If left untreated, hypertension can lead to the thickening of arterial walls causing its lumen, or blood passage way, to narrow in diameter. As a result, the heart must work harder to pump blood through the narrowed arterial openings. In addition, people with hypertension may be more susceptible to stroke. High blood pressure dangers: Hypertension’s effects on your body High blood pressure is a risk factor for more than heart disease. Discover what complications high blood pressure can cause. High blood pressure (hypertension) can quietly damage your body for years before symptoms develop. Left uncontrolled, you may wind up with a disability, a poor quality of life or even a fatal heart attack. Fortunately, with treatment and lifestyle changes, you can control your high blood pressure to reduce your risk of life-threatening complications. Here’s a look at the complications high blood pressure can cause when it’s not effectively controlled. Damage to your arteries Healthy arteries are flexible, strong and elastic. Their inner lining is smooth so that blood flows freely, supplying vital organs and tissues with adequate nutrients and oxygen. If you have high blood pressure, the increased pressure of blood flowing through your arteries gradually can cause a variety of problems, including: Artery damage and narrowing. High blood pressure can damage the cells of your arteries’ inner lining. That launches a cascade of events that make artery walls thick and stiff, a disease called arteriosclerosis (ahr-teer-e-o-skluh-ROE-sis), or hardening of the arteries. Fats from your diet enter your bloodstream, pass through the damaged cells and collect to start atherosclerosis (ath-ur-o-skluh-ROE-sis). These changes can affect arteries throughout your body, blocking blood flow to your heart, kidneys, brain, arms and legs. The damage can cause many problems, including chest pain (angina), heart attack, heart failure, kidney failure, stroke, blocked arteries in your legs or arms (peripheral artery disease), eye damage, and aneurysms. Aneurysm. Over time, the constant pressure of blood moving through a weakened artery can cause a section of its wall to enlarge and form a bulge (aneurysm). An aneurysm (AN-yoo-riz-um) can potentially rupture and cause life-threatening internal bleeding. Aneurysms can form in any artery throughout your body, but they’re most common in the aorta, your body’s largest artery. Damage to your heart Your heart pumps blood to your entire body. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage your heart in a number of ways, such as: Coronary artery disease. Coronary artery disease affects the arteries that supply blood to your heart muscle. Arteries narrowed by coronary artery disease don’t allow blood to flow freely through your arteries. When blood can’t flow freely to your heart, you can experience chest pain, a heart attack or irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias). Enlarged left heart. High blood pressure forces your heart to work harder than necessary in order to pump blood to the rest of your body. This causes the left ventricle to thicken or stiffen (left ventricular hypertrophy). These changes limit the ventricle’s ability to pump blood to your body. This condition increases your risk of heart attack, heart failure and sudden cardiac death. Heart failure. Over time, the strain on your heart caused by high blood pressure can cause your heart muscle to weaken and work less efficiently. Eventually, your overwhelmed heart simply begins to wear out and fail. Damage from heart attacks adds to this problem. Damage to your brain Just like your heart, your brain depends on a nourishing blood supply to work properly and survive. But high blood pressure can cause several problems, including: Transient ischemic attack (TIA). Sometimes called a ministroke, a transient ischemic (is-KEE-mik) attack is a brief, temporary disruption of blood supply to your brain. It’s often caused by atherosclerosis or a blood clot — both of which can arise from high blood pressure. A transient ischemic attack is often a warning that you’re at risk of a full-blown stroke. Stroke. A stroke occurs when part of your brain is deprived of oxygen and nutrients, causing brain cells to die. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to stroke by damaging and weakening your brain’s blood vessels, causing them to narrow, rupture or leak. High blood pressure can also cause blood clots to form in the arteries leading to your brain, blocking blood flow and potentially causing a stroke.
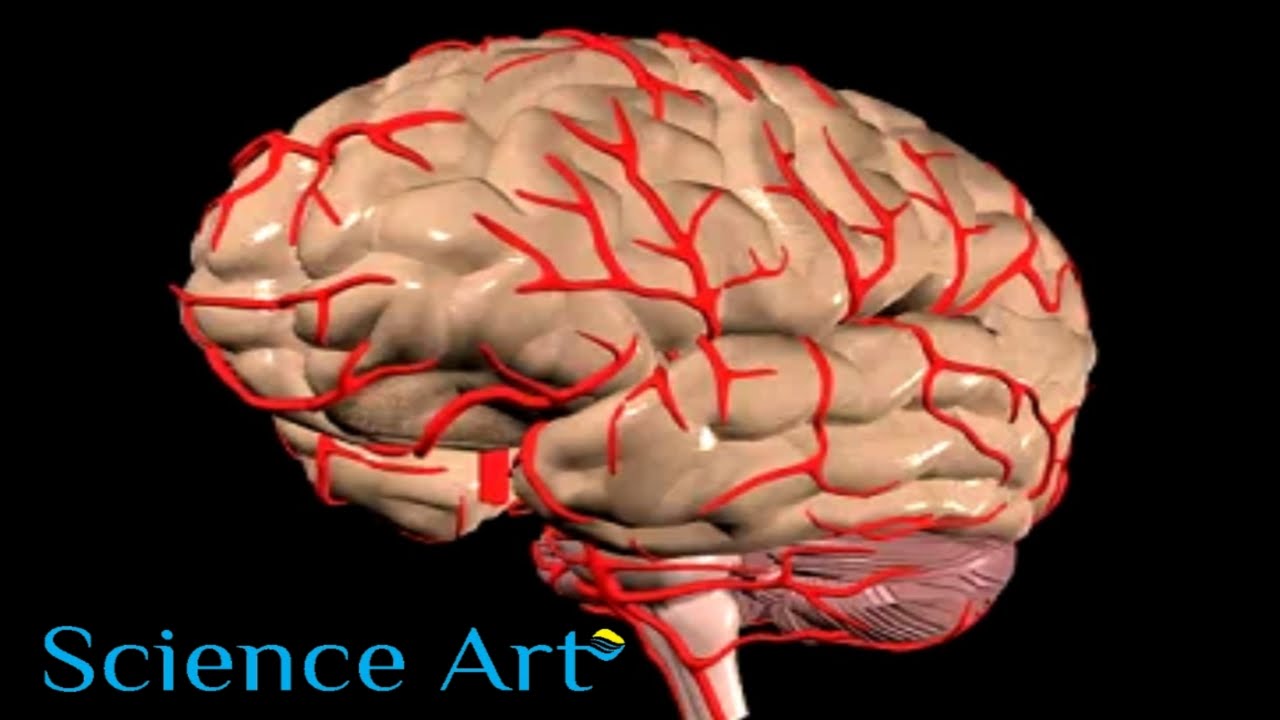
What are the Risks of Not Treating High Blood Pressure? – Hypertension Effects Animation HT Dangers
- Post author:
- Post published:May 28, 2021
- Post category:Uncategorized
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like
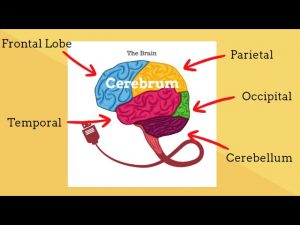
Parts of the Brain-Human Brain Structure and Function
Laser Surgeries Video – 2

Is Whey Protein SAFE at Age under 18 | Guru Mann | Health & Fitness
What is Heart Attack explained in Hindi by Dr. Vinod Sharma.

Thyroid System Animation
Diabetes

BUTTERFLY WORKOUT FOR CHEST
Isotroin Capsule Review in Hindi || by Mt Discuss

Aroma Oils Video – 4
Holozoic Nutrition

Physical Fitness Defined | The Definition of Physical Fitness

Foods to Boost Lactation

Circulatory System Heart BP And Asanas Video – 6
Antioxidant power of plant foods versus animal foods
ENT Surgery Video – 3

The Right Way To Side Plank | Side Plank for Beginners | Fitness Video | How to Plank? I OZiva

7 Erroneous Beliefs About Anatomy for Artists

Gaspari omega-3 complete review in hindi | Best omega-3 supplement | Benefits of fish oil |
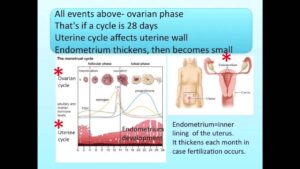
Female Reproduction Song

Top 10 Best Pharmaceutical Companies In India 2021

Nutrition Advice : What Vitamins Help Arthritis?

Dr. Oz Discusses the Total 10 Rapid Weight-Loss Plan
These 3 Vitamins May Stop Brain Loss And Prevent Alzheimer’s Disease

How to Do a Crunch | Ab Workout

My lipid profile is showing high triglyceride levels. Should I worry?
Vascular Surgery Video – 5
Shrugs-3

Flexibility Stretching Video – 3

What is testosterone and why it is important

Vitamins Minerals For Health Video – 2
How To: Skull Crushers
??♂️ #1 Exercise For Preventing Erectile Dysfunction & Improving Your Performance In The Bedroom

Is the Traditional BMI Chart Accurate?

20 Side Plank Exercise Variations

Athletics Video – 1

Yoga Exercises for Lungs

RHMD Advanced Cardiac Lipid Profile

What is Jaundice?
What is a Protein? Learn about the 3D shape and function of macromolecules

Forearm Training Tips

BCAA Supplement vs Protein Supplement – Know Your Supps – BPI Sports

