Endocrine system – Control and Coordination CBSE Biology Class 10 Science lesson by by Soma Mukhopadhyay. CBSE Biology Class 10 Science lesson Endocrine System SuccessCDs Education ( https://www.youtube.com/successcds1 ) is an online education channel focused on providing education through Videos as per CBSE, ICSE and NCERT syllabi upto Class 12 (K-12) for English, Maths, Hindi, Science,Social Science, Sanskrit and other subjects. Also visit our Channel for Entrance Exams in India FAQs & Application Process, GK & Current Affairs, Communication Skills Our website ( https://www.successcds.net ) is one of the leading portal on Entrance Exams and Admissions in India. Follow us: https://www.facebook.com/SuccessCD https://google.com/+successcds https://twitter.com/entranceexam https://twitter.com/successcds https://www.youtube.com/successcds1 https://www.youtube.com/englishacademy1 About this Video: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM IT IS ALSO CALLED THE HORMONAL SYSYTEM. IT OFTEN OPERATES IN CO ORDINATION WITH NERVOUS SYSTEM. CHARACTERISTICS OF HORMONES : The hormones are secreted in small amounts by the endocrine glands. The hormones are poured directly into the blood and carried throughout the body by blood circulatory system The hormones have their effect at the sites different from the sites where they are made. So, they are also called chemical messengers.. The hormones act on target organs. The hormones coordinate the activities and the growth of the body. The excess or deficiency of hormones has a harmful effect on our body. DIFFERENT ENDOCRINE GLANDS PRESENT IN THE BODY HYPOTHALAMUS GLAND AND PITUITARY GLAND The pituitary gland is a pea-sized gland located in the center of the skull. The pituitary gland acts as a master controlling gland, releasing a number of hormones that activate other glands. Hypothalamus gland is present in the brain. Hypothalamus produces ‘releasing hormones’ and ‘inhibitory hormones’. Hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland. PINEAL GLAND OR THE VESTIGIAL ORGAN The pineal gland which is present in the brain has no such function. Pineal gland is supposed to be a vestigial organ. ( Vestigial organs are those organs which no longer function.) The thyroid gland, located in the neck, secretes the hormone thyroxine. Thyroxine increases body metabolism, in which food is broken down and converted into heat and energy. The parathyroid glands are four small glands located in the neck behind the thyroid gland. These glands secrete a hormone that regulates the body’s use of calcium and phosphorus to maintain healthy bones. Parathyroid hormone also affects muscle contraction and the conduction of nerve impulses. Thymus gland lies in the lower part of the neck and upper part of chest. Thymus gland secretes thymus hormone which plays a role in the development of the immune system of the body. The pancreas is a long, narrow gland located in the abdomen behind the stomach and beneath the liver. The pancreas secretes insulin, a hormone that regulates the body’s use of sugar The adrenals are two small glands, each located on the top of one kidney. The adrenal glands releases the hormone epinephrine, which speeds up heart rate and increases blood pressure to help the body cope with emergencies. And also releases hormones that control the level of salts and water in the blood and help regulate the use of sugar. It also secretes small amounts of male sex hormones, or androgens, in both males and females. Males have sex glands called testes that secrete androgens, male sex hormones. In addition to contributing to male sexual characteristics, androgens contribute to the production of sperm and the development of the prostate gland. Females have sex glands called ovaries that release hormones called estrogens. These hormones contribute to the development of female sexual characteristics, including skin, hair, and breast development. Estrogens work with certain pituitary hormones to control the menstrual cycle. Also See Other Science Lessons Central Nervous System – (Control and Coordination) CBSE Biology Class 10 Science https://youtu.be/oHgg4S9xIiA Control and Coordination in plants CBSE Class X Science Lesson https://youtu.be/85GnMnN91PM background Music danosongs.com Also See Playlist – CBSE Class X Science Lessons https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL9vL8QnJ37pIcbCcbjmPekDkj5SjWfqOa
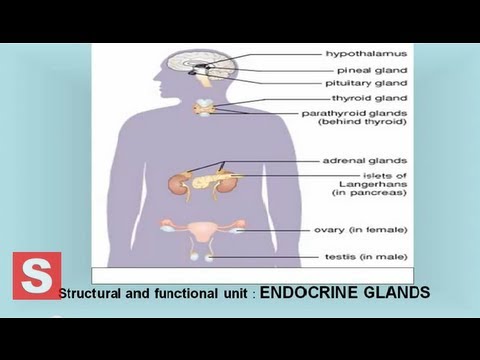
Endocrine system – Control and Coordination CBSE Class X Science ( Biology) Lesson
- Post author:
- Post published:May 7, 2021
- Post comments:0 Comments
You Might Also Like
What Is Semen

Cardio-Thoracic Physiotherapy Video – 12
Massage Video – 3

Gynecomastia in Ireland from riber Medical Cosmetic Surgery

MY MUSCLE GROWTH ANIMATION
Holistic Spa Video – 1

Shockwave Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction Demonstrated and Reviewed
Propranolol
Anabolic Steroids in Meat

Light Cardio and Stretching Cool Down Workout – Relaxing Stretches for Flexibility

Importance of Vitamin B-Complex to our health

Top 5 Best Protein Powders Ever
Orthopedic Physiotherapy Video – 13

What Happens To Your Body During Exercise?

How to Do the Overhead Shoulder Press | Arm Workout

Atenolol or Tenormin Medication Information (dosing, side effects, patient counseling)

Benefits of Omega 3 Fish Oil Supplements ft. Naturyz Triple Strength Omega 3 Fish Oil Supplement

(CC) How to Pronounce pantoprazole (Protonix) Backbuilding Pharmacology

ECG in Dextrocardia

8 Healthy Foods High in Antioxidants

Erector Spinae Back Extension-16

What Losing Weight Does To Your Body And Brain | The Human Body

TUESDAY: Complete Back Workout! (Hindi / Punjabi)

One Hand Triceps Extension-4

How to Treat and Bring Down High Blood Sugar Levels

6 Killer Exercises for HUGE Shoulder Gains barbell part 2

Fatty Acids (Omega 3 & Omega 6) Deficiency: Symptoms & Sources by Dr Berg

Is Whey Protein SAFE at Age under 18 | Guru Mann | Health & Fitness

BIOLOGY – Gareth Williams – Diabetes

Why You Should Warm Up and Cool Down

Your Brain on LSD and Acid

High Intensity Training Video – 1

Sports Surgeries Video – 4
Heart Protective Medicine Atenolol

Spa Products Video – 1
5 Workouts That Burn belly fat Like Crazy

Parle-G TVC 2018 | Roomie | #YouAreMyParleG

Human Body, Body Building Muscle Building Anatomy Physiology Video – 42

Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate – Increase & Decrease ESR

Lunges Exercise-4

Triceps – Cable Rope Overhead Triceps Extension Exercise Guide