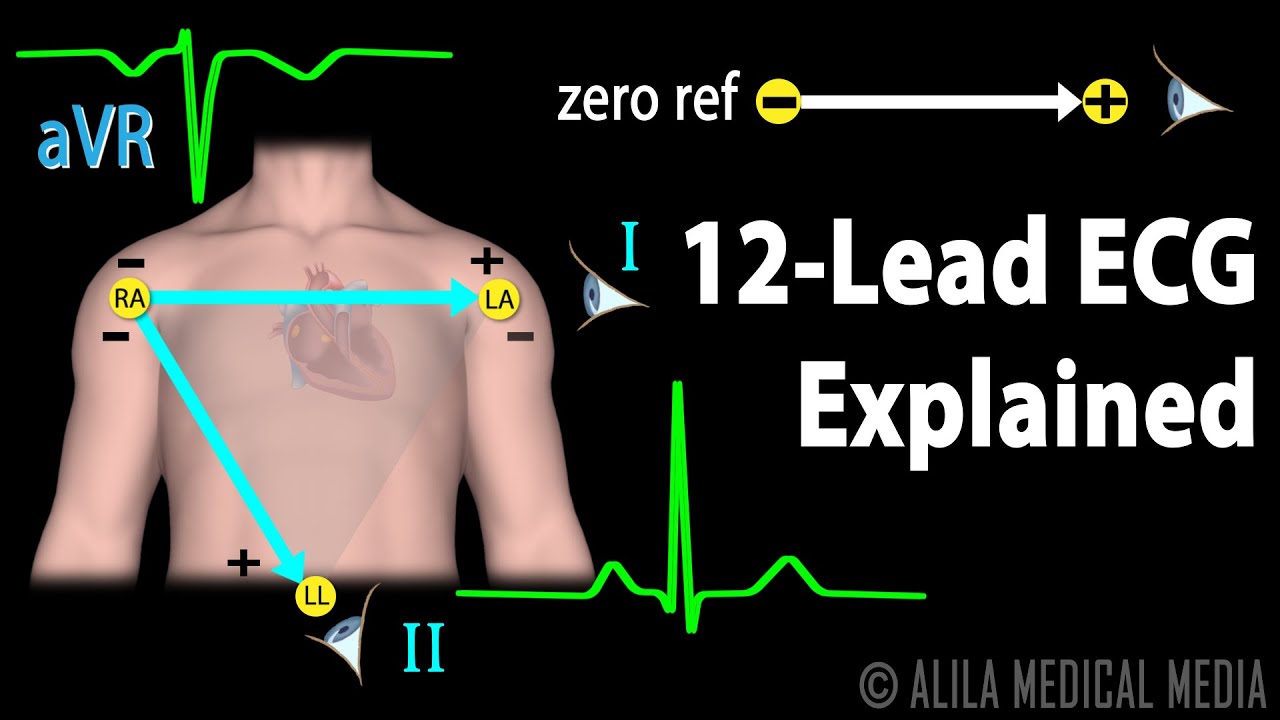
(USMLE topics, cardiology) Understanding the standard 12-lead EKG – Basics of electrocardiography explained. This video is available for instant download licensing here: https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/ekgecg/-/medias/4d57ce72-0d39-4525-b523-329941b9edcf-12-lead-ecg-explained-narrated-animation ©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved. Voice by: Sue Stern. Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Electrical activities of the heart can be picked up on the skin via electrodes. An ECG machine records these activities and displays them graphically. The graphs show the heart’s OVERALL electrical potential, or voltage, as it changes over time during a cardiac cycle. The 12 leads of the ECG represent 12 electrical views of the heart from 12 different angles. The conventional 12-lead procedure involves attaching 10 electrodes to the body: one to each limb and six across the chest. There are 6 limb leads and 6 chest leads. The 6 limb leads look at the heart in a vertical plane and are obtained from three electrodes attached to the right arm, left arm, and left leg. The electrode on the right leg is an earth electrode. The measurement of a voltage requires 2 poles: negative and positive. The ECG machine uses the negative pole as zero reference. Thus, the position of the positive pole is the “point of view”, and the line connecting the 2 poles is the “line of sight”. Leads I, II, and III are BI-polar – they measure electrical potential between 2 of the 3 limb electrodes: Lead I represents the voltage between the right arm – negative pole – and the left arm – positive pole, and thus looks at the heart from the left. Lead II sees signal movements between the right arm – negative – and the left leg –positive – forming the INFERIOR LEFT view. Similarly, lead III measures electrical potential between the left arm – negative – and the left leg –positive, looking at the heart from an INFERIOR RIGHT angle. Leads aVR, aVL, and aVF, or “augmented limb leads”, are UNIpolar. They use ONE limb electrode as the positive pole, and take the average of inputs from the OTHER two as the zero reference. Hence, aVR looks at the UPPER RIGHT side of the heart; aVL looks at the UPPER LEFT side of the heart; and aVF looks at the INFERIOR wall of the heart. The chest leads, or precordial leads, view the heart in a HORIZONTAL plane. These are unipolar leads. The corresponding chest electrodes serve as the positive poles. The reference negative value is the same for all chest leads and is calculated as the average of inputs from the three limb electrodes. DE-polarization TOWARD a lead produces a POSITIVE deflection; DE-polarization AWAY from a lead gives a NEGATIVE deflection. The REVERSE is true for RE-polarization. Thus, leads that look at the heart from different angles may have waves pointing in different directions.
12 Lead ECG Explained, Animation
- Post author:
- Post published:June 5, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like

Orlidiet Testimonios Orlidiet 120 Mg Potente Quema Grasa

Opposing Muscle Group Supersets for muscle growth Gainz
Digestion Animation – Six Parts Water

Does Eating Before Bed Make You Fat and Gain Weight? | Weight Loss Tips

Get abs: Crunch with knees to the chest

Personal Trainer/ Gym Instructor Video – 2

EASY TIP – How to Preacher Curl for Big Gains

क्रिएटिन कब कैसे और क्यों लेना चाहिए | Creatine – Benefits, Side-effects & Dosage | Hindi
Creatine: How to Best Use It for Muscle Growth (Avoid Side Effects)!

BICEPS – Preacher Machine Curl

Bowflex® How-To | Dumbbell Row for Beginners

Yoga Diet Video – 1

Baby Cries During Breastfeeding – Reasons and Solutions

Surya Namaskar Video – 2
Laproscopic Surgeries Video – 4
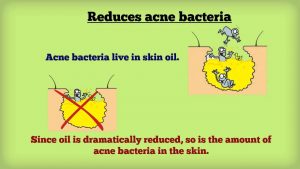
How Accutane Works for You

Intermittent Fasting & Fasting Video – 17

How to Do a Crunch | Ab Workout
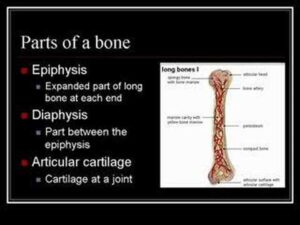
Skeletal System And Asanas Video – 6

The science behind hair loss

Spa Business Video – 3

Nutrition Local Applications (Skin & Hair) Video – 2
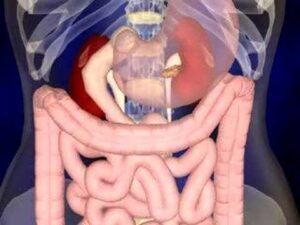
The Digestive System animation

Soccer/ Football Video – 2

No Bull BCAA Tablets by Raw Barrel Supplements (Best BCAA Tablets/Pills?)

How to Fix Hair FALL & Hair THINNING | Important Tips by Guru Mann
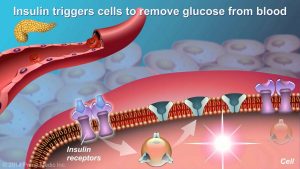
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes

Developmental Psychology Video – 1
Coronary Heart Disease Animation

How to make oats IN HINDI with English subtitles

Cycling Video – 1

Pancreatic Hormones (Insulin, Glucagon, Somatostatin)

Side Effects of Omega 3 Supplements | BestFishOill.com

Estrogen Dominance

Lipid profile in psoriasis patients – Video abstract: 32539

Practical Demo of Bone Mineral Density (BMD) (Hindi) (720p HD)

BCAA Supplement vs Protein Supplement – Know Your Supps – BPI Sports

Triceps – Cable Rope Overhead Triceps Extension Exercise Guide

Best Protein Powder for WEIGHT LOSS & MUSCLE BUILDING | Shake to Build Muscle | Top Supplements 2017

Triceps Pulley – RJNet Training
Effects of High Blood Pressure

